Coursebook Evaluation
- 1. CoursebookAnalysis Dannae Del Campo, Gabriela Quezada, Angel Sandoval Universidad Católica de la Santísima Concepción (UCSC)
- 2. Teacher’s Interview As Paula Morales expresses course books are important to guide teachers in certain specific topics using grammar, pronunciation and listening. However, according to Miss Morales’ point of view some sequences of units are not coherent to be followed step by step. Therefore, she states that when the activities are boring and not appealing to students’ interests it is important to adapt and supplement them by taking into account students’ background, students’ age and their likes and dislikes. Moreover, her own preferences are another important fact because if she can find another activity that suits the class better and that deals with the features that students have to learn, she changes it. For this reason, she explains that the way for adapting and supplementing the activities of the course book it is based on having present the level of students and the topics covered in the book so they become motivated. Although Miss Morales supplements a big part of the course book she uses, she finds very useful the speaking activities it has. She mentions that she develops the speaking parts because students can practice grammar and phonetics at the same time, being grammar one of the aspects which students found boring. At last but not the least, Miss Morales considers that course books are useful as a guide for teachers although is not advisable to be ruled by them. Moreover she expresses that she would like them to have more music and more kinesthetic activities that allow students to move and speak at the same time.
- 3. FACTUAL DETAIL Title Author Straight Forward Pre-intermediate Student’s book Philip Kerry Publisher Macmillan Publishers Limited Price $14.720 ISBN 978 1405 01057 3 978 0230 02079 5 (with CD Rom) 159 pages N° of pages Components Level Workbook without key and CD pack Workbook with key and CD pack Teacher’s book Class CDs Portfolio Pre-intermediate level Length One year Units 12 units Lesson/sections 48 lessons (four per unit, ABCD) Target Skills Speaking (is the main skill to be emphasized) Listening Reading Writing Young adults and adults Target Learners Assessment (* Poor ** Fair *** Good Factor Rating Rationale **** Availability * **** Excelent Comments It can be said that the book integrate the four skills in a very balanced form. It integrate functional language The Straight forward book is available in LibreriaInglesa in Concepción.
- 4. Layout/graphics **** The straight forward book is appropriate for young adults and adults due to the images, pictures, graphics and some cartoons are authentic pictures and full of color. Selection/grading ** Authenticity **** Cultural bias **** The units of the book are not graded due to every of them has independent topics and target language. In terms of dialogues the “Straight Forward” course book presents very authentic material, in which most of the dialogues are related to reallife situations and conversations and spoken by native speakers. The book is British oriented primarily, due to the CD audio is mainly recorded by British native speakers This course book includes components that help to stimuli the students in their own learning. It contains workbook and CDs that also help students to improve properly their abilities development. The course book units are not interrelated, so the teacher could skip some units without affecting the learning process. Stimulus/practice//revision **** Flexibility ****
- 5. The following activities were taken from the pages 46-49 and 52-53 of the book “Straight Forward”. Lesson U5D: Holiday heaven. We decide to put first the lesson 5D because it makes more sense to deal with the places of destination than mean of tranport. (Planes) Select / Adopt Reject Adapt Reading (part 1): Read the Reading (part Vocabulary(1).Speaking webpage and match the 2): Read about (1,2). pictures A-H to the some more different holidays. holidays. These activities What type of will be adapted It worth retaining this holiday are by mixing them activity because it is a they? in just one good introduction to the activity. With topic. We do not the vocabulary intend to use provided the Reading (part 3): Match this activity student has to the paragrahpd 1-4 to the because the create a dialogue holidays in the webpage part 1 of the in which he/she advertisement. reading is is a tourist guide enough as an of her/his own It is worth retaining this introduction city so they have activity because students to the topic. to decide what can relate the use of the he/she intends to vocabulary in a real Vocabulary do with the context. (part 2,3) tourists to present it in Pronunciation (1,2,3). We do not class. intend to use It is worth retaining this this activity In this way it activity because students because they would be easier can practice and learn the have to for the student new vocabulary of the prepare a to create the unit. dialogue and dialogue with it will be the new boring to have vocabulary two similar because the activities. activity will be more personalized. U 5B: Speaking: Work in pairs. Think of Planes a long/interesting/boring/frightening journey you have been on. Describe your journey. Pronunciation: Vocabulary (1) Intonation Listening (1) (1.45,1.46, 6) These activities will be We do not adapted by mixing intend to use them. Students will Extra Material
- 6. It is worth retaining this activity these because it is an effective way to activities introduce the topic. because there are more like Vocabulary (2) : Put the phrases listening in the correct order. activities than pronunciation It is worth retaining this activity practice and because student can identify the they already verbs often used with the new practice vocabulary. listening. Listening (2,3): Roleplay (7). It is worth retaining these activities because they have to acquire listening skills and this is a good way to develop it. We do not intend to use these activities because they already had other listening activities that we considered more important that this one and having a similar one would be boring for them. Pronunciation: Intonation (1.45) It is worth retaining this activity because it is important for second language students to acquire the correct intonation as a part of the pronunciation. Functional (1). language: Requests It is worth retaining this activity because completing the chart with the different ways of responding the request it is a good way of learning them by hard. Functional language: Requests (2). Find 5 more mistakes in the dialogue and correct them. We do not intend to use this activity because it is not necessary if they complete the chart with the correct form. have to find new vocabulary in the pictures above and after that describe what is happening in each picture. In this way it would be better for the student to use the new vocabulary previously recognized in the pictures to create sentences.
