Chartered accountant firm in India
- 1. KEY FEATURES OF BUDGET 2023-2024 February, 2023 MININSTRY OF FINANCE BUDGET DIVISION
- 2. LAST FULL TIME UNION BUDGET BY MODI GOVERNMENT BEFORE THE 2024 ELECTIONS Full Budget means- A Full Budget includes the passage of a finance bill to get Parliament's approval for any tax related changes. Vote on account or an Interim Budget- In an election year, the outgoing government doesn't tinker with the taxes or announce new schemes and sops as these are left at the disposal of the new government. In order to manage its expenditure for the interim period till a new government takes over and announces the Budget, the outgoing government presents what is called a vote on account or an interim budget to get the Parliament's approval for expenditure to be incurred for the next few months. KEY POINTS IN TODAY’s BUDGET VISION FOR AMRIT KAAL Empowered & Inclusive Economy Opportunities for citizens with focus on the youth. Growth and Job creation. Strong and stable Macro- Economic environment. FM added that to service these focus areas in our journey to India@100, the following four opportunities can be transformative during Amrit Kaal: Economic Empowerment of Women: Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Rural Livelihood Mission has achieved remarkable success by mobilizing rural women into 81 lakh Self Help Groups and we will enable these groups to reach the next stage of economic empowerment through formation of large producer enterprises or collectives with each having several thousand members and managed professionally. PM VIshwakarma KAushal Samman (PM VIKAS): For centuries, traditional artisans and craftspeople, who work with their hands using tools, have brought renown for India and they are generally referred to as Vishwakarma. The art and handicraft created by them represents the true spirit of Atmanirbhar Bharat. The Finance Minister informed that for the first time, a package of assistance for them has been conceptualized and the new scheme will enable them to improve the quality, scale and reach of their products, integrating them with the MSME value chain. The components of the scheme will include not only financial support but also access to advanced skill training, knowledge of modern digital techniques and efficient green technologies, brand promotion, linkage with local and global markets, digital payments, and social security. This will greatly benefit the Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, OBCs, women and people belonging to the weaker sections. Tourism: The Finance Minister said that the country offers immense attraction for domestic as well as foreign tourists, as there is a large potential to be tapped in tourism. She added that the sector holds huge opportunities for jobs and entrepreneurship for youth in particular and emphasized that promotion of tourism will be taken up on mission mode, with active participation of states, convergence of government programmes and public- private partnerships. Green Growth: Dwelling on the subject of Green Growth, the FM said that India is implementing many programmes for green fuel, green energy, green farming, green
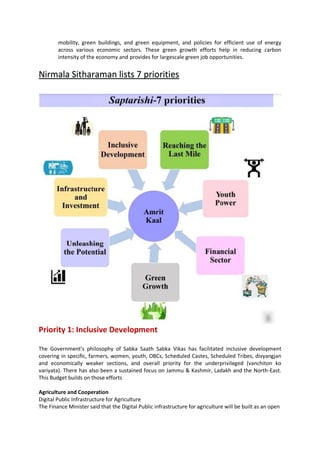
- 3. mobility, green buildings, and green equipment, and policies for efficient use of energy across various economic sectors. These green growth efforts help in reducing carbon intensity of the economy and provides for largescale green job opportunities. Nirmala Sitharaman lists 7 priorities Priority 1: Inclusive Development The Government’s philosophy of Sabka Saath Sabka Vikas has facilitated inclusive development covering in specific, farmers, women, youth, OBCs, Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, divyangjan and economically weaker sections, and overall priority for the underprivileged (vanchiton ko variyata). There has also been a sustained focus on Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh and the North-East. This Budget builds on those efforts Agriculture and Cooperation Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture The Finance Minister said that the Digital Public infrastructure for agriculture will be built as an open
