Chapter five
- 1. Creating Long-Term Loyalty Relationships Dr. Shahzad Ahmad Khan Assistant Professor Email: shahzad.ahmad@riphah.edu.pk CHAPTER :5 Faculty of Management Sciences
- 2. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 2 of 34 Discussion Questions 1. What are customer value, satisfaction, and loyalty, and how can companies deliver them? 2. What is the lifetime value of customers, and how can marketers maximize it? 3. How can companies attract and retain the right customers and cultivate strong customer relationships? 4. What are the pros and cons of database marketing?
- 3. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 3 of 34 Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty Holistic Marketing • Inform • Engage • Energize
- 4. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 4 of 34 Figure 5.1 Traditional Organization vs. Customer-Oriented Organization
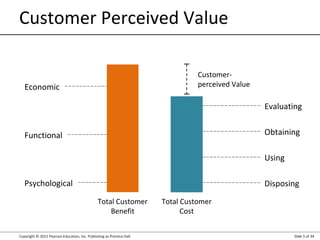
- 5. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 5 of 34 Customer Perceived Value Total Customer Cost Total Customer Benefit Customer- perceived Value Functional Economic Psychological Evaluating Obtaining Using Disposing
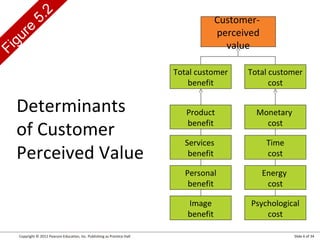
- 6. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 6 of 34 Figure 5.2 Customer- perceived value Total customer benefit Total customer cost Product benefit Monetary cost Services benefit Time cost Personal benefit Energy cost Image benefit Psychological cost Determinants of Customer Perceived Value
- 7. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 7 of 34 Value Concepts - Caterpillar Worth to farmer: $20,000 Cost to produce: $14,000 Profit Price Customer Value $6,000 $20,000 -0- 5,000 19,000 $1,000 4,000 18,000 2,000 3,000 17,000 3,000 2,000 16,000 4,000 1,000 15,000 5,000 -0- 14,000 6,000
- 8. Defined “A deeply held commitment to rebuy or repatronize a preferred product or service in the future despite situational influences and marketing efforts having the potential to cause switching behavior.” -- Oliver Customer Loyalty
- 9. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 9 of 34 Value Proposition Core positioning: • Safety Volvo Other benefits: • Good performance • Design • Environmentally friendly
- 10. Defined A person’s feelings of pleasure or disappointment that result from comparing a product’s perceived performance to (or outcome) to expectations. Satisfaction
- 11. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 11 of 34 Customer Satisfaction Expectations
- 12. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 12 of 34 Customer Expectations Expectations Previous purchases Friends advice Marketers’ / competitors
- 13. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 13 of 34 Monitoring Satisfaction Customer Complaints Measurement Techniques Influence of Customer Satisfaction
- 14. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 14 of 34 Measurement Techniques Customer Loss Rate Mystery Shopper Surveys
- 15. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 15 of 34 Influence of Customer Satisfaction Customer satisfaction Speed of communication
- 16. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 16 of 34 Customer Complaints 25% Dissatisfied 5% Complain 95% Stop buying 54% - 70% Buy again if resolved 95% If resolved quickly Tell 5 people Tell 11 people
- 17. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 17 of 34 Product and Service Quality Performance Conformance
- 18. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 18 of 34 Maximizing Customer Lifetime Value 20% of Customers 80% of Profits Customers
- 19. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 19 of 34 Customer Profitability Customer Profitability Analysis Profitable Unprofitabl e
- 20. Defined A person, or company that over time yields a revenue stream exceeding by an acceptable amount the company’s cost stream for attracting, selling, and serving that customer. A Profitable Customer
- 21. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 21 of 34 Figure 5.3 Customer-Product Profitability Analysis
- 22. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 22 of 34 Cultivating Customer Relationships Customer Information • Differentiate • Customize • Personalize • Share
- 23. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 23 of 34 Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Personalizing Marketing Customer Empowerment Customer Reviews & Recommendations
- 24. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 24 of 34 Personalizing Marketing