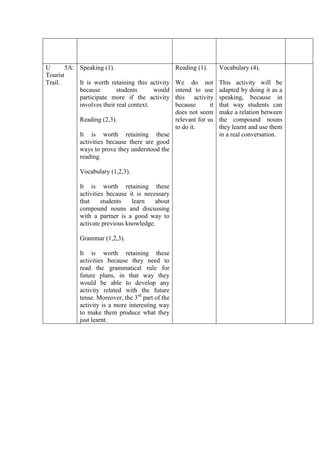
- 7. U 5A: Speaking (1). Tourist Trail. It is worth retaining this activity because students would participate more if the activity involves their real context. Reading (2,3). It is worth retaining these activities because there are good ways to prove they understood the reading. Vocabulary (1,2,3). It is worth retaining these activities because it is necessary that students learn about compound nouns and discussing with a partner is a good way to activate previous knowledge. Grammar (1,2,3). It is worth retaining these activities because they need to read the grammatical rule for future plans, in that way they would be able to develop any activity related with the future tense. Moreover, the 3rd part of the activity is a more interesting way to make them produce what they just learnt. Reading (1). Vocabulary (4). We do not intend to use this activity because it does not seem relevant for us to do it. This activity will be adapted by doing it as a speaking, because in that way students can make a relation between the compound nouns they learnt and use them in a real conversation.
- 8. The following activities were taken from pages 48-49 and 50-51 of the book “Straight Forward”. Lesson: Planes 5B 1. Speaking: This activity is Communicative of the social kind because although the book give the students the topic they have to discuss, they can answer however is more convenient to them and also giving freedom in their answers. 2. Vocabulary (1): This is a Pre-communicative activity of the quasi-communication type because students have to relate the vocabulary words studied with the images provided of a real context. 3. Vocabulary (2): This is a Pre-communicative activity of the structural type because students have to practice the grammatical rules previously learnt at the moment of ordering the phrases. 4. Listening (1): This is a Communicative activity of the functional type because they have to produce a speaking by making a relation with the structures previously learnt. 5. Listening (2): This is a Communicative activity of the functional type because is a controlled activity and they have to relate the new vocabulary with the images of the book. 6. Listening (3): This is a Communicative activity of the functional type because students have to listen and make a relation between what they learnt and what they are hearing of a real context situation. 7. Functional Language: requests (1): This is a precommunicative activity of the structural type because they are learning the grammatical structure of requests by identifying them in a text and completing a chart. 8. Functional Language: requests (2): This is a precommunicative activity of the structural type because they have to correct grammar mistakes inside a text. 9. Pronunciation (5): This is a Communicative activity of the functional type because students have to listen and make a relation between what they learnt and what they are hearing of a real context situation. 10. Pronunciation (6): This is a pre-communicative activity of the quasi-communicative type because students have to practice with a given situational dialogue which is more a controlled activity. 11. Role play (7): This is a communicative activity of the functional type because they have to use the language they learnt in a given situation.
- 9. Lesson: 5C A weekend break. 1. Vocabulary and speaking: Hotels (1): This is a Precommunicative activity of the quasi-communicative type because they are relating the new words learnt from the box to the use of language in a real context. 2. Vocabulary and speaking (2): This is a Pre-communicative activity of the quasi-communicative type because they are choosing from a given list of activities so they are making relations between what they learnt and a real context. 3. Vocabulary and speaking (3): This is a Communicative activity of the functional type because there is not an interaction with other person so it cannot be social. 4. Vocabulary and speaking (4): This is a communicative activity of the functional type because students have to answer to specific question so it is more guided. 5. Listening (1): This is a Communicative activity of the functional type because they have to explain why they would like to stay there using the language they have learnt. 6. Listening (2): This is a Communicative activity of the functional type because students have to listen and make a relation between what they learnt and what they are hearing of a real context situation. 7. Listening (3): This is a Communicative activity of the functional type because of the same reasons of the listening above. 8. Listening (4): This is a communicative activity of the functional type because they have to retell a story which was given using the structures learnt. 9. Grammar (1): This is a Communicative activity of the functional type because students have to complete a sentence with the words given so they solve the problem. 10. Grammar (2): This is a Communicative activity of the functional type because the students have to make a decision on what to say in a real context. 11. Grammar (3): This is a Communicative activity of the functional type because although it seems as a grammar activity they have to decide which verb it is the best in a sentence which they already learnt the grammatical structure. 12. Grammar (4): This is a Pre-communicative activity of the quasi-communicative type because although they have to practice a dialogue in pairs, this is a situational dialogue which means it was given. 13. Did you know? (1): This is a communicative activity of the functional type because students have to infer what it is the answer of the question before reading the text. 14. Did you know? (2): This is a Communicative activity of the functional type because students have to answer the given questions which makes the activity more guided.