- 4. source, open standard and inter operable public good. She said, this will enable inclusive, farmer- centric solutions through relevant information services for crop planning and health, improved access to farm inputs, credit, and insurance, help for crop estimation, market intelligence, and support for growth of agri-tech industry and startups. Agriculture Accelerator Fund The FM announces that an Agriculture Accelerator Fund will be set-up to encourage agristartups by young entrepreneurs in rural areas, which will aim at bringing innovative and affordable solutions for challenges faced by farmers. It will also bring in modern technologies to transform agricultural practices, increase productivity and profitability Enhancing productivity of cotton crop To enhance the productivity of extra-long staple cotton, Government will adopt a clusterbased and value chain approach through Public Private Partnerships (PPP). This will 9 mean collaboration between farmers, state and industry for input supplies, extension services, and market linkages. Atmanirbhar Horticulture Clean Plant Programme Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman announced that the Government will launch an Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme to boost availability of disease-free, quality planting material for high value horticultural crops at an outlay of Rs 2,200 crore. Global Hub for Millets: ‘Shree Anna’ Smt. Sitharaman quoted Prime Minister as saying, “India is at the forefront of popularizing Millets, whose consumption furthers nutrition, food security and welfare of farmers”. She said that India is the largest producer and second largest exporter of ‘Shree Anna’ in the world as it grows several types of 'Shree Anna' such as jowar, ragi, bajra, kuttu, ramdana, kangni, kutki, kodo, cheena, and sama. She mentioned that these have a number of health benefits, and have been an integral part of our food for centuries and acknowledged with pride that the huge service done by small farmers in contributing to the health of fellow citizens by growing these ‘Shree Anna’. She added that to make India a global hub for 'Shree Anna', the Indian Institute of Millet Research, Hyderabad will be supported as the Centre of Excellence for sharing best practices, research and technologies at the international level. Agriculture Credit Dwelling on welfare measures for farmers, the Finance Minister announced that the agriculture credit target will be increased to Rs 20 lakh crore with focus on animal husbandry, dairy and fisheries. She informed that the Government will launch a new sub-scheme of PM Matsya Sampada Yojana with targeted investment of Rs 6,000 crore to further enable activities of fishermen, fish vendors, and micro & small enterprises, improve value chain efficiencies, and expand the market. Cooperation For farmers, especially small and marginal farmers, and other marginalized sections, the government is promoting cooperative-based economic development model. A new Ministry of Cooperation was formed with a mandate to realize the vision of ‘Sahakar Se Samriddhi’. To realise this vision, the government has already initiated computerization of 63,000 Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) with an investment of Rs 2,516 crore In consultation with all stakeholders and states, model bye-laws for PACS were formulated enabling them to become multipurpose PACS. A national cooperative database is being prepared for country- wide mapping of cooperative societies.
- 5. Smt. Sitharaman said that Government will implement a plan to set up massive decentralized storage capacity, which will help farmers store their produce and realize remunerative prices through sale at appropriate times. The government will also facilitate setting up of a large number of multipurpose cooperative societies, primary fishery societies and dairy cooperative societies in uncovered panchayats and villages in the next 5 years. Health, Education and Skilling Medical & Nursing Colleges The Finance Minister announced that one hundred and fifty-seven new nursing colleges will be established in co-location with the existing 157 medical colleges established since 2014. She also informed that a Mission to eliminate Sickle Cell Anaemia by 2047 will be launched, which will entail awareness creation, universal screening of 7 crore people in the age group of 0-40 years in affected tribal areas, and counseling through collaborative efforts of central ministries and state governments. On Medical Research, she said that facilities in select ICMR Labs will be made available for research by public and private medical college faculty and private sector R&D teams for encouraging collaborative research and innovation. Teachers’ Training Smt. Sitharaman said that Teachers’ training will be re-envisioned through innovative pedagogy, curriculum transaction, continuous professional development, dipstick surveys, and ICT implementation. She added that the District Institutes of Education and Training will be developed as vibrant institutes of excellence for this purpose. She also informed that a National Digital Library for Children and Adolescents will be set-up for facilitating availability of quality books across geographies, languages, genres and levels, and device agnostic accessibility. States will be encouraged to set up physical libraries for them at panchayat and ward levels and provide infrastructure for accessing the National Digital Library resources.
