Crm new1
- 1. TINKER YOUR GREY CELLS ON THIS………………… ‘You can please some of the people most of the time and most of the people some of the time, but can you please all the people all the time’
- 2. CRM “Customer Relationship Management is a strategy for optimizing the value an enterprise derives through customer relationships” “CRM is a comprehensive strategy & process of acquiring, retaining & partnering with selective customers to create superior value for the company & the customer” “CRM is about acquiring, developing and retaining customers; achieving profitable growth and creating economic value in a company’s brand’
- 3. Customer Life Cycle Management Customer need assessment & acquisition Customer Customer development retention & through referrals for CRM personalization new & customers customization Cross selling & up selling
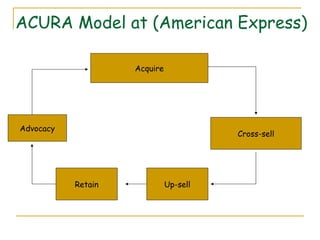
- 4. ACURA Model at (American Express) Acquire Advocacy Cross-sell Retain Up-sell
- 5. Types of CRM Operational CRM Collaborative CRM Analytical CRM Customer
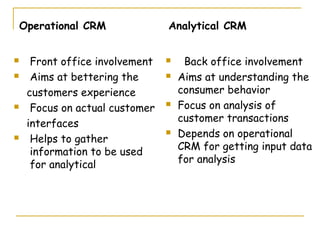
- 6. Operational CRM Analytical CRM Front office involvement Back office involvement Aims at bettering the Aims at understanding the customers experience consumer behavior Focus on actual customer Focus on analysis of customer transactions interfaces Depends on operational Helps to gather CRM for getting input data information to be used for analysis for analytical
- 7. Sales Intelligence CRM- is similar to Analytical CRM, but is intended as a more direct sales tool. Features include alerts sent to sales staff regarding: Cross-selling/Up-selling opportunities Customer drift & trend Sales performance Collaborative CRM covers aspects of a company's dealings with customers that are handled by various departments within a company, such as sales, technical support and marketing. Staff members from different departments can share information collected when interacting with customers. For example, feedback received by customer support agents can provide other staff members with information on the services and features requested by customers. Collaborative CRM's ultimate goal is to use information collected by all departments to improve the quality of services provided by the company.
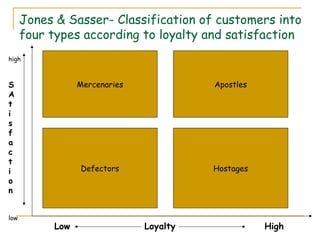
- 8. Jones & Sasser- Classification of customers into four types according to loyalty and satisfaction high S Mercenaries Apostles A t i s f a c t i Defectors Hostages o n low Low Loyalty High
- 9. Apostles A loyal customer who is completely satisfied and keeps returning to the company. They also share their strong feelings with others Mercenaries Happy and contended customers who are not loyal to the company and tend to shop around and compare. On a lookout for a better opportunity Defectors Customers who are disappointed in their business relations with the company and tell everybody about their bad experience and often leave the services without informing Hostages due to certain exit barriers unable to change their service provider though dissatisfied
- 10. Types of Customers on the basis of Profitability and Loyalty Butterflies- high profitability and short term customers Strangers- Low profitability and Short term customers Barnacles- Low Profitability but long term customers True Friends- High Profitability and long term customers
- 11. Types of Customer Value Economic Value Economic Value Psychological Psychological Functional Value Functional Value Value Value
- 12. Types of Customer Value Economic Value- It is the economic benefit a customer derives from using a product i.e. the net monetary advantage from using a product versus its alternatives over the life of a product. The economic benefit is derived by comparing the total lifecycle cost of products not just initial purchase prices
- 13. Functional Value- It provides functional benefit to customers. Here value is provided by the performance features of a product like luggage capacity, fuel economy etc Psychological Value- The economic and functional values reflect the tangible benefits of a product or service whereas psychological values focuses on intangible aspects like brand name and its association with customers