- 25. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 25 of 34 One-to-One Marketing Differentiate customers Interact with each customer Customize Identify prospects and customers
- 26. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 26 of 34 Customer Reviews/Recommendations Customer ratings Negative reviews Create Buzz
- 27. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 27 of 34 Customer Retention Acquiring new customers costs 5x more than retaining current customers The average company loses 10% Of its customers yearly Reducing customer defections by 5% can increase profits from 25% to 85%
- 28. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 28 of 34 Attracting and Retaining Customers • Reduce the rate of defection • Increase longevity • Enhance share of wallet • Terminate low-profit customers • Focus more effort on high-profit customers
- 29. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 29 of 34 Figure 5.4 The Marketing Funnel
- 30. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 30 of 34 Building Loyalty Develop loyalty programs Interact with customers Create institutional ties
- 31. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 31 of 34 Databases & Database Marketing Customer databases • Name, address, telephone # • Purchase history • Demographics • Psychographics • Mediagraphics Data Warehouses Data mining
- 32. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 32 of 34 Using the Database • To identify prospects • To target offers • To deepen loyalty • To reactivate customers • To avoid mistakes
- 33. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 33 of 34 Don’t Build a Database When • The product is a once-in-a-lifetime purchase • Customers do not show loyalty • The unit sale is very small • The cost of gathering information is too high
- 34. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 34 of 34 Thank
Editor's Notes
- The cornerstone of a well-conceived holistic marketing orientation is strong customer relationships. Marketers must connect with customers—informing, engaging, and maybe even energizing them in the process. Customer centered companies are adept at building customer relationships, not just products; they are skilled in market engineering, not just product engineering. Creating loyal customers is at the heart of every business. As marketing experts Don Peppers and Martha Rogers say: The only value your company will ever create is the value that comes from customers— the ones you have now and the ones you will have in the future. Businesses succeed by getting, keeping, and growing customers. Customers are the only reason you build factories, hire employees, schedule meetings, lay fiber-optic lines, or engage in any business activity. Without customers, you don’t have a business.
- Managers who believe the customer is the company’s only true “profit center” consider the traditional organization chart in Figure 5.1 (a)—a pyramid with the president at the top, management in the middle, and frontline people and customers at the bottom—obsolete. Successful marketing companies invert the chart as in Figure 5.1 (b). At the top are customers; next in importance are frontline people who meet, serve, and satisfy customers; under them are the middle managers, whose job is to support the frontline people so they can serve customers well; and at the base is top management, whose job is to hire and support good middle managers. We have added customers along the sides of Figure 5.1 (b) to indicate that managers at every level must be personally involved in knowing, meeting, and serving customers.
- Consumers are better educated and informed than ever, and they have the tools to verify companies’ claims and seek out superior alternatives. Customer-perceived value (CPV) is the difference between the prospective customer’s evaluation of all the benefits and all the costs of an offering and the perceived alternatives. Total customer benefit is the perceived monetary value of the bundle of economic, functional, and psychological benefits customers expect from a given market offering because of the product, service, people, and image. Total customer cost is the perceived bundle of costs customers expect to incur in evaluating, obtaining, using, and disposing of the given market offering, including monetary, time, energy, and psychological costs. Customers look to maximize value within the bounds of any search costs and limited knowledge, mobility, and income.
- Customers estimate which offer they believe—for whatever reason—will deliver the most perceived value and act on it.
