Cloud computing for banking
- 1. IBM Sales and Distribution Thought Leadership White Paper Banking Cloud computing for banking Driving business model transformation
- 2. 2 Cloud computing for banking Executive summary The banking industry is facing unprecedented changes. Control is now in the hands of the customer, rather than the bank. Customers are driving new business models. Their use of technology—in addition to changes in social and household dynamics—is driving business transformation. Banks need to react to this new customer-driven environment with innovation in business models, operations and IT. For banks, the value proposition for cloud computing affects the entire business. Cloud technology offers a new model for deliv- ering innovative client experiences, effective collaboration, improved speed to market and increased IT efficiency. Cloud deployments are spreading and the technology is proving to be secure. More businesses are adopting cloud computing. In fact, accord- ing to the 2010 IBM CIO study, “Sixty percent of CIOs plan to use Cloud—up from thirty-three percent two years ago.”2 Today, cloud technology is not just a tool being used in IT, but a paradigm shift to an entirely new business model. Banking Industry Trends With the rise of existing and new, non-traditional competition, banking faces a changing business landscape. Satisfying customer demands has become more complex as customers demand more convenience and control over their banking services. At the same time, regulators are ushering in a new era of government over- sight. Banks currently face challenges in a number of key areas: ●● Capital inadequacy that depresses profit margins ●● Emboldened customers who expect rapidly evolving new services and offerings ●● Fierce competition for customers has spawned industry consolidation and the entrance of nontraditional firms ●● Changing business models have shifted from product- centric to customer-centric ●● Enhanced regulation increases government oversight and intervention ●● Increasing social and government pressure for financial inclusion To drive growth and innovation in banking, it is increasingly necessary to dramatically leapfrog the competition using IT and business model transformation. Google Wallet, Apple Wallet, PayPal and others are driving billion dollar revenues. However, many of today’s existing bank payment solutions are 30 years old. These established solutions have served the industry well, but problems now exist. Transaction volumes and regulatory compli- ance burdens also increase operational risk. The dramatic changes taking place in banking require new ways to maximize profitability and returns. By modernizing and transforming older back office systems into modular building blocks, banks can create a flexible and agile banking environment that can quickly respond to new business needs. “Globally, ninety percent of financial services clients surveyed1 believe they need to transform from the status quo for future profitability” Cloud computing is revolutionizing ecosystems in multiple industries, and banking is no exception. Cloud technology offers secure deployment options that can help banks develop new customer experiences, enable effective collaboration and improve speed to market—all while increasing IT efficiency. Cloud adoption is growing rapidly because it can be made secure for business. In fact, according to the IBM 2010 CIO Study, “Sixty percent of CIOs plan to use Cloud—up from thirty-three percent two years ago.”2 However, in developing or updating a bank’s cloud strategy and infrastructure, it is important to keep
- 3. 3IBM Sales and Distribution security in mind. You need to understand which delivery models are appropriate based on security and trust requirements with connecting systems. You can apply a methodology such as the IBM Security Framework to measure what you need in areas such as governance, architecture, applications and assurance. The framework can help you define the set of assurance and security measures you need to take to meet security requirements. Banks that take advantage of cloud computing are better posi- tioned to respond to economic uncertainties, interconnected global financial systems and demanding customers. They can use information to enhance customer segmentation techniques and to develop more focused services that are aligned with customer needs. Banks also can optimize their channel investments and differentiate themselves through customer service excellence. Armed with new insights, banking leaders can identify and elimi- nate the cost of complexity in their operations and use new and existing forms of information to optimize risk. New opportunities and demands require new approaches For banks, today’s changing business realities and expanding markets represent tremendous growth potential. The financial wealth in emerging markets will reach USD14 trillion by 20153 and 2.7 billion adults in developing nations lack access to finan- cial services.4 Global financial assets are set to triple by 2020 to USD37 trillion.5 Cloud computing can play a significant role in a bank’s efforts to reinvent its business and operating models. In technical terms, a