- 6. Additionally, to build a culture of reading, and to make up for pandemic-time learning loss, the National Book Trust, Children’s Book Trust and other sources will be encouraged to provide and replenish non-curricular titles in regional languages and English to these physical libraries Priority 2: Reaching the Last Mile The Finance Minister said that Prime Minister Vajpayee’s government had formed the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and the Department of Development of North-Eastern Region to provide a sharper focus to the objective of ‘reaching the last mile’. She said that Modi Government has formed the ministries of AYUSH, Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying, Skill Development, Jal Shakti and Cooperation. Aspirational Districts and Blocks Programme Smt. Sitharaman informed that building on the success of the Aspirational Districts Programme, the Government has recently launched the Aspirational Blocks Programme covering 500 blocks for saturation of essential government services across multiple domains such as health, nutrition, education, agriculture, water resources, financial inclusion, skill development, and basic infrastructure. Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development Mission The Finance Minister said that to improve socio-economic conditions of the particularly vulnerable tribal groups (PVTGs), Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development Mission will be launched. This will saturate PVTG families and habitations with basic facilities such as safe housing, clean drinking water and sanitation, improved access to education, health and nutrition, road and telecom connectivity, and sustainable livelihood opportunities. An amount of Rs 15,000 crore will be made available to implement the Mission in the next three years under the Development Action Plan for the Scheduled Tribes. Smt. Sitharaman announced that in the next three years, centre will recruit 38,800 teachers and support staff for the 740 Eklavya Model Residential Schools, serving 3.5 lakh tribal students. Water for Drought Prone Region The Finance Minister said that in the drought prone central region of Karnataka, central assistance of Rs 5,300 crore will be given to Upper Bhadra Project to provide sustainable micro irrigation and filling up of surface tanks for drinking water. PM Awas Yojana In an important announcement, the Finance Minister said that the outlay for PM Awas Yojana is being enhanced by 66 per cent to over Rs 79,000 crore. Bharat Shared Repository of Inscriptions’ will be set up in a digital epigraphy museum, with digitization of one lakh ancient inscriptions in the first stage. Priority 3: Infrastructure & Investment Smt. Sitharaman said, investments in Infrastructure and productive capacity have a large multiplier impact on growth and employment and in view of this capital investment outlay is being increased steeply for the third year in a row by 33 per cent to Rs 10 lakh crore, which would be 3.3 per cent of GDP. She said that this will be almost three times the outlay in 2019-20. The ‘Effective Capital Expenditure’ of the Centre is budgeted at Rs 13.7 lakh crore, which will be 4.5 per cent of GDP.
- 7. Support to State Governments for Capital Investment The Finance Minister informed that the Government has decided to continue the 50-year interest free loan to state governments for one more year to spur investment in infrastructure and to incentivize them for complementary policy actions, with a significantly enhanced outlay of Rs 1.3 lakh crore. Railways The Finance Minister announced that a capital outlay of Rs 2.40 lakh crore has been provided for the Railways, which is the highest ever outlay and about 9 times the outlay made in 2013- 14. She also informed that one hundred critical transport infrastructure projects, for last and first mile connectivity for ports, coal, steel, fertilizer, and food grains sectors have been identified and they will be taken up on priority with investment of Rs 75,000 crore, including Rs 15,000 crore from private sources. Smt. Sitharaman said that fifty additional airports, heliports, water aerodromes and advance landing grounds will be revived for improving regional air connectivity. The Finance Minister announced that an Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (UIDF) will be established through use of priority sector lending shortfall, which will be managed by the National Housing Bank, and will be used by public agencies to create urban infrastructure in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities. She said that States will be encouraged to leverage resources from the grants of the 15th Finance Commission, as well as existing schemes, to adopt appropriate user charges while accessing the UIDF. Government will make available Rs 10,000 crore per annum for this purpose.
- 8. Priority 4: Unleashing the Potential The Finance Minister said that for enhancing ease of doing business, more than 39,000 compliances have been reduced and more than 3,400 legal provisions have been decriminalized. She added that for furthering the trustbased governance, Government has introduced the Jan Vishwas Bill to amend 42 Central Acts. Centres of Excellence for Artificial Intelligence The Finance Minister said that for realizing the vision of “Make A-I in India and Make A-I work for India”, three centers of excellence for Artificial Intelligence will be set-up in top educational institutions. Leading industry players will partner in conducting interdisciplinary research, develop cutting-edge applications and scalable problem solutions in the areas of agriculture, health, and sustainable cities, which will galvanize an effective A-I ecosystem and nurture quality human resources in the field. National Data Governance Policy. The FM said that to unleash innovation and research by start-ups and academia, a National Data Governance Policy will be brought out, which will enable access to anonymized data. She also announced that An Entity DigiLocker will be set up for use by MSMEs, large business and charitable trusts for storing and sharing documents online securely, whenever needed, with various authorities, regulators, banks and other business entities. On 5G Services, she announced that one hundred labs for developing applications using 5G services will be set up in engineering institutions to realize a new range of opportunities, business models, and employment potential. The labs will cover, among others, applications such as smart classrooms, precision farming, intelligent transport systems, and health care applications. Priority 5: Green Growth Smt. Sitharaman said that Prime Minister has given a vision for “LiFE”, or Lifestyle for Environment, to spur a movement of environmentally conscious lifestyle. India is moving forward firmly for the ‘panchamrit’ and net-zero carbon emission by 2070 to usher in green industrial and economic transition. She said, this Budget builds on the focus on green growth. The recently launched National Green Hydrogen Mission, with an outlay of Rs 19,700 crores, will facilitate transition of the economy to low carbon intensity, reduce dependence on fossil fuel imports, and make the country assume technology and market leadership in this sunrise sector. The target is to reach an annual production of 5 MMT by 2030. The Budget also provides Rs35,000 crore for priority capital investments towards energy transition and net zero objectives, and energy security by Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas. The Finance Minister said that to steer the economy on the sustainable development path, Battery Energy Storage Systems with capacity of 4,000 MWH will be supported with Viability Gap Funding. She also informed that the Inter-state transmission system for evacuation and grid integration of 13 GW renewable energy from Ladakh will be constructed with investment of Rs 20,700 crore including central support of Rs 8,300 crore.