- Suppose the buyer for a large construction company wants to buy a tractor for residential construction from either Caterpillar or Komatsu. He wants the tractor to deliver certain levels of reliability, durability, performance, and resale value. The competing salespeople carefully describe their respective offers. The buyer decides Caterpillar has greater product benefits based on his perceptions of those attributes. He also perceives differences in the accompanying services—delivery, training, and maintenance—and decides Caterpillar provides better service as well as more knowledgeable and responsive staff. Finally, he places higher value on Caterpillar’s corporate image and reputation. He adds up all the economic, functional, and psychological benefits from these four sources—product, services, personnel, and image—and perceives Caterpillar as delivering greater customer benefits. Suppose Caterpillar concludes the buyer sees its offer as worth $20,000. Further, suppose Caterpillar’s cost of producing the tractor is $14,000. This means Caterpillar’s offer generates $6,000 over its cost, so the firm needs to charge between $14,000 and $20,000. If it charges less than $14,000, it won’t cover its costs; if it charges more, it will price itself out of the market.
- The value proposition consists of the whole cluster of benefits the company promises to deliver; it is more than the core positioning of the offering. For example, Volvo’s core positioning has been “safety,” but the buyer is promised more than just a safe car; other benefits include good performance, design, and safety for the environment. The value proposition is thus a promise about the experience customers can expect from the company’s market offering and their relationship with the supplier. Whether the promise is kept depends on the company’s ability to manage its value delivery system. The value delivery system includes all the experiences the customer will have on the way to obtaining and using the offering. At the heart of a good value delivery system is a set of core business processes that help deliver distinctive consumer value.
- In general, satisfaction is a person’s feelings of pleasure or disappointment that result from comparing a product’s perceived performance (or outcome) to expectations. If the performance falls short of expectations, the customer is dissatisfied. If it matches expectations, the customer is satisfied. If it exceeds expectations, the customer is highly satisfied or delighted. Customer assessments of product performance depend on many factors, especially the type of loyalty relationship the customer has with the brand. Consumers often form more favorable perceptions of a product with a brand they already feel positive about.
- How do buyers form their expectations? Expectations result from past buying experience; friends’ and associates’ advice; and marketers’ and competitors’ information and promises. If marketers raise expectations too high, the buyer is likely to be disappointed. If it sets expectations too low, it won’t attract enough buyers (although it will satisfy those who do buy). Some of today’s most successful companies are raising expectations and delivering performances to match. Korean automaker Kia found success in the United States by launching low-cost, high-quality cars with enough reliability to offer 10-year, 100,000 mile warranties.
- Many companies are systematically measuring how well they treat customers, identifying the factors shaping satisfaction, and changing operations and marketing as a result. Wise firms measure customer satisfaction regularly, because it is one key to customer retention. A highly satisfied customer generally stays loyal longer, buys more as the company introduces new and upgraded products, talks favorably to others about the company and its products, pays less attention to competing brands and is less sensitive to price, offers product or service ideas to the company, and costs less to serve than new customers because transactions can become routine. Greater customer satisfaction has also been linked to higher returns and lower risk in the stock market.
- MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES Periodic surveys can track customer satisfaction directly and ask additional questions to measure repurchase intention and the respondent’s likelihood or willingness to recommend the company and brand to others. Companies need to monitor their competitors’ performance too. They can monitor their customer loss rate and contact those who have stopped buying or who have switched to another supplier to find out why. Companies can hire mystery shoppers to pose as potential buyers and report on strong and weak points experienced in buying the company’s and competitors’ products. Managers themselves can enter company and competitor sales situations where they are unknown and experience firsthand the treatment they receive, or they can phone their own company with questions and complaints to see how employees handle the calls.
- INFLUENCE OF CUSTOMER SATISFACTION For customer-centered companies, customer satisfaction is both a goal and a marketing tool. Companies need to be especially concerned with their customer satisfaction level today because the Internet provides a tool for consumers to quickly spread both good and bad word of mouth to the rest of the world. Some customers set up their own Web sites to air grievances and galvanize protest, targeting high-profile brands such as United Airlines, Home Depot, and Mercedes-Benz.
- CUSTOMER COMPLAINTS Some companies think they’re getting a sense of customer satisfaction by tallying complaints, but studies show that while customers are dissatisfied with their purchases about 25 percent of the time, only about 5 percent complain. The other 95 percent either feel complaining is not worth the effort or don’t know how or to whom to complain. They just stop buying.
