Covalent bonds ch 9 2
- 2. Naming MoleculesBinary molecular compoundCovalently bonded compound containing only two different elementsComposed of 2 different nonmetalsNo ions or metals
- 3. Naming Binary Molecular CompoundsName the 1st element first using complete name.Name the 2nd element using the root of the element and adding the suffix –idePrefixes are used to indicate the number of atoms that are present in the compoundException: first element in formula never uses mono-Hydrogen bonded to 7A halogens (drop mono)
- 4. Nonmetal rootsPrefixesH - hydC - carbN - nitrP - phosphAs - arsenO - ox S - sulfSe - selenF - fluorCl - chlorBr - bromI - iod1 - mon(o) 2 - di 3 - tri 4 - tetr(a) 5 - pent(a) 6 - hex(a) 7 - hept(a) 8 - oct(a) 9 - non(a) 10 - dec(a)
- 5. Practice problems:COP2O5CCl4As2O3NF3SO2Carbon monoxideDiphosphoruspentoxideCarbon tetrachlorideDiarsenic trioxideNitrogen trifluorideSulfur dioxide
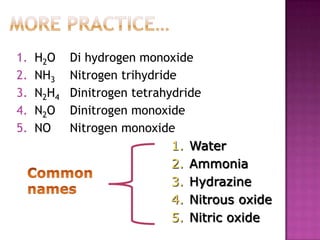
- 6. More practice…H2ONH3N2H4N2ONODi hydrogen monoxideNitrogen trihydrideDinitrogentetrahydrideDinitrogen monoxideNitrogen monoxideWaterAmmoniaHydrazineNitrous oxideNitric oxideCommon names
- 7. AcidsMolecules can be put in aqueous solution (water) and they make acidsCompound classified as an ACID if it releases H+ ions when put in water solutionOnly name acids if molecule is put in water!!!Two typesBinary AcidsOxyacids
- 8. Binary AcidsHydrogen & one other elementSometimes there are more than 2 elementsTo name hydrogen, use prefix Hydro-Second element use Root (or form of root) followed by suffix –icIf there are more than 2 elements involved, use the root of the polyatomic ion that acid containsAdd the word acid to the endExample: HClHydrochloric acidExample: HCNHydrocyanic acid
- 9. OxyacidsAcids that contain OXYANIONWhat is an oxyanion?Polyatomic ion that contains oxygenFirst: Determine anion presentUse a form of the root of the anionAdd suffixAnion suffix –ate….oxyacid suffix= -icAnion suffix –ite….oxyacid suffix= -ousAdd the word acidExample:HNO3Oxyanion: nitrate NO3-Oxyacid name: nitric acidExample:HNO2Oxyanion: nitrite NO2-Oxyacid: nitrous acidHydrogen is not named in oxyacids!!!
- 11. Practice…HIHClO3H2SO4H2SHClO2Hydroiodic acidChloric acidSulfuric acidHydrosulfuric acidChlorous acidFirst determine if it’s a Binary acid or an oxyacid
- 12. Name to formulasWrite the symbols for the elements in the order mentioned in the name. Write subscripts indicated by the prefixes. If the first part of the name has no prefix, assume it is mono. Prefixes tell you SUBSCRIPTS for each elementExampleCarbon tetrachloride CCl4
- 13. Writing Formulas for Binary Covalent Compounds: Examplesnitrogen dioxideNO2diphosphorus pentoxideP2O5xenon tetrafluorideXeF4sulfur hexafluorideSF6
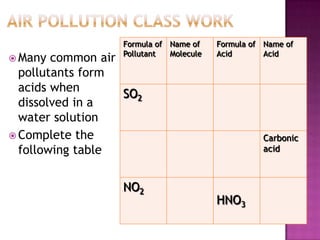
- 14. Air Pollution Class WorkMany common air pollutants form acids when dissolved in a water solutionComplete the following table