- 14. Types of Customer Value by Barnes Choice based value Choices created in how customers deal with the company how they can pay for their purchases how they want them shipped or how they receive information Employee based value Information value Association Value- Customers derive value from being associated with a certain product/service provider with whom they associate positive attributes or values
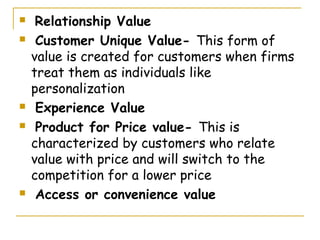
- 15. Relationship Value Customer Unique Value- This form of value is created for customers when firms treat them as individuals like personalization Experience Value Product for Price value- This is characterized by customers who relate value with price and will switch to the competition for a lower price Access or convenience value
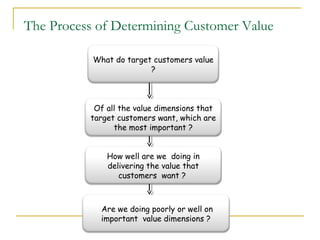
- 16. The Process of Determining Customer Value What do target customers value ? Of all the value dimensions that target customers want, which are the most important ? How well are we doing in delivering the value that customers want ? Are we doing poorly or well on important value dimensions ?
- 17. Customer Value Management Understand what causes customer purchase and repurchase behavior Predict the future purchase behavior of customers and potential customers
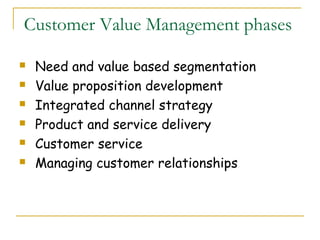
- 18. Customer Value Management phases Need and value based segmentation Value proposition development Integrated channel strategy Product and service delivery Customer service Managing customer relationships
- 19. CRM Value Chain Customer portfolio analysis: this involves an analysis of the actual and potential customer base to identify which customers you want to serve in the future Customer intimacy: you will get to know the identity, profile, history, requirements, expectations and preferences of the customers that you have chosen to serve Network development: you will identify, brief and manage relationships with your company's network members. The network can include external members such as suppliers, partners and owners/investors, as well as one important internal party, employees
- 20. Value proposition development: this involves identifying sources of value for customers and creating a proposition and experience that meet their requirements, expectations and preferences Manage the customer lifecycle: the customer lifecycle is the customer's journey from 'suspect' towards 'advocate status'. Managing the lifecycle requires attention to both process and structure:
- 21. CRM Model
- 23. formation Management/Governance Performance Planning process PURPOSE Role specification/ Team Structure Customer Value, PROGRAMS Communication Satisfaction, Continuity Mktg Retention Programs 1-TO-1 Mktg Partnering Employee training / Programs motivation Monitoring process Customer Evolution
- 24. The Cog Wheel Process Designing a CRM Strategy Process People Strategy Technology
- 25. Stages Of CRM STAGE STATE CULTURE Meet customer needs & respond to complaints. Satisfaction Reactive Minimal evaluation of Based customer service Performance Evaluate customer perception & identify Based Proactive customer retention factors Commitment Evaluate customer needs & continuous Based Very Proactive inbound/outbound flow & feedback
- 26. Role of CRM in Stages of Sales Cycle Pre-purchase Stage Purchase Stage • Easy procedures to purchase • Provide a complete solution • Training & Installation
- 27. Role of CRM in Stages of Sales Cycle Usage Stage • Easy access to after sales service • Easy availability & trouble shooting • Engaging customers with updated features Repurchase Follow up
- 28. eCRM Steps in eCRM Setting the objectives of eCRM Methodologies for e-Business initiative Processes Partnerships IT service providers Content management Call Centres Supply chain integration Knowledge Management Evaluating the performance of the eCRM System
- 29. Analytical Models Decile Analysis Deciles are grouping customers and ranking them on the basis of Purchasing types of products How frequently purchasing Going for new services RFM Model Recency, Frequency & Monetary Value The RS Matrix Recency Customer’s sales Rate Total time since a customers first purchase ______________________________________ The number of times purchased
