Creativity and innovation
- 1. Creativity and innovation Tehreem zafar Afifa tariq Fareena abbas Muniba syed Amatusalam Iqra hafeez
- 2. Definition – “creativity can be referred to as divergent thinking namely, the ability to find unusual and non-obvious solutions to a problem!” – the act of turning new and imaginative ideas into reality. Creativity involves two processes: thinking, then producing.
- 3. Creativity in marketing – The extent to which an ad contains brand or executional elements that are different, novel, unusual, original, unique, etc.
- 4. Elements of creativity in context to marketing What We Create • Creating Added Value • Creativity in… – Advertising – Public Relations – Sales Promotion
- 5. Creativity in advertising – Interest in an ad is influenced by… – Surprise (Good) – Information (Better) – Benefits (Best) – How about All 3? – Example: Surprising information tied into benefits.
- 6. Creativity in public relation All brands have ads Good PR about those ads adds extra value But it has to be “newsworthy!” Every year, a company has an anniversary. Creative PR can make it something special.
- 7. Creativity in sales promotion – A Creative Approach can provide to buy on top of the Incentive!
- 8. Building brand value – Creativity Can Build Brand Values – It can Reinforce Existing Feelings – It can Create New Feelings and Attitudes • It can Add Image and Imagery
- 9. How creativity works – Effective Creativity persuades – Three Cornerstones of Persuasion – It connects to the Target – It communicates the Benefit – Effective Creativity gets to “Yes” – It gets you to “Just Do It”
- 10. Effective surprise – It could be a Big Surprise! – The “AHA” – I never thought of it that way before (NIKE) – It could be a Small Surprise Effective Surprise! – The “Oh yeah!” – That’s just the way I feel.
- 11. Creative action plan – 1. Client – 2. Target – 3. Competition – 4. Old/New Thought – 5. Main Claim – 6. Support – 7. Added Tools
- 12. Now its time to think of big idea!!! – Big Ideas are great but they must be tied back to your market objectives and budget. – Don’t let an Advertising agencies big idea over ride your marketing objectives. – Golden rule: If I was paying for the campaign would I pay for it out of my own pocket?
- 13. Creating ideas that sell – 1. Connect with your target market – • Example: Federal Express understand the importance of care and on time package delivery. – 2. Beat the competition – • Example: Japan Airlines Premium Economy instead of Business Class…
- 14. Selling creative ideas – Presentations Need Planning – A Good Presentation Format: – Present Problem/Assignment – Unique Interpretation of Problem – The Insight is introduced – “The Reveal” – Be ready for questions, comments and criticisms
- 15. Producing creative idea – Now other specialized professionals and suppliers join the creative team. – Print team members – Art buyers and Photographers – Radio team members – Announcers and Composers – Television team members – Actors and producers
- 16. Creative advertising – Creative advertising is more memorable, longer lasting, works with less media spending, and builds a fan community faster!
- 17. Creativity in pharmaceutical marketing – On a degree of difficulty scale, marketing prescription pharmaceuticals rates high on the list. It’s an industry like no other — categorized by heavy restrictions, a shed load of data, and an audience that is limited and hugely intelligent – To top that off, there’s also limited time to monetize the new drug before generics flood the market. – educate those at the upper end of the knowledge chain. – build brand loyalty and value above just price, and remain within the confines.
- 18. Strategies for pharma industries marketing – 1. Know Your Target – And by this, we don’t mean your sales targets. We mean knowing intimately the niche your product is designed for. This is where pharmaceutical companies have an edge on traditional marketing – E.g.: Take, for instance, a drug that has been recently PBS-listed for reducing nerve pain in patients, with slightly more efficacy than an incumbent. – But changing drugs comes with risks attached. – Doctors remain prescribing what they are familiar with. – Creativity or strategy in this case is: look more closely at the product to find something that is different from
- 19. 2. Leave a Breadcrumb, Not a Loaf – It’s common practice to want to put every possible piece of data into marketing materials like leave-behinds, brochures, print and digital ads, and iDetailers. – we know that information overload acts as barrier to action. – Ask any sales rep in the field, and they’ll verify this: “Do you feel like you’re always presenting your doctors with compelling data but their behaviour doesn’t change?” – Creativity or strategy : – Try and condense the information to what is going to be relevant to the identified target audience.
- 20. 3. Lead with the Problem – If you look at current pharmaceutical marketing, most of the messaging leads with a solution, with no real set-up of a problem. – For instance, a newly launched bronchodilator in the marketplace would usually lead with messaging like “The first PBS-listed dual bronchodilator for treatment of COPD” – The audience has been presented with a treatment for COPD (the solution) with no real set-up of why the solution is needed (the problem it’s solving). As such, the audience has to work harder to connect how to fit the solution into their world.