cloud computing platform automatically assembles, connects, configures and reconfigures virtualized technology resources to meet business goals. In business terms, it eliminates constraints around where physical IT resources are located or what specific technologies are employed, which makes it possible to deploy business services rapidly and at a lower cost. For banks, cloud computing can offer benefits in many areas, as shown in Table 1. Driving sales and profitability A mortgage company implemented a cloud-based integrated collaboration mortgage solution, so customers can apply and complete loans electronically. Instead of going into a branch, customers can initiate, review and sign applications electroni- cally through services delivered over the cloud. The solution not only improved customer satisfaction, but also helped the mortgage company reduce loan application processing times from seven days to 24 hours. It also reduced the loan closing process time to 10 to 15 days, compared to the typical industry figures of 30 to 45 days, which gives the mortgage company a competitive advantage. The solution also contributed to a thirty-four percent increase in loan volume, reduced errors on the mortgage applications, lowered overall costs and increased annual revenues. To drive sustainable shareholder value, banking leaders are looking to increase flexibility and streamline operations while working to create a more innovative customer-focused enter- prise. Cloud computing can help transform these aspects of enterprise IT in banking. Build customer relationships According to the IBM 2010 CEO Study, eighty-nine percent of financial services CEOs said their focus over the next five years would be “getting closer to the customer.” In banking, customer- focused enterprises deliver a superior customer experience by engaging customers in insightful conversations. Banks aren’t just providing a pleasant banking experience. Because of cloud applications, they can now offer a consistent, cross-channel expe- rience, much like customers receive from retailers and airlines. Additionally, the business model transformation enabled through cloud can help banks accelerate and optimize the capture and analysis of multi-channel data to allow banks to better monetize customer relationships, not just transactions.
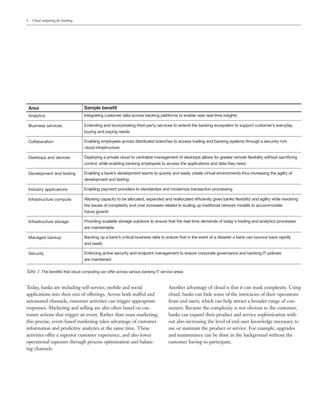
- 4. 4 Cloud computing for banking Area Sample benefit Analytics Integrating customer data across banking platforms to enable near real-time insights Business services Extending and incorporating third-party services to extend the banking ecosystem to support customer’s everyday buying and paying needs Collaboration Enabling employees across distributed branches to access trading and banking systems through a security-rich cloud infrastructure Desktops and devices Deploying a private cloud to centralize management of desktops allows for greater remote flexibility without sacrificing control, while enabling banking employees to access the applications and data they need Development and testing Enabling a bank’s development teams to quickly and easily create virtual environments thus increasing the agility of development and testing Industry applications Enabling payment providers to standardize and modernize transaction processing Infrastructure compute Allowing capacity to be allocated, expanded and reallocated efficiently gives banks flexibility and agility while resolving the issues of complexity and cost increases related to scaling up traditional network models to accommodate future growth Infrastructure storage Providing scalable storage solutions to ensure that the real-time demands of today's trading and analytics processes are maintainable Managed backup Backing up a bank’s critical business data to ensure that in the event of a disaster a bank can bounce back rapidly and easily Security Enforcing active security and endpoint management to ensure corporate governance and banking IT policies are maintained Table 1. The benefits that cloud computing can offer across various banking IT service areas Today, banks are including self-service, mobile and social applications into their mix of offerings. Across both staffed and automated channels, customer activities can trigger appropriate responses. Marketing and selling are also often based on cus- tomer actions that trigger an event. Rather than mass marketing, this precise, event-based marketing takes advantage of customer information and predictive analytics at the same time. These activities offer a superior customer experience, and also lower operational expenses through process optimization and balanc- ing channels. Another advantage of cloud is that it can mask complexity. Using cloud, banks can hide some of the intricacies of their operations from end users, which can help attract a broader range of con- sumers. Because the complexity is not obvious to the customer, banks can expand their product and service sophistication with- out also increasing the level of end-user knowledge necessary to use or maintain the product or service. For example, upgrades and maintenance can be done in the background without the customer having to participate.
