Costing for Hospitals - How to arrive at service level cost ?
- 1. Healthcare Service Level Costing The Challenges & Solution
- 2. CA.S.Manivannan • Business Strategist & Healthcare Consultant • 19+ years experience in P/L Management, Board Participation, Hospital Operations, Costing & Budgeting, HCIT, SCM and consulting •Previous Exp.: Apollo Hospital Group, KLES-Belgaum, SRM Medical Collage & Hospital,AIIMS – New Delhi, Star Health Insurance, Knowledge Partner to Institute of Cost Accountants of India and Ministry of Health in healthcare costing, Medall Healthcare and 100 plus projects •Member FICCI Task Force on pricing of healthcare, Healthcare Costing, Federation of Indian Chamber of Commerce (FICCI). •Specialising in Costing for hospitals from 2007 onwards…..
- 3. Contents Why costing is important to you ? Developments in cost transformation and optimization What costing will deliver to you ? – improving profits without spending money ! What do you mean by costs ? Methods of costing The process for Time Driven Activity Based Costing What is Value Based Care reimbursement and the future Conclusion
- 4. Why Costing is important to you ? An industry under pressure – incremental changes not producing results Awareness & pressure on costs among all the stakeholders – Govt, payers & Consumers Government trying to reduce cost of implants & consumables
- 5. Why Costing is important to you ? Hospitals facing double whammy – Price Pressure and Cost Pressure Increasing manpower costs both medical and non-medical Advanced technology leading to increase in cost of treatment
- 6. Why Costing is important to you ? Clustered Distribution of hospitals resulting in competition Pressure from Insurance companies to reduce claims Shift from Top Line Management to Bottom Line Management
- 7. Why Costing is important to you ? Need to generate Return on Investment for For- Profit Hospitals Need to generate surplus for Not-For-profit hospitals to maintain and grow
- 8. Developments in Cost Transformation and Optimization Generate capital for GrowthGenerate capital for Growth Government and Corporate buying healthcare services at lesser prices offering higher volumes – Public Private Partnership Models Government and Corporate buying healthcare services at lesser prices offering higher volumes – Public Private Partnership Models Bridging GAP between operating performance and financial performance Bridging GAP between operating performance and financial performance Changing care models due to Internet of Things & AI and Machine learning Changing care models due to Internet of Things & AI and Machine learning Value Based Care – Linking reimbursement to clinical outcomes Value Based Care – Linking reimbursement to clinical outcomes
- 9. What Costing will deliver to you ? • Understand your true MarginsToTo • opportunities to reduce costsIdentifyIdentify • Total costs of both inpatient and outpatient ServicesUnderstandUnderstand • Capacity utilization of your hospital facilities and address under-utilization IdentifyIdentify
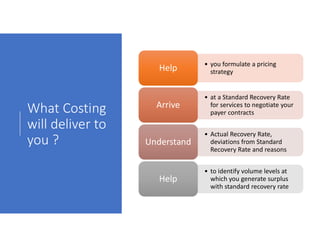
- 10. What Costing will deliver to you ? • you formulate a pricing strategyHelpHelp • at a Standard Recovery Rate for services to negotiate your payer contracts ArriveArrive • Actual Recovery Rate, deviations from Standard Recovery Rate and reasons UnderstandUnderstand • to identify volume levels at which you generate surplus with standard recovery rate HelpHelp
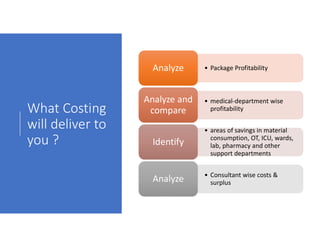
- 11. What Costing will deliver to you ? • Package ProfitabilityAnalyzeAnalyze • medical-department wise profitability Analyze and compare Analyze and compare • areas of savings in material consumption, OT, ICU, wards, lab, pharmacy and other support departments IdentifyIdentify • Consultant wise costs & surplusAnalyzeAnalyze
- 12. What Costing will deliver to you ? • Benchmarks for monitoringDevelopDevelop • A Dashboard to top managementDevelopDevelop • To outsource or notDecisionDecision
- 13. What do you mean by costs ? When Government talks of costs, it means the amount reimbursed or amount spent in state run service providers When Consumers talk of costs, it means the amount spent by them for treatment or health insurance premium & uncovered compensation of the treatment. For insurance companies, the claims to be paid to the service providers For the service providers, costs incurred within their system to provide treatment to the patients