- 21. Creativity or strategy: A better way to structure the messaging in this example could be by leading with the problem. Take, for example, this messaging: • Are your patients complaining of breathlessness at night? • Are monotherapies no longer working for your COPD patients? Instantly, we’ve created a hook that speaks directly to the audience by planting our solution into a problem they encounter in their patients. • highly effective way to drive engagement in a digital medium, where attention is limited and ad size small. Leading with the problem sets up questions and then a strong call to action: • Are monotherapies no longer effective for your COPD patient? Click here to find out how what more can be done
- 22. Use an A3 Discussion Guide – Leave-behinds have long been used by the pharmaceutical sales and marketing departments to serve as a reminder of sales conversations. – At Step Change, we’ve found conversion rates double and triple across businesses in all categories by producing these in an A3 format and structuring the information as a discussion guide rather than a brochure. – Creativity : – It provides detailed information about your product.
- 25. An innovation is… – According to Oxford English Dictionary – Innovation means introduction of something new. Thus Innovation can be defined as the introduction of a new product, service or process into the market place. – The National Innovation Initiative (NII) of USA defines - innovation as the intersection of invention and insight, leading to the creation of social and economic value.
- 26. – Schumpeter argued that innovation comes about through new combinations made by an entrepreneur, resulting in – a new product, – a new process, opening of new market, – new way of organizing the business – new sources of supply
- 27. Many definitions of Innovation – • To sum up… Innovation = Invention + Commercial Exploitation – It is a use of new knowledge to offer a new product or service that customers want. Thus, it is – Invention + Commercialization. – “Innovation is the search for and the discovery, developed, improvement, adoption and commercialization of new processes, new products and new organization structures and procedures.”
- 28. In pharmaceutical sense: – Any change in the marketing mix that customers perceive as new. – It can be a change in products, services, or processes.
- 29. Bill Ford on Innovation – “..if we want to succeed as a company – and as an industry – we must drive innovation into everything we do: into technology, into safety, into design and into real-world solutions for environmental issues, like the impact of energy usage on our world.” – “Innovation is going to be the compass by which this company sets its direction.”
- 34. WHY INNOVATE ??? OTHERWISE THEIR SURVIVAL CHANCES ARE SERIOUSLY THREATENED ORGANIZATION PREPARE THEMSELVES TO INNOVATE ON A CONTINUING BASIS TURBULENT AND RAPIDLY CHANGING ECONOMY
- 35. GOALS OF INNOVATION – Improving quality – Creation of new markets – Extension of the product range – Reducing labor cost – Improving production process – Reducing materials – Reducing environmental damage – Replacement of products/services – Reducing energy consumption – Conformance to regulations
- 36. Importance of Innovation to Companies 20% 80% Companies say it is important... ...But Few Feel Good at it Find innovation unimportant Find innovation important to their business 4% 96% Good at innovation Think they are bad at innovation
- 37. Process of Innovation – a) Idea generation (Making) – b) idea screening (test ) – c) feasibility (Practically) – d) implementation (Completion) – e) commercialization
- 40. • The process of innovation involves search & selection, exploration & synthesis, cycles of divergent thinking & convergence. Innovation process needs support at three levels. • At the macro level i.e. National Level, Innovation in a nation directly depends upon national government’s policies and support.
- 41. At the next level i.e. Enterprise Level, Innovation in enterprises depends upon top management’s support and commitment. It is the top management which sets the direction and environment for the innovation in an organization. • Lastly at the bottom level ie. Individual Level, Organizations should create mutifunctional teams and encourage individuals involved in the innovation process. Innovation largely depends upon actions and motivation of multifunctional teams and individuals involved in the innovation process. • Innovation is largely responsibility of enterprise
- 42. CHARACTERISTICS OF INNOVATION – There is an object or target which is being changed. – It can be a product, a process, an individual’s lifestyle, an organization's strategy, a society culture. – Innovation vary in extent or magnitude i.e. degree to which one deviates from the past. – It is closely related to problem solving since generation & implementation of ideas for change never transpire without difficulty. – A final characteristic is the impact of the change, the significance or range of its effects.