- 5. 5IBM Sales and Distribution Because of its expanded computing power and capacity, a cloud can store information about user preferences, which can enable product or service customization. The context-driven variability provided using cloud computing makes it possible for banks to personalize customer interactions and adapt to subtle changes, which leads to a more user-centric experience. Deliver IT flexibility Cloud computing can help increase flexibility and streamline operations. Using cloud technology, banks can drive higher growth and profit margins with improved efficiency ratio and operating leverage. They can align business, operations and technology to drive out complexity and cost. Cloud computing can help banking organizations reduce fixed IT costs because they can shift expenses from capital to opera- tional costs. IT capital expenses typically include enterprise Building a permanent connection to your brand A large bank implemented a cloud environment to create marketing campaigns to deliver personalized product offers to customers across multiple channels in real-time. The bank realized improved processes, a thirty-five percent reduction in marketing costs and shorter cycle times. Additionally, the personalized customer experiences enabled through the cloud delivered €20million increase in corporate earnings while enhancing customer connections and improving response rates. Shifts fixed to variable cost Pay as and when needed New value nets Potential new businesses Provides limitless, cost-effective computing capacity to support growth Faster time to market Supports experimentation Expands product sophistication Simpler for customers/users User defined experiences Increases relevance Ecosystem connectivity Cost flexibility Business scalability Market adaptability Masked complexity Context- driven variability Cloud Figure 1. Cloud computing can enable new business models that can fundamentally shift competitive landscapes.6
- 6. 6 Cloud computing for banking software licenses, servers and networking equipment. These costs tend to be less fluid, more expensive and harder to forecast than routine IT operating expenses. With cloud applications, there is no longer a need to build hard- ware, install software or pay dedicated software license fees. Adopting cloud services allows banks to shift costs from capital to operational or from fixed to variable. The bank pays for what it needs when it needs it. This pay-per-use model is more flexi- ble and eliminates the need for significant capital expenditures. Cloud offers more than just IT scalability; it allows a bank to scale its business operations. By allowing for rapid provisioning of resources without scale limitations, using cloud technology enables a company to benefit from economies of scale without needing to add more servers. More standardization; more OPEX savings; faster time to value Traditional On-Premises Infrastructure as a Service Platform as a Service Software as a Service Applications Data Runtime Middleware O/S Virtualization Servers Storage Networking Traditional Cloud Figure 2. Cloud drives down capital expenses (fixed costs) and delivers flexible operating expenses (pay-as-you-go) benefits Increasing time to market A global bank wanted to dramatically reduce time to market by rapidly accelerating the development cycles for the company’s more than 20,000 internal application developers, who were typically forced to wait up to 45 days for server resources to be provisioned. The bank built an internal cloud, which enabled self-service requests, automated provisioning and internal chargeback capabilities, while at the same time boosting utilization rates and improving operational efficiencies. With the IBM solution, the bank slashed server provisioning times from 45 days to less than 20 minutes, speeding develop- ment cycles and allowing the company to put new features and enhancements in the hands of customers more quickly.