- 14. Service Level Costing Per Patient Cost Per Bed Cost Per Procedure Cost Which one to prefer…
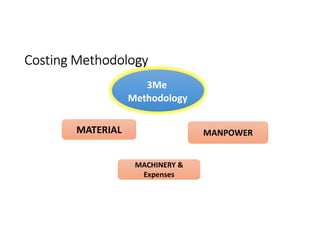
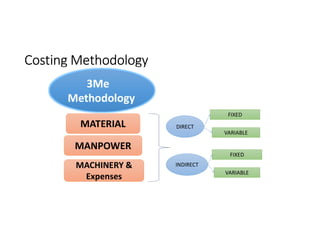
- 15. Concept of Costs & Cost Classification for hospitals • Classification of Costs in • Direct Costs • Indirect Costs • With Cost drivers such as labour, materials, & overheads conventionally but reclassified for convenience as Manpower, Materials, Machinery & expenses
- 16. Concept of Costs & Cost Classification for hospitals • Classification of by department • Medical Departments • Medical Support Departments • Service Departments
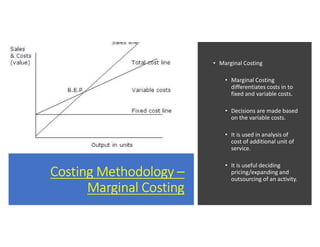
- 19. Costing Methodology – Marginal Costing • Marginal Costing • Marginal Costing differentiates costs in to fixed and variable costs. • Decisions are made based on the variable costs. • It is used in analysis of cost of additional unit of service. • It is useful deciding pricing/expanding and outsourcing of an activity.
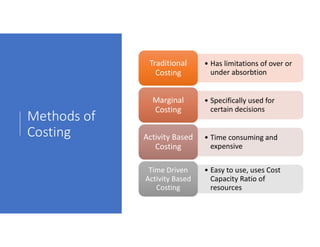
- 20. Methods of Costing • Has limitations of over or under absorbtion Traditional Costing Traditional Costing • Specifically used for certain decisions Marginal Costing Marginal Costing • Time consuming and expensive Activity Based Costing Activity Based Costing • Easy to use, uses Cost Capacity Ratio of resources Time Driven Activity Based Costing Time Driven Activity Based Costing
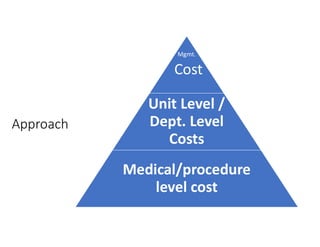
- 21. Approach Mgmt. Cost Unit Level / Dept. Level Costs Medical/procedure level cost
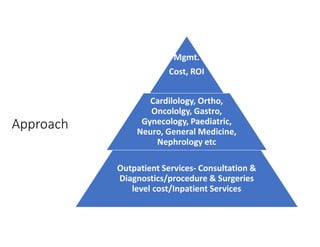
- 22. Approach Mgmt. Cost, ROI Cardilology, Ortho, Oncololgy, Gastro, Gynecology, Paediatric, Neuro, General Medicine, Nephrology etc Outpatient Services- Consultation & Diagnostics/procedure & Surgeries level cost/Inpatient Services
- 23. Methods of Costing Time Driven Activity Based Costing is the method for Value Based Care Concept
- 24. The Process for Time Driven Activity Based Costing • The Clinical ProcessesMappingMapping • Clinical & Non-Clinical Resources MappingMapping • For each Resource Find Cost Capacity Ratio - CCR Find Cost Capacity Ratio - CCR • Cost of resources for every patient based on CCR – Based on consumption of units of resources Find outFind out
- 25. Time Driven Activity Based Costing (TDABC) • Time-driven ABC requires estimates of only two parameters: • The unit cost of supplying capacity (Supply Cost Ratio) • The time required to perform a transaction or an activity
- 26. Important Parameters Determine measurement of Unit of Cost each resource…It could per hour, per patient, per Bed or the number of surgeries/procedures Determine the capacity of each resource….It could be std no of hours for OT or Equipment or minutes per procedure or number of procedures per day for a surgeon
- 27. Important Parameters Find out number of units of resource consumed for the procedure Cost per unit of resource and the number of units of resource per procedure lead to cost of the resource
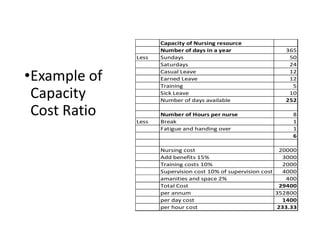
- 28. •Example of Capacity Cost Ratio Capacity of Nursing resource Number of days in a year 365 Less Sundays 50 Saturdays 24 Casual Leave 12 Earned Leave 12 Training 5 Sick Leave 10 Number of days available 252 Number of Hours per nurse 8 Less Break 1 Fatigue and handing over 1 6 Nursing cost 20000 Add benefits 15% 3000 Training costs 10% 2000 Supervision cost 10% of supervision cost 4000 amanities and space 2% 400 Total Cost 29400 per annum 352800 per day cost 1400 per hour cost 233.33
- 29. Time Driven Activity Based Costing (TDABC)
- 30. Important observations arising from costing exercise…. Appropriate technology and not necessarily advanced technology Capacity Utilization and cost recovery Areas of saving OT, consumable, pharmacy and wards Consultant wise costs and profitability Brand VS Generic Imported VS Indigenous
- 31. FICCI REPORT
- 32. Depth of Work Involved • Standard templates were developed • 10 surgeries from across specialties • 10 hospitals of different sizes from different locations • Each Surgery had cost allocation sheets of 25 departments approximately.
