Chapter 5 Growth
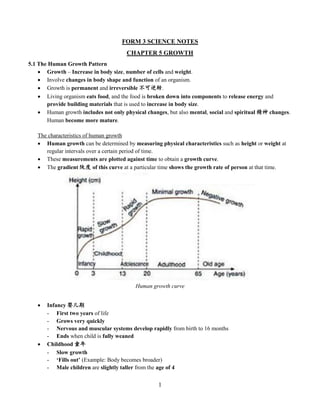
- 1. 1 FORM 3 SCIENCE NOTES CHAPTER 5 GROWTH 5.1 The Human Growth Pattern Growth – Increase in body size, number of cells and weight. Involve changes in body shape and function of an organism. Growth is permanent and irreversible 不可逆转. Living organism eats food, and the food is broken down into components to release energy and provide building materials that is used to increase in body size. Human growth includes not only physical changes, but also mental, social and spiritual 精神 changes. Human become more mature. The characteristics of human growth Human growth can be determined by measuring physical characteristics such as height or weight at regular intervals over a certain period of time. These measurements are plotted against time to obtain a growth curve. The gradient 陡度 of this curve at a particular time shows the growth rate of person at that time. Infancy 婴儿期 - First two years of life - Grows very quickly - Nervous and muscular systems develop rapidly from birth to 16 months - Ends when child is fully weaned Childhood 童年 - Slow growth - ‘Fills out’ (Example: Body becomes broader) - Male children are slightly taller from the age of 4 Human growth curve
- 2. 2 Adolescence 青春期 - Rapid growth - Puberty is achieved - Girls reach puberty much earlier than boys Adulthood 成年 - From early 20s to about 65 - Minimal growth Old age (Senescence) 衰老 - Negative growth because body tissues break down more quickly than they can be repaired. Growth curves of boys and girls During infancy, both growth rates are same. From age 4, boy’s growth rate is faster than girl. As children grow, bodies change and start to look more like adult. These changes happen during puberty. There is a marked increase in growth rate known as adolescent growth spurt 迅速增长 at puberty. In the beginning, girl’s growth rate is faster than boy’s. From age of 14, boys grow faster than girls. Growth curves of height for boys and girls
- 3. 3 Effects of the nutrition on the growth of children Every child requires nutritious food (balanced diet) for healthy growth. Healthy living includes: - Eating nutritious food - Frequent exercise - Staying away from cigarettes, drugs and alcohol Healthy living leads to good physical, mental and spiritual development in child. Carbohydrates give energy and enable a child to carry out physical activities. Proteins are body-building foods. Proteins are needed for growth and repair of damaged tissues. Fibre cannot be digested by body but prevents constipation and helps move the bowels 肠 of child. Fats provide twice the energy needed when compared to carbohydrates. They give warmth and are stored for future use. Minerals / Vitamin Effects of deficiency Proteins Kwashiorkor Iron Anaemia Calcium Rickets Vitamin A Night-blindness Vitamin B Beri-beri Vitamin C Scurvy Main minerals and vitamins children need Children suffering from kwashiorkor