- 7. 7IBM Sales and Distribution Improve speed and dexterity Ecosystem connectivity is another business enabler powered by cloud computing. Using cloud services, it is easier to collaborate with partners and customers, which can lead to improvements in productivity and increased innovation. Cloud-based platforms can bring together disparate groups of people who can collabo- rate and share resources, information and processes. The ability to respond to rapidly changing customer needs is a key competitive differentiator. Like companies in other indus- tries, banks are continuously seeking ways to improve their agility and adjust to market demands. By enabling businesses to rapidly adjust processes, products and services to meet the changing needs of the market, cloud computing can facilitate rapid prototyping and innovation, which helps speed time to market. IBM cloud delivery models IBM offers an array of cloud delivery models—private, hybrid and public—all of which can help a bank transform its opera- tions to become a more efficient and customer-focused enterprise. Private cloud The infrastructure in a private cloud is operated solely for the bank. The bank can own the private cloud or they can engage a third party, such as IBM, to host it, either on site or off. A private cloud provides restricted access to the computing capabilities and resources to be shared by employees, internal departments such as IT or marketing, and external partners such as third-party vendors. Private clouds help drive efficiency, standardization and best practices in the services it provides and lets a bank retain greater customization and control than public clouds would permit. Figure 3. Cloud delivery models Evolve existing infrastructure to Cloud Accelerate adoption with integrated systems Immediate access to a managed platform with flexible cost Access public cloud SaaS business solutions Flexible business service delivery and consumption models Public CloudsHybridPrivate Clouds
- 8. 8 Cloud computing for banking Figure 4. Potential cloud delivery models for infrastructure and platform capabilities Deploy Cloud platforms into your existing infrastructure Accelerate deployments of cloud infrastructure, platform and data services with integrated and optimized systems Immediate access to managed services Platform as a Service Technologies Infrastructure as a Service Technologies An integrated pool of abstracted application services to build & run Cloud services A policy-based, scalable environment for managing the delivery of computing resources and Cloud services “on demand” Existing Infrastructure Public cloud The infrastructure in a public cloud is owned and managed by an organization selling cloud computing services and is made available to the general public. In this model, computing capa- bilities and services such as standardized business processes, applications and infrastructure services are accessed by multiple subscribing clients on a flexible, pay-per-use basis. Hybrid cloud The infrastructure in a hybrid cloud consists of a combination of both private cloud and public cloud features. In this model, com- puting capabilities and resources are owned and maintained by both the bank and the cloud provider. A bank uses public cloud computing capabilities and services for general computing, but stores customer and sensitive data in its private cloud to ensure security. For IBM enterprise cloud customers, the potential delivery models for infrastructure and platform capabilities include: 1. Using core technologies from IBM® SmartCloud™ Foundation to build and manage private clouds. 2. Using expert integrated systems that are part of the IBM SmartCloud Foundation portfolio, such as IBM PureSystems™ to accelerate deployment of private clouds. 3. Consuming infrastructure as a service and platform as a service (PaaS) from IBM, which provide immediate access to managed services in the SmartCloud Services portfolio.
- 9. 9IBM Sales and Distribution Enhance business agility while reducing IT expense and complexity Cloud computing services and solutions from IBM give banks a cost-effective way to respond to the rapidly changing dynamics of the financial world. With more than four thousand successful cloud client engagements, over two hundred million daily cloud transactions processed, and over one million managed virtual machines, IBM has demonstrated its leadership and vast experi- ence in helping clients across multiple industries, including banking, realize the value of cloud. Examples of IBM cloud ser- vices and solutions for the banking industry include: IBM Strategy and Transformation IBM Strategy and Transformation (S&T) integrates manage- ment consulting capabilities that can help banks gain the benefits of converting to a cloud environment. S&T uses a proven methodology and assessment tools for developing a business- based cloud adoption strategy that is tailored to your business outcomes. With nearly 3,500 strategy professionals worldwide, S&T is part of IBM Global Business Services, one of the world’s leading management consulting practices. These professionals have the skills, experience and understanding across many