- 30. Customer Retention Stages Welcome Stage Up-selling Cross-selling Renewal Lapsed Customers Inactive customers
- 31. Transactional Marketing Relationship Marketing Functional marketing Cross-functional marketing Focus on a single sale Focus on customer Orientation on Product retention features Orientation to customer values Short time scale Long time scale Little emphasis on High emphasis on customer service customer service Quality is everyone’s Quality is a concern of concern production
- 32. The CRM Cycle Process Assessment Phase Execution Phase Planning Phase
- 33. The Assessment phase develops a model of the behavior of target customers, using a combination of in-house data and external demographic, psychographic, and other data. Here, marketing will explore a number of questions, including: Who are the customers? What are their demographics and lifestyle? Where do they live? What are they worth? What is their lifetime value potential? What and how do they buy? What are their purchasing patterns? Is there a model of their profitability or the risk associated with doing business with them? How can they be reached? How have they responded to promotions in the past and through which channels do they prefer to be contacted?
- 34. During the Planning Phase, marketing decides how best to approach the customers defined in the assessment stage by designing marketing campaigns and strategies The Execution Phase of the cycle is where an organization puts all this knowledge to work, using all of the customer touchpoints available.
- 35. Framework for building CRM Strategy The Value Discipline Model Product The Best Products Leadership Operational Customer Excellence Intimacy The Best Total The Best Total Cost Solution
- 36. Eight Building Blocks of CRM CRM Vision CRM strategy Valued customer experience understand requirements monitor expectations satisfaction versus competition collaboration and feedback customer communication Organizational collaboration culture and structure customer understanding people skills and competencies incentives and compensations employee communication partners and suppliers
- 37. CRM processes: customer life cycle and knowledge management CRM information: data analysis, one view across channels CRM Technology: applications, infrastructure CRM Metrics: value, retention, satisfaction, loyalty, cost to serve
- 38. CRM Metrics Customer Contact Intensity Customer satisfaction and delight Customer Profitability Customer Penetration Customer Loyalty Index
- 39. True Vs Spurious Loyalty Strong Attitudinal Behavioral commitment Loyalty Loyalty Repeat purchasing Behavior True Loyalty True Loyalty Low Spurious Spurious Inertia commitment Loyalty Loyalty
- 40. Advantages of e-CRM Lowers the cost Adaptability and Availability Helps data construction Increased customer interaction Managing data reservoir Lesser response time New customer service opportunities Reach and service personalization Automatic self documentation User control
- 41. Technologies of e-CRM Voice Portals These allow the users to access the content on a website through a cell phone. Commercial voice portals such as BeVocal, TellMe and Shoptalk provide voice access to stock quotes, movie listings and daily news Web phones It is also known as Internet Protocol telephony. Web phone technology supports voice communications over the internet
- 42. Technologies of e-CRM BOTs Software Robots or BOTs are used to locate websites. They use plain english to locate content on the web and are also used as conversational engines that work in the real time or through e-mail messages Virtual Customer Representative
- 43. Few CRM Software's Siebel Oracle MySAP CRM PeopleSoft Clarify
- 44. Applications of e-CRM Customer Interaction Management (CIM) It is a technology that makes use of the valuable customer information contained in CRM applications and takes customer relationships to a much more personalized level Customer Relationship Portal Interactive Relationship Management
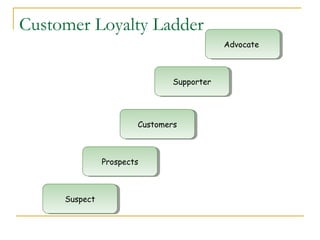
- 45. Customer Loyalty Ladder Advocate Advocate Supporter Supporter Customers Customers Prospects Prospects Suspect Suspect