- Satisfaction will also depend on product and service quality. What exactly is quality? Various experts have defined it as “fitness for use,” “conformance to requirements,” and “freedom from variation.” We will use the American Society for Quality’s definition: Quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs. This is clearly a customer-centered definition. We can say the seller has delivered quality whenever its product or service meets or exceeds the customers’ expectations. A company that satisfies most of its customers’ needs most of the time is called a quality company, but we need to distinguish between conformance quality and performance quality (or grade). A Lexus provides higher performance quality than a Hyundai: The Lexus rides smoother, goes faster, and lasts longer. Yet both a Lexus and a Hyundai deliver the same conformance quality if all the units deliver their respective promised quality.
- Ultimately, marketing is the art of attracting and keeping profitable customers. Yet every company loses money on some of its customers. The well-known 80–20 rule states that 80 percent or more of the company’s profits come from the top 20 percent of its customers. Some cases may be more extreme—the most profitable 20 percent of customers (on a per capita basis) may contribute as much as 150 percent to 300 percent of profitability. The least profitable 10 percent to 20 percent, on the other hand, can actually reduce profits between 50 percent to 200 percent per account, with the middle 60 percent to 70 percent breaking even. The implication is that a company could improve its profits by “firing” its worst customers.
- A profitable customer is a person, household, or company that over time yields a revenue stream exceeding by an acceptable amount the company’s cost stream for attracting, selling, and serving that customer. Note the emphasis is on the lifetime stream of revenue and cost, not the profit from a particular transaction. Marketers can assess customer profitability individually, by market segment, or by channel. Customer profitability analysis (CPA) is best conducted with the tools of an accounting technique called activity-based costing (ABC). ABC accounting tries to identify the real costs associated with serving each customer—the costs of products and services based on the resources they consume. The company estimates all revenue coming from the customer, less all costs. With ABC, the costs should include the cost not only of making and distributing the products and services, but also of taking phone calls from the customer, traveling to visit the customer, paying for entertainment and gifts—all the company’s resources that go into serving that customer. ABC also allocates indirect costs like clerical costs, office expenses, supplies, and so on, to the activities that use them, rather than in some proportion to direct costs. Both variable and overhead costs are tagged back to each customer. Measuring CLV The case for maximizing long-term customer profitability is captured in the concept of customer lifetime value. Customer lifetime value (CLV) describes the net present value of the stream of future profits expected over the customer’s lifetime purchases. The company must subtract from its expected revenues the expected costs of attracting, selling, and servicing the account of that customer, applying the appropriate discount rate (say, between 10 percent and 20 percent, depending on cost of capital and risk attitudes). Lifetime value calculations for a product or service can add up to tens of thousands of dollars or even into six figures.
- A useful type of profitability analysis is shown in Figure 5.3. Customers are arrayed along the columns and products along the rows. Each cell contains a symbol representing the profitability of selling that product to that customer. Customer 1 is very profitable; he buys two profit-making products (P1 and P2). Customer 2 yields mixed profitability; he buys one profitable product (P1) and one unprofitable product (P3). Customer 3 is a losing customer because he buys one profitable product (P1) and two unprofitable products (P3 and P4).
- Companies are using information about customers to enact precision marketing designed to build strong long-term relationships.49 Information is easy to differentiate, customize, personalize, and dispatch over networks at incredible speed. But information cuts both ways. For instance, customers now have a quick and easy means of doing comparison shopping through sites such as Bizrate.com, Shopping.com, and PriceGrabber.com. The Internet also facilitates communication between customers. Web sites such as Epinions.com and Yelp.com enable customers to share information about their experiences with various products and services. Customer empowerment has become a way of life for many companies that have had to adjust to a shift in the power with their customer relationships.
- Customer relationship management (CRM) is the process of carefully managing detailed information about individual customers and all customer “touch points” to maximize loyalty. A customer touch point is any occasion on which a customer encounters the brand and product— from actual experience to personal or mass communications to casual observation. For a hotel, the touch points include reservations, check-in and checkout, frequent-stay programs, room service, business services, exercise facilities, laundry service, restaurants, and bars.