- 9. GOBARdhan scheme Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman announced that 500 new ‘waste to wealth’ plants under GOBARdhan (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan) scheme will be established for promoting circular economy. These will include 200 compressed biogas (CBG) plants, including 75 plants in urban areas, and 300 community or cluster-based plants at total investment of Rs 10,000 crore. She said, in due course, a 5 per cent CBG mandate will be introduced for all organizations marketing natural and bio gas and for collection of bio-mass and distribution of bio-manure, appropriate fiscal support will be provided. Bhartiya Prakritik Kheti Bio-Input Resource Centres The Finance Minister announced that over the next 3 years, the Centre will facilitate one crore farmers to adopt natural farming. For this, 10,000 Bio-Input Resource Centres will be set-up, creating a national-level distributed micro-fertilizer and pesticide manufacturing network. The Finance Minister said that in furtherance of the vehicle scrapping policy mentioned in Budget 2021-22, she has allocated adequate funds to scrap old vehicles of the Central Government and States will also be supported in replacing old vehicles and ambulances. Priority 6: Youth Power The Finance Minister said that to empower the youth and help the ‘Amrit Peedhi’ realize their dreams, Government has formulated the National Education Policy, focused on skilling, adopted economic policies that facilitate job creation at scale, and have supported business opportunities. She also announced that Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 will be launched to skill lakhs of youth within the next three years. On-job training, industry partnership, and alignment of courses with needs of industry will be emphasized. The scheme will also cover new age courses for Industry 4.0 like coding, AI, robotics, mechatronics, IOT, 3D printing, drones, and soft skills.
- 10. National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman said that to provide stipend support to 47 lakh youth in three years, Direct Benefit Transfer under a pan-India National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme will be rolled out. Unity Mall The FM said that States will be encouraged to set up a Unity Mall in their state capital or most prominent tourism centre or the financial capital for promotion and sale of their own ODOPs (one district, one product), GI products and other handicraft products, and for providing space for such products of all other States. Priority 7: Financial Sector Credit Guarantee for MSMEs The Finance Minster said that last year, she proposed revamping of the credit guarantee scheme for MSMEs and announced happily that the revamped scheme will take effect from 1st April 2023 through infusion of Rs 9,000 crore in the corpus. This will enable additional collateral-free guaranteed credit of Rs 2 lakh crore. Further, the cost of the credit will be reduced by about 1 per cent. Smt. Sitharaman said that a National Financial Information Registry will be set up to serve as the central repository of financial and ancillary information. This will facilitate efficient flow of credit, promote financial inclusion, and foster financial stability. A new legislative framework will govern this credit public infrastructure, and it will be designed in consultation with the RBI. She also announced that a Central Processing Centre will be setup for faster response to companies through centralized handling of various forms filed with field offices under the Companies Act. Senior Citizens The Finance Minister announced that the maximum deposit limit for Senior Citizen Savings Scheme will be enhanced from Rs 15 lakh to Rs 30 lakh. Also, the maximum deposit limit for Monthly Income Account Scheme will be enhanced from Rs 4.5 lakh to Rs 9 lakh for single account and from Rs 9 lakh to Rs 15 lakh for joint account Fiscal Management Fifty-year interest free loan to States Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman said that the entire fifty-year loan to states has to be spent on capital expenditure within 2023-24. Most of this will be at the discretion of states, but a part will be conditional on states increasing their actual capital expenditure. She said, parts of the outlay will also be linked to, or allocated for, the following purposes: like Scrapping old government vehicles, Urban planning reforms and actions, Financing reforms in urban local bodies to make them, creditworthy for municipal bonds, Housing for police personnel above or as part of police stations, Constructing Unity Malls, Children and adolescents’ libraries and digital infrastructure and State share of capital expenditure of central schemes. The Revised Estimate of the total receipts other than borrowings is Rs 24.3 lakh crore, of which the net tax receipts are Rs 20.9 lakh crore. The Revised Estimate of the total expenditure is Rs 41.9 lakh crore, of which the capital expenditure is about Rs 7.3 lakh crore. Similarly, the Revised Estimate of the fiscal deficit is 6.4 per cent of GDP, adhering to the Budget Estimate
