Chapter08 -- network operating systems and windows server 2003-based networking
- 1. Chapter 8: Network Operating Systems and Windows Server 2003-Based Networking Network+ Guide to Networks
- 2. 2 Objectives: Discuss the functions and features of a network operating system Define the requirements for a Windows Server 2003 network environment Describe how Windows Server 2003 fits into an enterprise-wide network
- 3. 3 Objectives (continued) Perform a simple Windows Server 2003 installation Manage simple user, group, and rights parameters in Windows Server 2003 Understand how Windows Server 2003 integrates with other popular network operating systems
- 4. 4 Introduction to Network Operating Systems • Centrally manage network resources • Secure access to network • Allow remote users to connect • Allow users to connect to other networks • Back up data and make sure it’s available • Allow for simple additions of clients and resources • Monitor status and functionality of network elements • Distribute programs and software updates to clients • Ensure efficient use of a server’s capabilities • Provide fault tolerance
- 5. 5 Introduction to Network Operating Systems (continued) • Selecting a Network Operating System • Compatible with existing infrastructure? • Provide the security required by resources? • Can technical staff manage it effectively? • Will applications run smoothly on it?
- 6. 6 Introduction to Network Operating Systems (continued) • Selecting a Network Operating System • Will it accommodate future growth? • Does it support the additional services users require? • Does it fit budget? • What additional training will it require? • Support from its manufacturer?
- 7. 7 Introduction to Network Operating Systems (continued) • Network Operating Systems and Servers • How many clients will connect to the server? • What kinds of applications will run on the server? • How much storage space will each user need? • How much downtime, if any, is acceptable? • What can the organization afford?
- 8. 8 Network Operating System Services and Features • Client Support • Creating and managing client accounts • Enabling clients to connect to the network • Allowing clients to share resources • Managing clients’ access to shared resources • Facilitating communication between clients
- 9. 9 Network Operating System Services and Features (continued) • Client/Server Communication • Credentials- user name and password • Redirector- intercepts the request • Authentication- matching credentials
- 10. 10 Network Operating System Services and Features (continued) • Users and Groups • Access a client (or user) has depends on user account and groups assigned
- 11. 11 Network Operating System Services and Features (continued) • Identifying and Organizing Network Elements • Directory • LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) • Object • Attributes • Schema • Containers, or Organizational Units (OUs).
- 12. 12 Network Operating System Services and Features (continued) • Sharing Applications • Ability to share resources, reducing costs and time required to manage the resources • Sharing Printers • Increase the efficiency of managing resources and reduce costs for an organization
- 13. 13 Network Operating System Services and Features (continued) • Sharing Printers • All NOSs can • Create an object that identifies the printer to the rest of the network • Assign the printer a unique name • Install drivers associated with the printer • Set printer attributes, such as location and printing preferences
- 14. 14 Network Operating System Services and Features (continued) • Sharing Printers • All NOSs can (continued) • Establish or limit access to the printer • Remotely test and monitor printer functionality • Update and maintain printer drivers • Manage print jobs, including modifying a job’s priority or deleting jobs from the queue
- 15. 15 Network Operating System Services and Features (continued) • Managing System Resources • Memory • Physical memory and Virtual memory • Multitasking • Preemptive multitasking • Multiprocessing • Processing and Threads
- 16. 16 Introduction to Windows Server 2003 • Four different, but related NOSs: • Standard Edition • Web Edition • Enterprise Edition • Datacenter Edition
- 17. 17 Why Choose Windows Server 2003? • General benefits, Standard Edition • Support for multiple processors, multitasking, and symmetric multiprocessing • Active Directory • Microsoft Management Console (MMC) • Integrated Web development and delivery services • Support for modern protocols and security
- 18. 18 Why Choose Windows Server 2003? (continued) • General benefits, Standard Edition • Excellent integration with NOSs and support for client operating systems • Integrated remote client services • Provisions for monitoring and improving server performance • Support for high-performance, large-scale storage devices
- 19. 19 Windows Server 2003 Hardware Requirements • Servers generally require more processing power, memory, and hard disk space than do client workstations • The Hardware Compatibility List (HCL) lists all computer components proven to be compatible with Windows Server 2003.
- 20. 20 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 • Windows Server 2003 Memory Model • Can use virtual memory • Assigns each application (or process) its own 32- bit memory area • Allows you to install more physical memory
- 21. 21 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 (continued) • Windows Server 2003 File Systems • FAT (File Allocation Table) • FAT16 & FAT32 • CDFS (CD-ROM File System) and UDF (Universal Disk Format) • NTFS (New Technology File System)
- 22. 22 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 (continued) • Microsoft Management Console (MMC) • All administrative tools are integrated into a single interface • Purpose is to gather multiple administrative tools into a convenient console for your network environment
- 23. 23 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 (continued) • Active Directory • Workgroups • Group of interconnected computers that share each other’s resources • Domains • Domain model • Domain controllers • Member servers.
- 24. 24 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 (continued)
- 25. 25 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 (continued)
- 26. 26 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 (continued) • Active Directory (cont.) • Organizational Units • NOSs use organizational units (OUs) to hold multiple objects that have similar characteristics • Windows Server 2003 OU can contain over 10 million objects
- 27. 27 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 (continued)
- 28. 28 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 (continued) • Trees and Forests • Domain tree • Root domain • Child domains • Forest • Collection of one or more domain trees
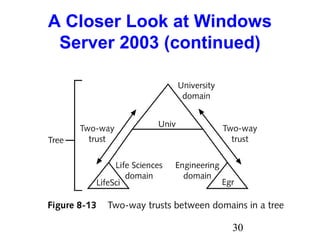
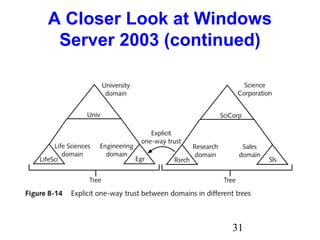
- 29. 29 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 (continued) • Trust Relationships • Two-way transitive trust • Explicit one-way trust
- 30. 30 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 (continued)
- 31. 31 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 (continued)
- 32. 32 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003 (continued) • Naming Conventions • Distinguished name (DN) • Relative distinguished name (RDN) • User principal name (UPN)
- 33. 33 A Closer Look at Windows Server 2003
- 34. 34 Planning for Installation • Create a plan for your server and its place in your network • Consider many factors, including organizational structure, server function, applications, number of users, LAN architecture, and optional services
- 35. 35 Installing and Configuring a Windows Server 2003 Server • The Installation Process • Can install from a CD-ROM or remotely over the network • Initial Configuration • Server still isn’t ready to support clients • You must configure the software
- 36. 36 Installing and Configuring a Windows Server 2003 Server (continued) • Establishing Users and Groups • Installation process creates two accounts: • Guest • limited privileges • Administrator • extensive privileges
- 37. 37 Internetworking with Other Network Operating Systems (continued) • Windows Server 2003 can communicate with almost any kind of client and, given the proper software and configuration, with the other major NOSs
- 38. 38 Chapter Summary • Functions and features of a network operating system • Define the requirements for a Windows Server 2003 network environment • Describe how Windows Server 2003 fits into an enterprise-wide network
- 39. 39 Chapter Summary (continued) • Perform a simple Windows Server 2003 installation • Manage simple user, group, and rights parameters in Windows Server 2003 • Understand how Windows Server 2003 integrates with other popular network operating systems