industries to be able to identify the right cloud opportunities for your organiza- tion and to develop an action-oriented cloud implementation strategy and roadmap for your bank. IBM PureSystems IBM PureSystems is a ready-to-run cloud-in-a-box. Software, hardware, middleware, networking equipments, management, and built-in security are all integrated, so there is no need to acquire and integrate components. This cloud offering solves the complex problems of IT delivery for a better user experience. With PureSystems, it is possible to run a private cloud in as little as four hours. PureSystems features: ●● Built-in expertise: Leverage the expertise drawn from IBM and best practices from IT industries ●● Integration by design: Integrate and tune hardware and software resources in a ready-to-go workload-optimized system ●● Simplified experience: Make every part of the IT lifecycle easier with integrated management of the entire system an a broad open ecosystem of optimized solutions IBM SmartCloud Foundation IBM SmartCloud Foundation is a set of technologies for build- ing and managing virtualized infrastructures and private and hybrid clouds. Together these technologies can help build a fully functional cloud management system that can help a bank’s transformation and enable a bank to deliver new services. Individually, these technologies can help nearly any cloud project make quick and incremental progress towards a longer-term cloud strategy. Some examples of key SmartCloud Foundation products include: ●● IBM SmartCloud Provisioning: An infrastructure-as-a- Service (IaaS) solution that reduces costs and offers near-zero downtime and automated recovery ●● IBM SmartCloud Workload Automation: A workload deployer that speeds application deployment to cloud and virtualization environments ●● IBM Security Identity and Access Assurance: Software that administers, protects and monitors user access to resources and provides compliance auditing
- 10. 10 Cloud computing for banking With the help of SmartCloud Foundation, banks can create and deliver infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and PaaS cloud environ- ments. They can do so in a way that includes end-to-end service assurance, the full power of automation and industry-leading security capabilities from IBM to optimize those environments whether the cloud is private, hybrid or public. IBM Infrastructure-as-a-Service IBM offers a range of enterprise-class IaaS offerings with a global reach that is based on open standards. IBM SmartCloud Enterprise is a self-service, public cloud IaaS that is suited to new born-on-the-cloud workloads and agile development. IBM SmartCloud Enterprise+ is a fully managed, isolated IaaS that is optimized for the demanding requirements of born-on- the-enterprise system-of-record workloads like SAP. IaaS offerings from IBM can enable a bank to gain access to enterprise-grade development and test environments and tools as a service, which can help accelerate a bank’s development and testing, perform batch processing or web analytics processing. Application development services for cloud Cloud-based applications can have advantages over traditional application deployment models. These applications use IT and development resources more efficiently and are less costly to maintain. However, developing cloud-based applications requires new approaches. IBM Application Development Services for Cloud delivers on the promise of cloud application development by building custom cloud applications from planning to design, development and deployment. IBM Cloud Computing Security IBM Cloud Computing Security helps customers regain visibil- ity and control through its end-to-end coverage for securing private, hybrid and public clouds. These capabilities empower a bank to dynamically monitor and quantify security risks to enable a bank to better: ●● Understand threats and vulnerabilities in terms of business impact. ●● Respond to security events with security controls that optimize business results. ●● Prioritize and balance a bank’s security investments. IBM offers security consulting services to help develop a strate- gic and comprehensive cloud infrastructures security program, and also offers security management solutions. IBM’s security software solutions enable a bank to: ●● Reduce the risk of data exposure and compromise. ●● Improve the security and reliability of service delivery. ●● Demonstrate compliance. IBM has the products, services and expertise to secure the critical dimensions of cloud, which spans across users, data, applications and the virtualized infrastructure. Smarter Commerce IBM Smarter Commerce™ turns customer insight into action. IBM offers a range of software as a service (SaaS) and cloud infrastructure offerings to help banks optimize their buy, market, sell, and servicing products and services. Leveraging these cloud offerings, banks can engage customers and prospects in a cross- channel dialogue and act on insights based upon past and cur- rent behaviors. They can turn site visitors into repeat customers and loyal advocates by orchestrating a compelling experience throughout each customer’s digital lifecycle.
