Continental Drift Theory
- 2. Continental Drift Theory ● Alfred Wegener was the first person to propose the theory of Continental Drift. ● Continental Drift is the movement of earth’s continents relative to each other, thus appearing to drift across the ocean bed. ● Continental Drift theory is the theory that once all the continents were joined in a super-continent which scientists call the Pangaea. Alfred Wegener
- 4. Pangaea ● Wegener’s theory of continental drift states that the existing continents of the earth were once glued together forming a super landmass. ● Over time, the landmass broke and drifted away and is still drifting to this day. In his proposal, he stated that the super content, which he named Pangaea, meaning ‘’all earth” once existed. ● As a result of movement of the supercontinent, Pangaea split into two super landmasses namely Laurasia and Gondwanaland. ● aurasia, makes up the northern continents of today. Gondwanaland makes up the southern continents of today.
- 5. Causes of Continental Drift ● The causes of continental drift are perfectly explained by the plate tectonic theory. The earth’s outer shell is composed of plates that move a little bit every year. Heat coming from the interior of the earth triggers this movement to occur through convection currents inside the mantle. ● Almost all plate movement occurs in boundaries which lie between different plates. When plates drift away from each other, there is formation of new crust at divergent boundaries. On the other hand, tectonic movement destroys crust during interaction of the plates. ● Continental drift has impacted the universe in many ways. It has affected the global climate, the world’s geographical positions and the evolution of animals.Continental drift also comes along with grave effects such as Volcanoes, Earthquakes, and Tsunamis.
- 6. Examples of Continental Drift
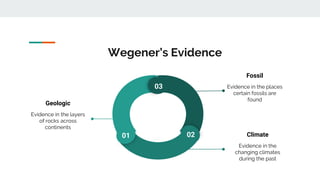
- 7. Wegener’s Evidence Geologic Evidence in the layers of rocks across continents Fossil Evidence in the places certain fossils are found Climate Evidence in the changing climates during the past 03 01 02
- 8. Geologic Evidence ● Rocks of the same age and type and displaying the same formations are found in south-east Brazil and South Africa. ● The trends of the mountains in the eastern USA and north-west Europe are similar when placed in their old positions. ● Similar glacial deposits are found in Antarctica, South America and India, now thousands of km apart.
- 9. Fossil Evidence There are many examples of fossils found on separate continents and nowhere else, suggesting the continents were once joined. If Continental Drift had not occurred, the alternative explanations would be: ● The species evolved independently on separate continents - contradicting Darwin’s theory of evolution. ● They swam to the other continent/s in breeding pairs to establish a second population.
- 10. Climate Evidence ● Glacial deposits at current equator. ● Fossilized palm trees in Greenland. ● South Africa today has a warm climate. Yet its rocks were deeply scratched by ice sheets that once covered the area. ● Greenland had once been near equator and had slowly moved to the Arctic Circle. ● South Africa, once closer to the South Pole, had moved slowly north to a warmer region.
- 11. Other Circumstantial Evidence The Jigsaw Fit The similarity in outline of the coastlines of eastern South America and West Africa had been noted for some time. The best fit is obtained if the coastlines are matched at a depth of 1,000 metres below current sea level. The Tectonic Fit Fragments of an old fold mountain belt between 450 and 400 million years ago are found on widely separated continents today. Pieces of the Caledonian fold mountain belt are found in Greenland, Canada, Ireland, England, Scotland and Scandinavia. When these land masses are re- assembled the mountain belt forms a continuous linear feature.
- 12. Thank You