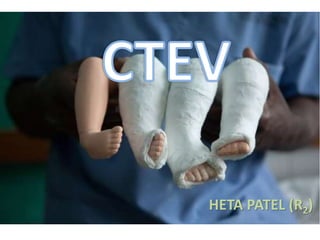
CTEV UG
- 2. Outline • What is CTEV? • Epidemiology • Causes • Anatomy and pathoanatomy • Clinical features • X-rays • Treatment
- 3. What is CTEV?? • Idiopathic clubfoot • Causing CAVE - midfoot Cavus/ increase in height -forefoot Adductus -hindfoot Varus -hindfoot Equinus/ plantarflex
- 4. Hind foot equinus Heel in varus Midfoot cavus
- 5. Epidemiology • Relatively common- 1 to 2 per thousand births • Boys affected twice • Bilateral in 1/3 of cases
- 6. Causes-unknown • germ defect • arrested development • neuromuscular disorder in neurological disorders and neural tube defect • postural deformity
- 7. Common Types 1. Congenital - uncommon bony problems present upon childbirth not related to any neuromuscular factor or symptoms. 2. Teratologic -a/w neurological conditions (eg: spina bifida) 3. Positional - in contorted position in utero 4 Syndromic -a/w standard hereditary issue, which includes arthrogryposis.
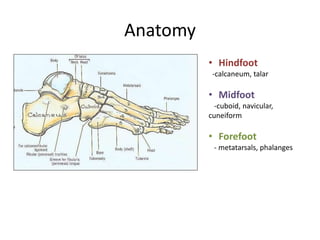
- 8. Anatomy • Hindfoot -calcaneum, talar • Midfoot -cuboid, navicular, cuneiform • Forefoot - metatarsals, phalanges
- 9. Pathological Anatomy Neck of Talus -pointing downward and deviates medially Body of Talus - Rotated outward Posterior part of calcaneum -held close to fibula by CF ligt -tilted into equinus and varus -rotated medially beneath ankle Navicular and forefoot -shifted medially -rotated into supination (composite varus deformity)
- 10. Pathological Anatomy • Skin and soft tissue of calf and medial side of foot are short and underdeveloped • If not corrected early, secondary growth changes occur in the bones-PERMANENT
- 11. Clinical Features • Heel is small and high • Deep creases appear posteriorly and medially • Abnormal thin calf
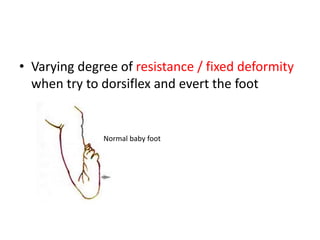
- 12. • Varying degree of resistance / fixed deformity when try to dorsiflex and evert the foot Normal baby foot
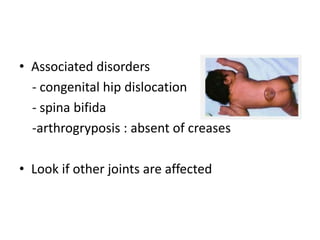
- 13. • Associated disorders - congenital hip dislocation - spina bifida -arthrogryposis : absent of creases • Look if other joints are affected
- 14. How to differentiate true and postural clubfoot? • True clubfoot – fixed deformity • Postural talipes – easily correctable by gentle passive movement
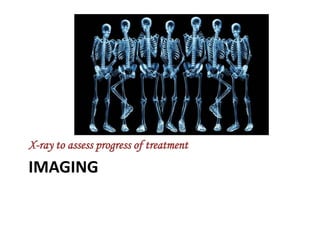
- 15. IMAGING X-ray to assess progress of treatment
- 16. Anterioposterior view Kite’s angle (talocalcaneal angle): normal 20-40 degree clubfoot angle almost parallel 30 degree plantarflex
- 17. Lateral Film (Turco view) Normal angle : 40 degree If less 20 degree: rocker bottom deformity - calcaneum seem to be dorsiflexed but it had broken at midtarsal level Foot dorsiflex
- 18. TREATMENT
- 19. Vision & Mission • Since CTEV can purely be therapeutic work we would not only treat also HABILITATE club foot to be normal. • Increase awareness and confidence of society with therapeutic staff.
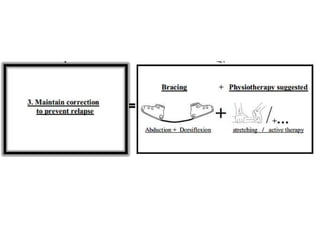
- 20. Aim To produce and maintain a PLANTIGRADE, supple foot that will function well
- 21. Non Operative Operative • Serial Manipulative and Casting (Ponsetti’s method) • -Posteromedial tissue release and tendon lengthening • -medial opening or lateral column- shortening osteotomy, or cuboidal decancellation • -triple arthrodesis • -tallectomy
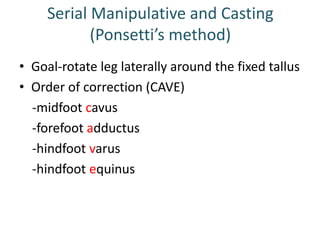
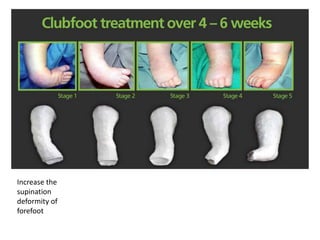
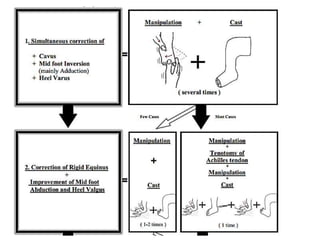
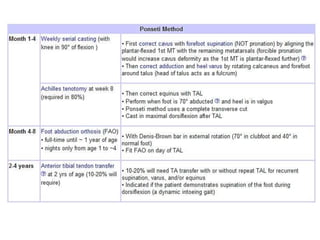
- 22. Serial Manipulative and Casting (Ponsetti’s method) • Goal-rotate leg laterally around the fixed tallus • Order of correction (CAVE) -midfoot cavus -forefoot adductus -hindfoot varus -hindfoot equinus
- 27. DON’T SLEEP. TQ
Editor's Notes
- rot