- 11. Concluding the Part-One of the General Budget, Ms Nirmala Sitharaman said that the total receipts other than borrowings and the total expenditure are estimated at Rs 27.2 lakh crore and Rs 45 lakh crore respectively. The net tax receipts are estimated at Rs 23.3 lakh crore. The fiscal deficit is estimated to be 5.9 per cent of GDP. She said that in her Budget Speech for 2021-22, she had announced that Government plans to continue the path of fiscal consolidation, reaching a fiscal deficit below 4.5 per cent by 2025-26 with a fairly steady decline over the period. She said that the Government has adhered to this path, and reiterated to bring the fiscal deficit below 4.5 per cent of GDP by 2025-26. Smt. Sitharaman said, to finance the fiscal deficit in 2023-24, the net market borrowings from dated securities are estimated at Rs11.8 lakh crore. The balance financing is expected to come from small savings and other sources. The gross market borrowings are estimated at Rs 15.4 lakh crore. Direct Tax Proposals Under the new personal tax regime under section 115BAC, six income slabs have been reduced to five. The government has also increased the tax exemption limits in some of these categories. 0-3 lakh- nil 3-6 lakh -5% 6-9 lakh - 10% 9-12 lakh-15% 12-15 lakh -20% Above 15 lakh - 30% The new tax regime will now be the default tax regime, but citizens can still avail of benefits under old tax regime on opt-out basis. No tax for income upto Rs 3 lakh/year Income rebate limit increased to Rs 7 lakh from Rs 5 lakh in new tax regime (i.e; Rebate increased to the specified limit) The government has proposed to reduce the highest surcharge rate from 37% to 25% under new tax regime, FM Sitharaman said while presenting the Budget 2023. Hence it can be said that maximum effective rate now will be 38% instead of 42.744% Taxpayers who have opted for the new tax regime for them the Budget announcements will lead to a saving of Rs 33,800, if earning up to Rs 7 lakh annually. Those with income up to Rs 10 lakh would save Rs 23,400 and Rs 49,400 saving would accrue to those earning up to Rs 15 lakh The income tax returns processing period has been reduced from 93 days to 16 days, says finance minister Finance minister has proposed to hike tax exemption on leave encashment on retirement of non-government salaried employees to Rs 25 lakh from Rs 3 lakh. "We are also making the new income tax regime the default tax regime however, citizens will continue to have the option to avail the benefits of the old tax regime. Old tax regime remains same
- 12. The government did not announce any changes for taxpayers who are still following the old tax regime, that provides for tax exemptions and deductions on investments and expenses such as HRA. In what is being seen as push for salaried class taxpayer to switch to new tax regime where no exemptions on investments is provided, the finance minister in her budget for 2023-24 allowed a standard deduction of Rs 50,000 under the new regime. Revenue Secretary Sanjay Malhotra said taxation will now be on net winnings since the nature of online gaming is such that one plays several games in a series. TDS was previously calculated on every Rs 10,000 in winnings. Malhotra said -- "Some companies were then keeping the winning lower at Rs 10,000, so we have removed that now". (For more details Refer Attached Annexure -A) Indirect Tax Proposals The indirect tax proposals announced in the budget by the Union Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs, Smt Nirmala Sitharaman emphasized on simplification of tax structure with fewer tax rates so as to help in reducing compliance burden and improving tax administration. The number of basic customs duty rates on goods, other than textiles and agriculture, has been reduced from 21 to 13. There are minor changes in the basic customs duties, cesses and surcharges on items including toys, bicycles, automobiles and naphtha. Excise duty exempted on GST-paid compressed bio gas contained in blended compressed natural gas. Customs Duty on specified capital goods/machinery for manufacture of lithium-ion cell for use in battery of electrically operated vehicle (EVs) extended to 31.03.2024 Customs duty exempted on vehicles, specified automobile parts/components, sub- systems and tyres when imported by notified testing agencies, for the purpose of testing and/ or certification, subject to conditions. Customs duty on camera lens and its inputs/parts for use in manufacture of camera module of cellular mobile phone reduced to zero and concessional