Csr
- 1. Chapter 5 (Lecture Outline and Line Art Presentation) Management’s Social and Ethical Responsibilities
- 2. Social Responsibility: Definition and Perspectives • Corporate Social Responsibility • The idea that business has social obligations above and beyond making a profit. • Business has an obligation to constituent groups in society other than stockholders and beyond that prescribed by law. managepedia.blogspot.com Lecture Outline Presentation and Line Art, 5–2
- 3. Social Responsibility: Definition and Perspectives (cont’d) • What Does Social Responsibility Involve? • Voluntary action • Action before lawsuits or other actions that are taken to force a firm to take action on a matter. • An emphasis on means, not ends • How the decision to act was reached, not the decision itself. managepedia.blogspot.com Lecture Outline Presentation and Line Art, 5–3
- 4. What Is the Role of Business in Society? (cont’d) • The Socioeconomic Model • Business has an obligation to meet the needs of the many groups in society besides stockholders in its pursuit of profit. • Stakeholder Audit: systematically identifying all the parties that could possibly be impacted by the company’s performance managepedia.blogspot.com Lecture Outline Presentation and Line Art, 5–4
- 5. Figure A Sample Stakeholder Audit for Wal- Mart, the World’s Largest Reailer managepedia.blogspot.com Lecture Outline Presentation and Line Art, 5–5
- 6. Arguments For and Against Social Responsibility • Arguments For • Business is unavoidably involved in social issues. • Business has the resources to tackle today’s complex societal problems. • A better society means a better environment for doing business. • Corporate social action will prevent government action. managepedia.blogspot.com Lecture Outline Presentation and Line Art, 5–6
- 7. Arguments For and Against Social Responsibility (cont’d) • Arguments Against: • Profit maximization ensures the efficient use of society’s resources. • As an economic institution, business lacks the ability to pursue social goals. • Business already has enough power. • Because business managers are not elected, they are not directly accountable to the people. managepedia.blogspot.com Lecture Outline Presentation and Line Art, 5–7
- 8. Toward Greater Social Responsibility • Iron Law of Responsibility • Those who do not use power in a socially responsible way will eventually lose it. • If business does not meet the challenge of social responsibility, then government reform legislation will force it to meet its obligations. managepedia.blogspot.com Lecture Outline Presentation and Line Art, 5–8
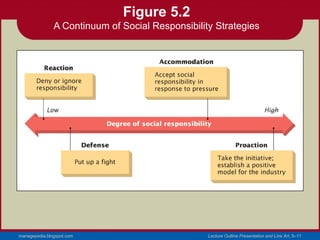
- 9. Social Responsibility Strategies • Reactive Strategy • Denying responsibility while striving to maintain the status quo by resisting change. • Defensive Strategy • Resisting additional social responsibilities with legal and public relations tactics. managepedia.blogspot.com Lecture Outline Presentation and Line Art, 5–9
- 10. Social Responsibility Strategies (cont’d) • Accommodation Strategy • Assuming social responsibility only in response to pressure from interest groups or the government. • Proactive Strategy • Taking the initiative in formulating and putting in place new programs that serve as role models for industry. managepedia.blogspot.com Lecture Outline Presentation and Line Art, 5–10
- 11. Figure 5.2 A Continuum of Social Responsibility Strategies managepedia.blogspot.com Lecture Outline Presentation and Line Art, 5–11
- 12. Who Benefits from Corporate Social Responsibility • Altruism • The unselfish devotion to the interests of others. • Research Findings • There is a positive correlation between industry leadership on a socially responsible issue (pollution control) and profitability. • Corporate social responsibility is a competitive advantage. managepedia.blogspot.com Lecture Outline Presentation and Line Art, 5–12
- 13. Who Benefits from Corporate Social Responsibility (cont’d) • Enlightened Self-Interest • A business ultimately helps itself by helping solve social problems. • An Array of Benefits for the Organization • Tax-free incentives to employees. • Retention of talented employees. • Help in recruiting the talented and socially conscious. • Help in swaying public opinion. • Improved community living standards. • …Others. managepedia.blogspot.com Lecture Outline Presentation and Line Art, 5–13