- 33. Key Findings- Comparison of Procedure Cost with AB-NHMP Package Rates
- 34. Key Findings- Deviation from Mean Value for Procedure Costs across Hospitals
- 35. Key Findings • Volumes have different impact on different cost components • Machinery and Materials • Clinical Teams • Smaller size hospital have cost challenges • Clinical teams- payment method • Equipment Renting
- 36. Key Findings (Contd.) • Difference in location has impact on cost components • Manpower • Real estate • Impact of land costs • Difference in costs between government and private hospitals
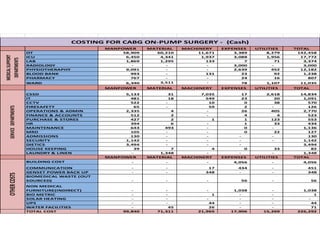
- 37. MANPOWER MATERIAL MACHINERY EXPENSES UTILITIES TOTAL OT 58,909 60,210 11,671 3,389 8,279 142,458 ICU 6,450 4,341 1,937 3,088 1,956 17,772 LAB 1,869 1,295 133 7 71 3,374 RADIOLOGY - - - 3,000 - 3,000 PHYSIOTHERAPHY 9,091 - - 2,639 452 12,182 BLOOD BANK 993 - 131 23 92 1,238 PHARMACY 767 - - 24 16 807 WARD 6,340 3,511 - 78 1,107 11,035 MANPOWER MATERIAL MACHINERY EXPENSES UTILITIES TOTAL CSSD 5,133 31 7,035 17 2,618 14,834 IT 481 18 549 23 20 1,091 CCTV 522 - 10 0 38 570 FIRESAFETY 65 - 59 2 - 126 OPERATIONS & ADMIN 2,335 4 - 26 405 2,770 FINANCE & ACCOUNTS 512 2 - 4 4 523 PURCHASE & STORES 427 2 1 1 123 553 HR 394 6 - 1 33 434 MAINTENANCE 643 493 - 0 - 1,136 MRD 105 - - 0 22 127 ADMISSIONS 130 - - - - 130 SECURITY 1,142 - - - - 1,142 DIETICS 3,494 - - - 3,494 HOUSE KEEPING 39 7 4 0 33 82 LAUNDRY & LINEN - 1,348 - - - 1,348 MANPOWER MATERIAL MACHINERY EXPENSES UTILITIES TOTAL BUILDING COST - - - 4,056 - 4,056 COMMUNICATION - - 17 434 - 451 GENSET POWER BACK UP - - 348 - - 348 BIOMEDICAL WASTE (OUT SOURCED) - - - 56 - 56 NON MEDICAL FURNITURE(INDIRECT) - - - 1,038 - 1,038 BIO METRIC - - 1 - - 1 SOLAR HEATING - - - - - - UPS - - 44 - - 44 WATER FACILITIES - 45 26 - - 71 TOTAL COST 99,840 71,311 21,965 17,906 15,269 226,292 OTHERCOSTS MEDICALSUPPORT DEPARTMENTS COSTING FOR CABG ON-PUMP SURGERY - (Cash) SERVICEDEPARTMENTS
- 38. What is Value Based Care and the future • Payers will pay a bundled sum for an outcome • This is irrespective of volume of services to the patient • The financial risk of treating the patient is with the service provider • All the stake holders in treating the patients including consultants and outsourcing partners should work closely to achieve outcome at an optimum cost • Value Based Care is the way forward with increasing role of insurance, public private partnership and government in reimbursing Medical bills