- 43. Drivers for innovation: – Financial pressures to reduce costs, increase efficiency, do more with less, etc – Increased competition – Value migration – Stricter regulation – Industry and community needs for sustainable development – Increased demend for accountability – Demographic, social and maket changes – Rising customer expectations regarding service and quality – Changing economy – Greater availability of potentially useful technologies coupled with a need to exceed the competition in these
- 44. Sources of new ideas: Suppliers Employees Management Distribution Channels Government Regulations Maverick Competitors Customers Technology Economy Rapidly Changing Environment
- 45. Innovation within the organization: It depends upon – Organizational Motivation – the basic orientation of the organization toward innovation; shared vision; providing rewards and recognition; lack of internal politics, and lack of overemphasis on the status quo. – Resources – everything the organization has available to aid in the area targeted for innovation, including time, funding, information and materials – Management Practices – allowing freedom and autonomy in the practice of work; providing challenge; specifying clear strategic goals and forming work teams comprised of individuals with diverse skills and perspectives
- 46. Types of innovation: In business and economics, innovation is often divided into five types: 1. Product innovation, which involves the introduction of a new good or service that is substantially improved. This might include improvements in functional characteristics, technical abilities, ease of use, or any other dimension . 2. Process innovation involves the implementation of a new or significantly improved production or delivery method. 3. Marketing innovation is the development of new marketing methods with improvement in product design or packaging, product promotion or pricing. 4. Organizational innovation (also referred to as social innovation) involves the creation of new organizations, business practices, ways of running organizations or new organizational behavior. 5. Business Model innovation involves changing the way business is done in terms of capturing value
- 47. A Suggested Innovation Framework Problem and/or Opportunity •Do not be afraid to fail •Take risks •Move your idea forward Just Do It • Seek novelty in design • Diversify • Stop looking for the right answer; look for many right answers Seek Novelty in Design • Define clearly your goals and objectivesSet Goals and Objectives • Challenge all assumptions • Seek opportunities to innovate Identify Problems and/or Opportunities • Open your mind • Mental Floss • Discover your creative rhythm • Health Makes Wealth Seek Opportunities • Become an expert in a field you love • Become passionate about your field Find what you love to do
- 49. –Incremental Innovation – Incremental Innovation is the most common form of innovation. It utilizes your existing technology and increases value to the customer (features, design changes, etc.) within your existing market. Almost all companies engage in incremental innovation in one form or another. – Examples include adding new features to existing products or services or even removing features (value through simplification). Even small updates to user experience can add value, for example below is an older version of Constant Contact’s email schedule page:
- 50. Disruptive Innovation – Disruptive innovation, also known as stealth innovation, involves applying new technology or processes to your company’s current market. This newer technology is often more expensive It is only after a few iterations that the newer tech surpasses the old and disrupts all existing companies. – There are quite a few examples of disruptive innovation, one of the more prominent being Apple’s iPhone disruption of the mobile phone market. Prior to the iPhone, most popular phones relied on buttons, keypads or scroll wheels for user input.
- 51. Architectural Innovation – Architectural innovation is simply taking the lessons, skills and overall technology and applying them within a different market. This innovation is amazing at increasing new customers as long as the new market is receptive. Most of the time, the risk involved in architectural innovation is low due to the reliance and reintroduction of proven technology.
- 52. Radical innovation – Radical innovation is what we think of mostly when considering innovation. It gives birth to new industries (or swallows existing ones) and involves creating revolutionary technology. The airplane, for example, was not the first mode of transportation, but it is revolutionary as it allowed commercialized air travel to develop and prosper.
- 57. Innovation in Pharmacy – Pharmacy practice not very innovative – – so far – Most changes are incremental – Many changes simply imitate competitors – Thus, pharmacies appear very similar to customers
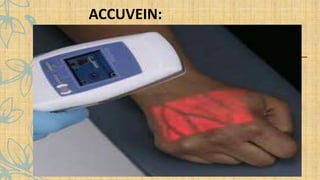
- 58. Examples of innovation in pharmaceutical and medical science: Nurses can now find veins more easily before taking blood or injecting medications with AccuVein, while residents can now describe an eye condition to a physician using EyeDecide. Patients can refill prescriptions with smartphone and tablet apps, text messages and secure email. Pharmacists can help patients improve their adherence to taking their medications by monitoring automated refill histories. Patient medical history, profiles, drug benefits and interactions are available online to both patients and pharmacists in many locations. Pharmacists can check for drug interactions and advise both doctors and patients on medication reconciliation and synchronization.
- 59. – Centralized pill dispensing automation is replacing manual dispensing onsite. The use of robotic dispensing systems and tablet counters improves accuracy and frees up pharmacist and staff time for patient questions and consultation. – Cloud-based inventory management systems enable pharmacies to share information across several locations, automatically re-order stock, and review past transactions. – Prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs) and electronic prescribing of controlled substances (EPCS) are helping to fight opioid abuse. – Innovation in vaccination i.e new and modified forms are being devolped and methods os administration are being innovated.
- 60. – Inovation in surgical procedures e.g use of laparoscopic gall bladder surgery instead of open surgery – Innovation in packaging i.e modified packaging including temper resistance, child resistance containers etc – Inovation in devices e.g devolpment of novapen for insulin administration in relation to conventional syringe. – Precision medicine – mHealth sensors – Nanotechnology – Artificial intelligence i.e use of artificial intelligence in research such as literature review of enormous amount of data can be done easily by usin AI.
- 61. ACCUVEIN:
- 62. NOVAPEN:
- 63. GALL BLADER SURGERY: LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY OPEN SURGERY