Compference 2017: Leading Human-Centered Change
- 2. Human-Centered Change Presented by Ben Grossman-Kahn CEO & Co-Founder of Catalyz
- 3. Agenda • What’s your transformation story? • Am I dealing with Technical or Adaptive change? • Mental models and frameworks for human- centered change
- 4. We are facing profound changes in every sector • Rise of Mobile • Cloud platforms and services • Open source • Machine Learning • AI • Automation • Internet of Things Technology • Multiple generations • Culture of entrepreneurship • Purpose driven economy • Competition for talent • Virtual staff Workforce • Expectations focused on speed, convenience and personalization • Technology driving new experiences Customers
- 7. What’s your Transformation story?
- 9. Employee resistance to change and management behaviors, not budget or resources, are the primary factors in 70% of failed change management programs -McKinsey 62% of employee respondents identified culture as the main hurdle to digital transformation. -CapGemini
- 13. Adaptive Leadership “…change that truly transforms an organization, be it a multibillion-dollar company or a ten-person sales team, demands that people give up things they hold dear: daily habits, loyalties, ways of thinking. In return for these sacrifices, they may be offered nothing more than the possibility of a better future.” -Heifetz & Linsky, HBR 2002
- 14. Adaptation
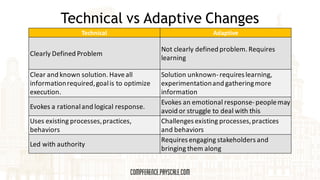
- 15. Technical vs Adaptive Changes Technical Adaptive Clearly Defined Problem Not clearly defined problem. Requires learning Clear and known solution. Have all information required, goal is to optimize execution. Solution unknown-requires learning, experimentation and gathering more information Evokes a rational and logical response. Evokes an emotional response-people may avoid or struggle to deal with this Uses existing processes, practices, behaviors Challenges existing processes, practices and behaviors Led with authority Requires engaging stakeholders and bringing them along
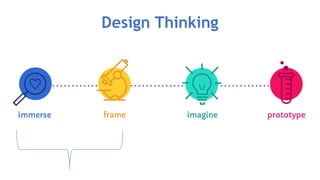
- 17. Design Thinking
- 19. People don’t fear change, they fear loss.
- 20. A framework for change Core • Company values • Who our customers are Emerging • New ways of working • New comp structure Legacy • Siloed teams • Some titles/roles
- 23. Design Thinking
- 25. D V F Desirability (Do people want this?) Viability (Should we do this?) Feasibility (Could we do this?)
- 28. Questions to consider • Is this a puzzle or a mystery? • What might people be afraid of losing? • What might be some competing commitments? • What have we done to build empathy and challenge our assumptions? • Have we designed with a focus on desirability and experience?
- 30. Appendix
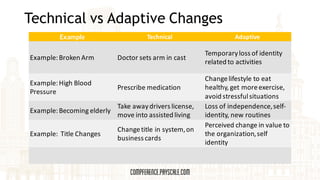
- 31. Technical vs Adaptive Changes Example Technical Adaptive Example: Broken Arm Doctor sets arm in cast Temporaryloss of identity related to activities Example: High Blood Pressure Prescribe medication Change lifestyle to eat healthy, get more exercise, avoid stressful situations Example: Becoming elderly Take away drivers license, move into assisted living Loss of independence, self- identity, new routines Example: Title Changes Changetitle in system, on business cards Perceived change in value to the organization, self identity
- 32. Each one of these thwarting tactics…grows out of people’s aversion to the organizational disequilibrium created by your initiative…people strive to restore order, maintain what is familiar to them, and protect themselves from the pains of adaptive change. -A Survival Guide for Leaders, HBR 2002
- 33. According to a McKinsey survey of 2,000 executives, programs that encourage and facilitate employees to take an active role in the transformation have a success rate five times higher than those led as top-down initiatives
- 34. C Communication Sharing thoughts, questions, ideas, & solutions C Collaboration Working together to reach a goal, putting talent, expertise, & smarts to work. C CriticalThinking Looking at problems in a new way and linking learning across subjects & disciplines C Creativity Trying new approaches to get things done equals innovation & invention 21st Century Skills