duty on lithium- ion cells for batteries extended for another year Basic customs duty reduced on parts of open cells of TV panels to 2.5 per cent Basic customs duty on electric kitchen chimney increased to 15 per cent from 7.5 per cent. Basic customs duty on heat coil for manufacture of electric kitchen chimneys reduced to 15 per cent from 20 per cent Denatured ethyl alcohol used in chemical industry exempted from basic customs duty. Basic customs duty reduced on acid grade fluorspar (containing by weight more than 97 per cent of calcium fluoride) to 2.5 per cent from 5 per cent. Basic customs duty on crude glycerin for use in manufacture of epicholorhydrin reduced to 2.5 per cent from 7.5 per cent. Duty reduced on key inputs for domestic manufacture of shrimp feed Basic customs duty reduced on seeds used in the manufacture of lab grown diamonds Duties on articles made from dore and bars of gold and platinum increased. Import duty on silver dore, bars and articles increased
- 13. Basic Customs Duty exemption on raw materials for manufacture of CRGO Steel, ferrous scrap and nickel cathode continued Concessional BCD of 2.5 per cent on copper scrap is continued Basic customs duty rate on compounded rubber increased to 25 per cent from 10 per cent or 30 per kg whichever is lower. National Calamity Contingent Duty (NCCD) on specified cigarettes revised upwards by about 16 per cent. (For more details Refer Attached Annexure-B) Legislative Changes in Customs Laws Customs Act, 1962 to be amended to specify a time limit of nine months from date of filing application for passing final order by Settlement Commission. Customs Tariff Act to be amended to clarify the intent and scope of provisions relating to Anti-Dumping Duty (ADD), Countervailing Duty (CVD), and Safeguard Measures. CGST Act to be amended: 1) to raise the minimum threshold of tax amount for launching prosecution under GST from one crore to two crore; 2) to reduce the compounding amount from the present range of 50 to 150 per cent of tax amount to the range of 25 to 100 per cent; 3) decriminalise certain offences; 4) to restrict filing of returns/statements to a maximum period of three years from the due date of filing of the relevant return/statement 5) to enable unregistered suppliers and composition taxpayers to make intra-state supply of goods through E-Commerce Operators (ECOs). INDIAN ECONOMY FIFTH LARGEST IN THE WORLD
- 14. Some of the notable achievements include: 11.7 crore household toilets under Swachh Bharat Mission. 9.6 crore LPG connections under Ujjawala. 220 crore Covid vaccination of 102 crore persons. 47.8 crore PM Jan Dhan bank accounts. Insurance cover for 44.6 crore persons under PM Suraksha Bima and PM Jeevan Jyoti Yojana Cash transfer of Rs.2.2 lakh crore to over 11.4 crore farmers under PM Kisan Samman Nidhi Budget announcements on digital initiatives focuses on artificial intelligence in the education sector Three centres of excellence for artificial intelligence will be established in top educational institutions 100 laboratories in engineering institutions will be developing applications using 5G services A national digital library will be set up for children and adolescents for facilitating the availability of quality books across geographies, languages and genres Centre to recruit 38,800 teachers and support staff for 749 Eklavya Model Residential Schools that will service 3.5 lakh tribal students. Big bonanza for senior citizens Budget 2023 has increased the maximum permissible investment in the senior citizen savings scheme, a popular investment among the elderly. The post office monthly income scheme, too, has been made more attractive. Finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman doubled the maximum limit under the Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS) to Rs 30 lakh from Rs 15 lakh. The scheme offers assured interest of Rs 8 percent per annum. The interest is paid quarterly. Additionally, the investment limit under the popular Post Office Monthly Income Scheme (POMIS) has been raised to Rs 9 lakh from Rs 4.5 lakh. In case of joint accounts held in POMIS, the investment limit has been hiked to Rs 15 lakh from Rs 9 lakh. The scheme pays monthly interest at the rate of 7.1 percent per annum. SOME INDUSTRY SPECIFIC KEY POINTS For Aviation Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on Wednesday announced hiking the capital expenditure by 33 per cent to Rs 10 lakh crore for infrastructure development for 2023-24 and will be at 3.3 percent of the GDP. Presenting the Budget, she said the newly established infrastructure finance secretariat will assist in attracting more private investment. With an aim to further improve regional air connectivity, she said the government will revive 50 additional airports, helipads, water aero drones and advanced landing grounds.
