Cost of quality
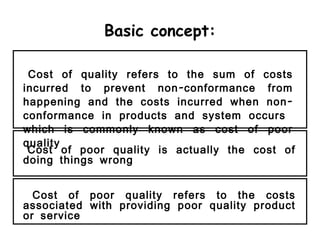
- 2. Basic concept: Cost of quality refers to the sum of costs incurred to prevent non-conformance from happening and the costs incurred when non-conformance in products and system occurs which is commonly known as cost of poor quality Cost of poor quality is actually the cost of doing things wrong Cost of poor quality refers to the costs associated with providing poor quality product or service
- 3. Why do we need to know COQ? This tool speaks in the language of management $$$$ Research shows that cost of poor quality can range from 15 % to 40 % of the business costs It can prioritize quality improvement actions Cost of quality data shows how profit is affected by quality It helps identify the redundant activities
- 4. Hidden Failure Costs Scrap Warranty Rework Decreased capacity Increased inventory Shop and field downtime Management time Engineering time Customer dissatisfaction Lost sales Lost customer trust
- 5. Cost of quality – categories 1 - Cost of achieving good quality Prevention Costs Appraisal Costs 2 - Cost of poor quality Internal failure Costs External failure Costs Quality costs fall into two main categories:
- 6. Preventive costs: Preventive costs are the cost of all activities specifically designed to prevent poor quality product or service. These costs are incurred to keep appraisal and failure costs at minimum.
- 7. Examples of preventive costs: Process Capability studies Market surveys Pilot scale projects and testing Procedure writing Vendor evaluation and testing Training and education Quality improvement projects Customer survey House keeping Design review
- 8. These are the costs associated with measuring, evaluating or auditing product or service to assure conformance to standard or performance requirement. Appraisal costs:
- 9. Internal audits Incoming material inspection Laboratory testing Calibration costs In process material inspection Equipment calibration Procedure evaluation Final product inspection Automated testing tools Examples of Appraisal costs:
- 10. These are the costs incurred when product or service fail to meet quality requirements prior to the transfer of ownership to the customer. Internal failure cost
- 11. Examples of internal failure costs: Rework Scrap Overtime Downtime Excess inventory Excess material handling Redesign Downgrading Retesting 100% sorting inspection Scrap & rework - supplier
- 12. These are the costs incurred by a business due to failure of product or service at the customer end. These costs results into warranty claims and loss of reputation. External failure cost
- 13. Warranty costs Customer dissatisfaction Loss of market share Price concession Premium freight Product recalls Time spent to resolve customer complaints Restocking costs Other penalties Examples of external failure costs:
- 14. Measuring cost of quality COQ data can be measured and presented in many different ways. % age of sales % age of profits % age of manufacturing cost Rs per direct labor hr Rs per unit of product
- 15. Steps in implementing quality costs The following sequence applies to most organizations Review the literature on quality costs or consult others in similar industries who are using the same tool. Select one organizational unit of the company to serve as a pilot site Discuss the objectives of the study with the key people in the organization Collect whatever cost data are conveniently available from the accounting system Make a proposal to management for a full study
- 16. Publish a draft of the categories defining the cost of poor quality Finalize the definitions and secure management approval Secure agreement on responsibility for data collection and report preparation Collect and summarize the data Present the cost results to management along with the results of a demonstration quality improvement project
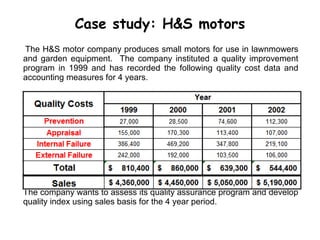
- 17. Case study: H&S motors The H&S motor company produces small motors for use in lawnmowers and garden equipment. The company instituted a quality improvement program in 1999 and has recorded the following quality cost data and accounting measures for 4 years. The company wants to assess its quality assurance program and develop quality index using sales basis for the 4 year period.
- 18. Key points of study: Approximately 75% of the H&S’s total quality costs are a result of internal and external failures. In 2000 company spent more money on product monitoring and inspection that resulted into high appraisal cost. With this strategy, H&S was able to identify more defective items, resulting in an apparent increase in internal failure cost and lower external failure cost. In year 2001 & 2002 company spent more money on prevention activities i.e. training of employees, redesigning the production process and planning how to build in product quality etc. Prevention costs increased by more than 300 % during the 4 year period resulted into decrease in overall quality costs.
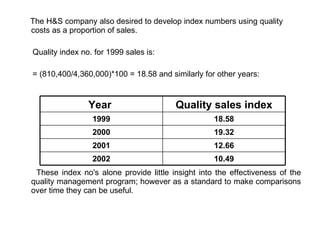
- 19. The H&S company also desired to develop index numbers using quality costs as a proportion of sales. Quality index no. for 1999 sales is: = (810,400/4,360,000)*100 = 18.58 and similarly for other years: These index no's alone provide little insight into the effectiveness of the quality management program; however as a standard to make comparisons over time they can be useful. 10.49 2002 12.66 2001 19.32 2000 18.58 1999 Quality sales index Year
- 20. Conclusion: When the cost of achieving good quality increases; cost of poor quality decreases automatically.
- 21. Benefits of using quality costs Quantify the size of the quality problem Identify major opportunities for cost reductions It helps in Identification of opportunities for reducing customer dissatisfaction and associated threats to product salability Measures the results of quality improvement activities Align quality goals with organizational goals Set cost reduction targets