Complement Activation Pathways: Key Mechanisms in Immune Defense
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
1 like•99 views
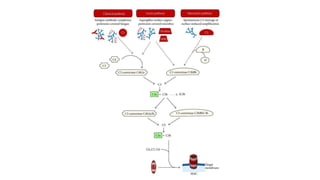
The complement system is a key part of the immune response, made up of proteins that eliminate pathogens. It is activated through three main pathways: Classical Pathway: Triggered by antibodies bound to antigens on a pathogen's surface. Lectin Pathway: Initiated by mannose-binding lectin binding to sugars on pathogens. Alternative Pathway: Activated spontaneously on pathogen surfaces without antibodies. All pathways converge to form C3 convertase, leading to the destruction of pathogens by marking them for immune attack and creating pores in their membranes. This process enhances the body's ability to fight infections quickly and effectively.
Report
Share
Report
Share