- 15. The Budget also allocated Rs 3,113.36 crore to the union civil aviation ministry For the defence sector While the Ministry of Defence has received the highest allocation among all ministries at Rs 5.94 lakh crore, it is not a significant jump from Rs 5.25 lakh crore for this FY Shares of Bharat Electronics, Bharat Dynamics, Hindustan Aeronautics, Paras Defence and BEML tumbled 5-9 percent after Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman completed her Budget speech. Under its ambitious Atmanirbhar Bharat scheme, the government has banned imports of several items, including crucial parts used in defence equipment. Which means they are being manufactured in India now. For renewable energy sector There is a 48% rise in allocation towards renewable energy sector in this budget. This year's allocation is Rs 6,900.68 crore (budget estimate) and 45.3% over the revised estimate (RE) of Rs 7,033 crore. Electric Vehicles Fully imported cars, including electric vehicles to cost more now. Customs duty on vehicles in completely built units (CBUs) costing less than USD 40,000 or with engine capacity less than 3,000 cc for petrol-run vehicles and less than 2,500 cc for diesel-run vehicles has been increased from 60% to 70%. Similarly, customs duty on electrically operated vehicles in CBU form, other than with cost, insurance and freight (CIF) value of more than USD 40,000, has also been raised to 70% from the previous 60%. For IT ministry The budget estimate for the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology has been increased to Rs 16, 549.04 crore from the Rs 11,719.95 crore. The allocation for the period of 2021-22 stood at Rs 8,118.65 crore, making this year's budget estimate nearly double of what it was two years back. For Road ministry Allocation for the road transport and highways ministry (MoRTH) has been increase by 36% to around Rs 2.7 lakh crore for 2023-24 in the Budget. National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has been allocated around Rs 1.62 lakh crore as part of MoRTH’s capital expenditure plan for 2023-24 As per the government's revised estimates the NHAI will spend Rs 798 crore as IEBR in 2022- 23. For Fintech Sector
- 16. Digital payments rose 76% in transaction and 91% in value terms in 2022 7,400 crore digital payments of Rs 126 lakh crore through UPI in 2022. Fiscal support for digital public infrastructure (DPI) will continue in 2023-2024 The scope of documents available in DigiLocker for individuals will be expanded An entity DigiLocker will be set up for use by MSMEs and large businesses PM VIKAS scheme will now include access to digital payments and social security. Subsidy for UPI expected to jump two-folds to Rs 2,137 crore in FY23 over previous fiscal. Allocation for digital payments promotion remains stagnant at Rs 1500 crore for last three years Health and family welfare ministry The Union health and family welfare ministry has been allocated Rs 89, 155 crore in the Union budget FY24 marking a rise of a meagre 12% when compared to the revised budget estimated for FY 23. For the upcoming financial year, Rs 86,175 crore has been allocated to the department of health and family welfare while Rs 2,980 crore has been allocated for the department of health research. In the ongoing fiscal, the budget spent on the department of health and family welfare is Rs 76, 370 while Rs 2,775 crore had been marked for the department of health research. For Road ministry Allocation for the road transport and highways ministry (MoRTH) has been increase by 36% to around Rs 2.7 lakh crore for 2023-24 in the Budget. National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has been allocated around Rs 1.62 lakh crore as part of MoRTH’s capital expenditure plan for 2023-24 As per the government's revised estimates the NHAI will spend Rs 798 crore as IEBR in 2022- 23 Agriculture The government announced an 11% hike in agriculture credit target to Rs 20 lakh crore for next fiscal year. The government has also announced to provide a 2% interest subsidy to ensure farmers get short-term loans of up to Rs 3 lakh at effective rate of 7% per annum. The RBI has decided to raise the limit for collateral-free agriculture loans from the previous amount of Rs 1 lakh to Rs 1.6 lakh.