- PERSONALIZING MARKETING The widespread usage of the Internet allows marketers to abandon the mass market practices that built brand powerhouses in the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s for new approaches that are a throwback to marketing practices from a century ago, when merchants literally knew their customers by name. Personalizing marketing is about making sure the brand and its marketing are as relevant as possible to as many customers as possible—a challenge, given that no two customers are identical.
- Don Peppers and Martha Rogers outline a four-step framework for one-to-one marketing that can be adapted to CRM marketing as follows: Identify your prospects and customers. Don’t go after everyone. Build, maintain, and mine a rich customer database with information from all the channels and customer touch points. Differentiate customers in terms of (1) their needs and (2) their value to your company. Spend proportionately more effort on the most valuable customers (MVCs). Apply activity-based costing and calculate customer lifetime value. Estimate net present value of all future profits from purchases, margin levels, and referrals, less customer-specific servicing costs. Interact with individual customers to improve your knowledge about their individual needs and to build stronger relationships. Formulate customized offerings you can communicate in a personalized way. Customize products, services, and messages to each customer. Facilitate customer interaction through the company contact center and Web site.
- Although the strongest influence on consumer choice remains “recommended by relative/friend,” an increasingly important decision factor is “recommendations from consumers.” With increasing mistrust of some companies and their advertising, online customer ratings and reviews are playing an important role for Internet retailers such as Amazon.com and Shop.com. Despite consumer acceptance of such reviews, however, their quality and integrity is always in question. In one famous example, over a period of seven years, the cofounder and CEO of Whole Foods Market, reportedly posted more than 1,100 entries on Yahoo! Finance’s online bulletin board under a pseudonym, praising his company and criticizing competitors.
- Why is retaining existing customers so important? Consider these facts:
- Companies seeking to expand their profits and sales must spend considerable time and resources searching for new customers. To generate leads, they develop ads and place them in media that will reach new prospects; send direct mail and e-mails to possible new prospects; send their salespeople to participate in trade shows where they might find new leads; purchase names from list brokers; and so on. Different acquisition methods yield customers with varying CLVs. One study showed that customers acquired through the offer of a 35 percent discount had about one-half the long-term value of customers acquired without any discount.69 Campaigns that target loyal customers by reinforcing the benefits they enjoy often also attract new customers. Two-thirds of the considerable growth spurred by UK mobile communication leader O2’s loyalty strategy was attributed to recruitment of new customers, the remainder from reduced defection. REDUCING DEFECTION It is not enough to attract new customers; the company must also keep them and increase their business. Too many companies suffer from high customer churn or defection. Adding customers here is like adding water to a leaking bucket.
- Figure 5.4 shows the main steps in attracting and retaining customers in terms of a funnel. The marketing funnel identifies the percentage of the potential target market at each stage in the decision process, from merely aware to highly loyal. Consumers must move through each stage before becoming loyal customers. Some marketers extend the funnel to include loyal customers who are brand advocates or even partners with the firm.
- INTERACTING WITH CUSTOMERS Listening to customers is crucial to customer relationship management. Some companies have created an ongoing mechanism that keeps their marketers permanently plugged in to frontline customer feedback. But listening is only part of the story. It is also important to be a customer advocate and, as much as possible, take the customers’ side and understand their point of view. USAA Insurance’s legendary quality of service has led to the highest customer satisfaction in the industry. USAA subscribers will often tell stories about how the company looks out for them, even counseling them not to take out more insurance than they need. With such levels of trust, USAA enjoys high customer loyalty and significant cross-selling opportunities. DEVELOPING LOYALTY PROGRAMS Frequency programs (FPs) are designed to reward customers who buy frequently and in substantial amounts. They can help build long-term loyalty with high CLV customers, creating cross-selling opportunities in the process. Pioneered by the airlines, hotels, and credit card companies, FPs now exist in many other industries. Most supermarket chains offer price club cards that grant discounts on certain items. Typically, the first company to introduce an FP in an industry gains the most benefit, especially if competitors are slow to respond. After competitors react, FPs can become a financial burden to all the offering companies, but some companies are more efficient and creative in managing them. CREATING INSTITUTIONAL TIES The company may supply customers with special equipment or computer links that help them manage orders, payroll, and inventory. Customers are less inclined to switch to another supplier when it means high capital costs, high search costs, or the loss of loyal-customer discounts. Win-Backs Regardless of how hard companies may try, some customers inevitably become inactive or drop out. The challenge is to reactivate them through win-back strategies. It’s often easier to reattract ex-customers (because the company knows their names and histories) than to find new ones. Exit interviews and lost-customer surveys can uncover sources of dissatisfaction and help win back only those with strong profit potential.