- 11. 11IBM Sales and Distribution Business analytics A key challenge for the banking industry is the ability to make informed, real-time decisions. Gaining insight across multiple disconnected sources can be complex, time-consuming and costly. When it comes to information about their customers, banks need a seamless, real-time view of each customer across segments, products, regions and channels. They also need the ability to perform analytics across transactions, which can feed both customer-centricity and operational dexterity. Equally, they need an integrated view of finance and risk data, both for risk analysis and regulatory requirements, with the ability to conduct complex what-if analysis and modeling to foresee opportunities and threats. With IBM Business Analytics Software in the Cloud, a banking organization’s business analytics deployments—from business intelligence (BI) to advanced analytics—can be up and running in less time than traditional deployments. These cloud solutions can help reduce the costs and risks associated with implementing and running business analytics software and infrastructure. Business analytics solutions can be hosted on a banking organi- zation’s private cloud, or IBM can handle the hosting on its cloud infrastructure. Collaboration With the right collaboration tools, employees can access the right expertise and information when they need it, enabling them to work together to meet business goals. Collaboration tools can help strengthen customer relationships, eliminate business-process bottlenecks and enable employees to make better decisions more quickly. Many banks lack clear communication channels among employ- ees or between employees and senior management. Information may be isolated, preventing a single view of customer-related activity. Regulatory compliance issues place additional restrictions on the sharing of customer data. Mergers and acquisitions can exacerbate the issue, adding new isolated areas of information and employees. The result is the people who most need customer data may not have access it. To meet business goals, all employees need secure, anytime, any- where access to the information that is relevant to their role. It should also be easy for employees to form virtual teams and tap into expertise elsewhere in the organization. By working smarter through collaboration and with the help of greater insight, employees can make quicker, more informed decisions that promote customer satisfaction and loyalty. IBM SmartCloud for Social Business integrates the essential tools for social business in the cloud: enterprise-grade file shar- ing, communities, instant messaging, web meetings, user pro- files, mail and calendar. The solution is designed to bring social business concepts into business processes that help accelerate collaboration, deepen customer relationships and generate new ideas more quickly. It helps foster a more effective workforce and makes it easier to work seamlessly with people inside and outside of the bank. Meet online, share files, chat, manage projects, network with potential clients, schedule meetings, and send and receive mail anywhere, anytime. Whether working remotely, managing remote teams, or needing one place to bring colleagues, partners and vendors together, SmartCloud for Social Business can help transform the bank into a social business.
- 12. 12 Cloud computing for banking Prepare for the future with cloud computing Getting started with cloud may be easier than you think. Cloud’s many starting points extend across financial services. Here are several examples of successful cloud implementations in the banking and financial services industry. ●● Cloud desktop: A global Japanese bank was concerned that it would suffer security and business continuity risks if the H1N1 virus were to spread to pandemic levels. The 34,000-employee bank is deploying an IBM private cloud to centralize management of desktops using an enterprise-class data center rather than at the user stations. This change gives the bank greater remote flexibility without sacrificing control. ●● Cloud collaboration: A central European bank facilitated continuous, standardized operations and enabled employees across its distributed branches to quickly access trading and banking systems through a security-rich cloud infrastructure. ●● Cloud analytics: A subsidiary of a large European bank designed a new sales platform based on an application package, which enables tellers to enter data into the system only once, instead of entering it up to 20 times for different applications. The new platform also gives the bank a 360-degree view of customer data, which when combined with embedded artificial intelligence can help generate more sales. ●● Cloud development and test: A leading retail bank in the UK simplified infrastructure management for its IT research efforts with a virtualized cloud architecture that can readily support multiple operating system instances. With the new infrastructure, research teams can quickly and easily create virtual testing environments without the delays common to typical configuration efforts. ●● Cloud storage: A Chinese financial services organization reduced system management costs, sped up deployment for resource requests, standardized software configuration for each deployment request and improved the tracking of system resource usage by implementing a cloud computing solution to deliver powerful provisioning capabilities that simplify system management and maintenance. IBM’s internal use of cloud computing demonstrates real bottom-line results, as shown in Table 2. Analytics Collaboration Develop/Test Desktop Storage Product support Blue Insight LotusLive™ Develop/Test cloud Workplace cloud Storage cloud Production cloud • 200,000 users, • 85 percent of web • Server setup from • 2,000 users in • File storage cloud • Private instance up 100 ported conference minutes 5 days to 1 hour the China develop- used by > 130K users and running applications • >275M meeting • >90 percent of new ment lab and applications • First applications • Predictive minutes in 2010 server requests • 200 user pilot SBDC • Block storage cloud migrated and modelling (SPSS) • >215M minutes for using this cloud on the IBM cloud with automated operating and data 1H2011 • Expanded tiering with • Refining platform, management deployments and 50 percent expanding use user base reduction $/GB SaaS SaaS IaaS IaaS IaaS IaaS Table 2. Case Study: IBM uses the cloud across its ongoing transformation agenda