- 10. Skills and Topic Tomlinson (2011) suggested that a course book aims to provide as much as possible in one book and is designed so that it could be used as the only book that the students necessarily use during a course. Such a course book frequently includes work related to the systems of the language, functions and the four skills. The Straight Forward course book seems to be very complete not only in terms of the four skills but also in terms of the system of the language, which are grammar, vocabulary and pronunciation, due to every unit has been divided into them in order to promote a complete learning of the language. Concerning grammar, the straight forward book emphasizes it through targeted activities at the end of each unit in which the grammatical rules are explained in detail. In terms of the skills, they are emphasized in a great number of activities. First of all, regarding to reading activities, the Straight Forward book contains a great number of reading activities (two or three per unit) that are associated with the interests of the students; moreover, the contents of the reading, and the vocabulary of it corresponds to the level of the pre-intermediate students level. in terms of listening, Ur (1996) argued that in listening comprehension activities the students should learn to function successfully in real-life listening situations, what means that is not very helpful for them to base listening exercises on passages that are read aloud and followed by comprehension questions, on the contrary, Ur(1996) highlighted that the listening activities should be based on simulated real-life situations, because it will be more interesting and motivating for the learners than contrived textbook comprehension exercises. In the case of the course book the reading and listening comprehension activities are presented in a contextualized way, in which the
- 11. students have the chance to predict before they start reading or listening the text or file; moreover, the organization of the activities follows the receptive skills lesson plan format which is pre-task, while-task and finally post-task. Listening activities are presented in at least one or two lessons in each unit and they are related to specific topic and real-life situations such as phone calls, school days experiences, and radio interview to mention some of them. As complements, there are two CDs recorded by British native speakers. The first volume is just for the recordings and there are 64 files that correspond to the 12 units presented in the book. The recordings emphasize some features of phonetics such as pronunciation, specifically intonation and stress. The second volume contains the activities and the tests from the 12 units. There is a wide variety of topics including social issues and other ones related to social life. The fact that the files are recorded by British native speakers makes it to promote real and authentic language. Speaking is one of the most important skills in a second language, due to it is the primarily form of communication, and as Ur (1996) mentioned, most of the foreign language learners are primarily interested in learning to speak. The Straight Forward book presents a lot of speaking activities; there are at least one or two speaking activities per lesson, which indicates that the book emphasizes speaking activities over the rest of the skills. McGrath (2002) argued that “drama activities” such as role play and to lesser extent simulation are used to provide opportunities for students to use language spontaneously and creatively; furthermore, Ur (1996) suggests that role-play activities are virtually the only way that gives learners the opportunity to practice improvising a range of real-life spoken language in the classroom and it is a particularly effective technique if the students are confident and cooperative. In the straight forward
- 12. book it can be found a lot of activities related to role-play, dialogues and describing that help students to become more flexible communicators in English language. Finally, in terms of writing, the straight forward book does not present many activities related to writing; moreover, in most of the activities the instructions and the structures the students have to follow are very clear, and also they are related to realcontext due to students are asked to write emails (formal and informal), descriptions (of their friends or family members and of their cities, for instance) restaurant and film reviews among others. Another important component of this book is related to its topics. Regarding this issue, the Straight Forward presents a wide range of topics, which are interrelated in every unit. The material presented in all the units are separated in different lessons connected to the main topic of the unit. The content of every lesson is sufficient for students’ interest due to it includes many themes, such as, education topics, tourist trials, global issues, fashion, and animal lovers among others. To complement this, Ur (1996) suggests that teachers can adapt some themes and make them even more interesting for students. For this reason, students are able to be involved sooner or later in the lessons. Together with this, students are put in different current situations while doing the activities; therefore, they can enrich their experience when learning the target language with highly sophisticated content carefully selected based on students’ level of English. In addition, the Straight Forward course book put especial emphasize on social and cultural contexts, so students can learn and use the language in common real situations and make use of it in order to promote fluent interaction with native English speakers. Another important aspects that is worthy to mention, is that this book does not
- 13. present genre preferences, in other words, it can be used for both, men and woman, with no disadvantages for any of them. Moreover, in several units this book presents different lessons related to different cultures around the world such as the Machu Picchu and the Empire of China, which makes this course book very flexible for the teacher due to its variety of content. As a conclusion, it can be mentioned that the book integrates the four skills in a real-life context activities and in a very organized form. Besides, it is necessary to highlight that the Straight Forward course book emphasizes speaking over the other skills with the intention to promote a communicative learning. This linked with a perfect variation of topics to cover up all students’ interests in order to make the lessons more catchy and interesting for them.
- 14. References McGrath, I. (2002). Materials evaluation and design for language teaching. Tomlinson, B. (Ed.). (2011). Materials development in language teaching.Cambridge University Press. UR, P. (1997). A course in Language Teaching: CambriageTeacher Training and Development. Practice and Theory.