- Marketers must know their customers. And in order to know the customer, the company must collect information and store it in a database from which to conduct database marketing. A customer database is an organized collection of comprehensive information about individual customers or prospects that is current, accessible, and actionable for lead generation, lead qualification, sale of a product or service, or maintenance of customer relationships. Database marketing is the process of building, maintaining, and using customer databases and other databases (products, suppliers, resellers) to contact, transact, and build customer relationships. Data Warehouses and Data Mining Savvy companies capture information every time a customer comes into contact with any of their departments, whether it is a customer purchase, a customer-requested service call, an online query, or a mail-in rebate card. Banks and credit card companies, telephone companies, catalog marketers, and many other companies have a great deal of information about their customers, including not only addresses and phone numbers, but also transactions and enhanced data on age, family size, income, and other demographic information.
- Marketers must know their customers. And in order to know the customer, the company must collect information and store it in a database from which to conduct database marketing. A customer database is an organized collection of comprehensive information about individual customers or prospects that is current, accessible, and actionable for lead generation, lead qualification, sale of a product or service, or maintenance of customer relationships. Database marketing is the process of building, maintaining, and using customer databases and other databases (products, suppliers, resellers) to contact, transact, and build customer relationships. Data Warehouses and Data Mining Savvy companies capture information every time a customer comes into contact with any of their departments, whether it is a customer purchase, a customer-requested service call, an online query, or a mail-in rebate card. Banks and credit card companies, telephone companies, catalog marketers, and many other companies have a great deal of information about their customers, including not only addresses and phone numbers, but also transactions and enhanced data on age, family size, income, and other demographic information.
- Marketers must know their customers. And in order to know the customer, the company must collect information and store it in a database from which to conduct database marketing. A customer database is an organized collection of comprehensive information about individual customers or prospects that is current, accessible, and actionable for lead generation, lead qualification, sale of a product or service, or maintenance of customer relationships. Database marketing is the process of building, maintaining, and using customer databases and other databases (products, suppliers, resellers) to contact, transact, and build customer relationships. Data Warehouses and Data Mining Savvy companies capture information every time a customer comes into contact with any of their departments, whether it is a customer purchase, a customer-requested service call, an online query, or a mail-in rebate card. Banks and credit card companies, telephone companies, catalog marketers, and many other companies have a great deal of information about their customers, including not only addresses and phone numbers, but also transactions and enhanced data on age, family size, income, and other demographic information.
- Marketers must know their customers. And in order to know the customer, the company must collect information and store it in a database from which to conduct database marketing. A customer database is an organized collection of comprehensive information about individual customers or prospects that is current, accessible, and actionable for lead generation, lead qualification, sale of a product or service, or maintenance of customer relationships. Database marketing is the process of building, maintaining, and using customer databases and other databases (products, suppliers, resellers) to contact, transact, and build customer relationships. Data Warehouses and Data Mining Savvy companies capture information every time a customer comes into contact with any of their departments, whether it is a customer purchase, a customer-requested service call, an online query, or a mail-in rebate card. Banks and credit card companies, telephone companies, catalog marketers, and many other companies have a great deal of information about their customers, including not only addresses and phone numbers, but also transactions and enhanced data on age, family size, income, and other demographic information.