- 13. 13IBM Sales and Distribution The cloud portfolio from IBM IBM is helping clients with their cloud journey by helping them build a cloud environment behind their firewall or by operating their cloud environments for them. IBM SmartCloud represents the IBM vision for cloud computing. The SmartCloud environment can have an order of magnitude impact on clients operating costs, all the while shifting them to an environment where they pay for only what they consume. In doing this, IBM introduces standardization and interoperability that empowers customers and yields enormous productivity savings on an ongoing basis. And with that savings, IBM can help free up clients to attack new channels, invest in social media and mobile, transform their front office, allow investment in bullet- proofing their infrastructure, and help them reach new markets. Compared to traditional deployment and services, cloud tech- nology can result in substantial ROI, as shown in Figure 5. Figure 5. Cloud ROI. (*Based on results from IBM’s Technology Adoption Program. Client-specific results can only be ascertained after a return on investment analysis.) ROI inputs: Capabilities From Server and storage utilization Self service Test provisioning Change management Deployment process Cost model Standardization Payback period for new services 10-20 percent (inefficient) None Weeks Months Labor intensive Nearly fixed Complex Years Shifting workloads to IBM SmartCloud Enterprise can help enable new opportunities and drive significant cost savings. Legacy server environments To* 70-90 percent (highly efficient) Unlimited Minutes Days or hours Automated By the hour Self service Months Cloud server environments
- 14. 14 Cloud computing for banking IBM offers a flexible portfolio of cloud computing capabilities that can address a bank’s cloud deployment and management needs, as shown in Figure 6. All of these capabilities exist today in IBM. Not only can IBM provide the right hardware, software and expertise to help your banking organization fully leverage the cloud, but also the company’s deep understanding of the banking industry and your business priorities will enable IBM help you build a personalized cloud roadmap of where to go and how to get there. Why IBM? IBM is a leader in cloud computing and this leadership extends to the delivery of enterprise-wide solutions. With IBM cloud computing offerings, your bank can cost-effectively address the infrastructure issues that affect the delivery of your services. IBM has a vision of what’s possible for banking and is an enabler of integration and interoperability with assets in cloud, analytics, Figure 6. The IBM portfolio of cloud deployment and management options. IBM Capabilities: Broad Narrow Cloud Analytics Software As A Service (SaaS) SaaS (SAP, Oracle) Application development / security Migrations / testing Industry solutions Strategy & planning Business Analytics & Optimization SaaS Implementation Services Enterprise Architecture Application Innovation Services Application Management Service Industry solutions Strategy & transformation
- 15. 15IBM Sales and Distribution collaboration and leading platforms. IBM also has a portfolio of unifying technologies and services for the construction of clouds. IBM cloud solutions offer: ●● Clear economic value, helping you work through the right mix of delivery models to realize the maximum benefit. ●● Secure solutions that are ready for business, based on the demanding needs of today’s businesses, with rapid provision- ing, clear visibility of assets, robust data governance and a seamless mix of delivery models. ●● Integration and open standards: IBM supports industry standards, has more than eight million developers and provides a platform for open innovation. ●● Global relevance: IBM has offices, delivery centers and partners in 174 countries. And having the experience of running a globally integrated enterprise, IBM understands what it takes to be a global business. ●● Design simplicity: From sourcing to usage to maintenance, IBM cloud solutions are designed to be simple, intuitive and built based on how people actually work. The world’s leading financial services institutions have turned to IBM to help address their most difficult challenges. IBM offers deep industry experience in integrating the hardware, software and services banks need to transform their operations. Tremendous opportunities exist for banks that invest in cloud technology. With the cloud, banks can gain new insights into their organizations and develop the capacity to act on those insights. Cloud computing can be a viable solution for reducing operating costs, simplifying business processes and collaborating more easily with partners. For more information To learn more about how cloud computing can help banking institutions, visit: ibm.com/services/cloud Additionally, IBM Global Financing can help you acquire the IT solutions that your business needs in the most cost-effective and strategic way possible. We’ll partner with credit-qualified clients to customize an IT financing solution to suit your business goals, enable effective cash management, and improve your total cost of ownership. IBM Global Financing is your smartest choice to fund critical IT investments and propel your business forward. For more information, visit: ibm.com/financing