Data
- 1. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 1
- 2. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN [ DATA: It can be figures,numbers,quantity anything Recorded Information They have implicit meaning Ex: Varna chithra, 100, 13, etc…. INFORMATION data It is meaning full and arranged Ex: Name = Varna chithra No : of cars = 100 Age = 13 KNOWLEDGE How we apply our information in a situation It is paired, shaped, interpreted, selected and transformed. Why we need information Addition Knowledge : How much of information in our hand that much of knowledge : More information more chance to apply for LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 2
- 3. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN knowledge Decision making: Information are helpful in making good decision at right time Can apply in different levels : Used for different purpose like weather forecasting, result analysis etc Increase in productivity: Avoid waiting of time, money, effort etc... DATA BASE Organized collection of inter related data stored together with controlled redundancy. Collection of data designed to be used by different people. Data are stored in such a fashion that they are independent of the programs of people using the data The data in the data base is integrated, which means that the database is a collection of distinct (not identical) files. These distinct files may have some duplicate data but the duplication of data is to the minimum. Thus data in the database Is Integrated Can be Shared Can con currently accessed ADVANTAGES OF HAVING DATA IN DATABASE or ADVANTAGES OVER TRADITIONAL FILE SYSTEM 1. Centralized control 2. Redundancy can be reduced 3. Inconsistency can be avoided 4. Data can be shared 5. Standard can be enforced 6. Security restriction can be applied 7. Integrity can be maintained 8. Conflicting requirements can be balanced LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 3
- 4. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN 1. Centralized control: Centralized control of the data 2. Redundancy can be reduced: Redundancy of data means repetition of the data So maximum it avoid multiple copies Note: Sometimes redundancy allowed, because technically & business reasons we need to store multiple copies. LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 4
- 5. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN 3. Inconsistency can be avoided It is corollary to the above statement. If same data is duplicated and change made to one of them lead to inconsistency. 4. Data can be shared More than one persons can access the same data or different data at same time Information is shared 5. Standard can be enforced Admin can enforce standard Ex: ID generation of staff in college 6. Security restriction can be applied Only access through proper channel Different types of access can be provided (retrieve, modify, delete, create etc...) 7. Integrity can be maintained It means data are accurate Permits admin to define constraints to the data base Ex: Admin adding a constraint “Minimum balance need to change an account to cheque book account is 1000 RS. 8. Conflicting requirement can be balanced Understanding the requirement correctly. LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 5
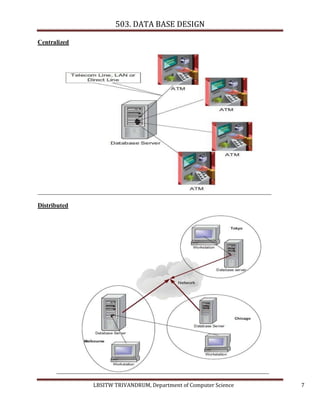
- 6. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN CHARACTERISTICS OF DATA IN DATABASE It should have the following features(we already discussed about this) 1. Shared 2. Persistence : It means the data exist permanently ,beyond the scope of the process 3. Validity/Integrity/Correctness 4. Security 5. Consistency 6. Non- redundancy 7. Independence : ( we will discuss it later) DATA BASE SYSTEM APPLICATIONS Some representative applications are SALES ONLINE RETAILERS MANUFACTURING HUMAN RESOURCES AIRLINES UNIVERSITIES BANKING For production(in factory),inventory(in ware house).order, supply chain For Order tracking, customized recommendation For Customer ,product, purchases Employee records, salaries, tax reduction For Reservation ,schedule information etc For Registration(student) ,grade etc For customer account ,loans, banking transaction etc TYPES OF DATABASE Centralized Distributed The entire data is located at a single site The data base is stored on several computer or mainframe system Allow for greater control over accessing and updating data The computer in a distributed system can communicate with each other via Ex: Bank ATM system various communication media(high Speed network or telephone lines) Ex: A multinational banking system. The bank database distributed across different branches. LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 6
- 7. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN Centralized Distributed LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 7
- 8. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN DATA BASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM It is a collection of programs that enables you to store ,modify data and extract information from a database. It varies from small to large It is a piece of software that provides services for accessing a database Components of DBMS are A. Transaction Management Transaction: Sequence of database operation that represent a logical unit of work Access and transform database from one state to another Include update, delete, modify a set of records If we want to save a transaction just do ‘commit’ If don’t want that change just rollback B. Concurrency Control Operate concurrently that access shared data and can potentially interface with one another Goal: Allow concurrency while maintaining the consistency of shared data. C. Recovery Management Ensures that database is returned to a consistent state even after the failure or aborts More concurrency more is the chance that an LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 8
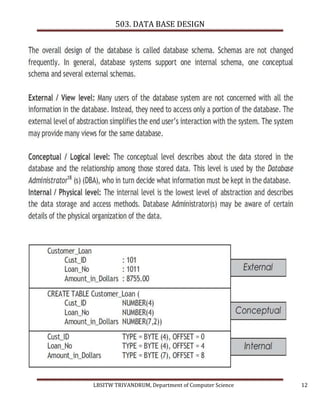
- 9. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN aborted transaction D. Security Management Protection of data against unauthorized access DBA give different access privileges to the users E. Language Interface Provide support languages These languages are used for definition and manipulation of data in the database. o Data Structure Creation : Used DDL(Data Definition Language) o Manipulation of Data : Used DML(Data Manipulation Language) F. Storage Management Permanent storage of data G. Data Catalog Management Also known as data dictionary It contains the metadata (data about the data , it actually contains description of the data) These are helpful to know the structure SCHEMAS AND INSTANCES INSTANCES The collection of information stored in the database at a particular moment is called an instance of the database. Database change over time as information is inserted and deleted. The value of variable in the program at appoint in time correspond to an instance of a database schema. SCHEMA The overall design of the database is called the database schema Schemas are changed infrequently Data base system have several schemas ,portioned according to the levels of abstraction LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 9
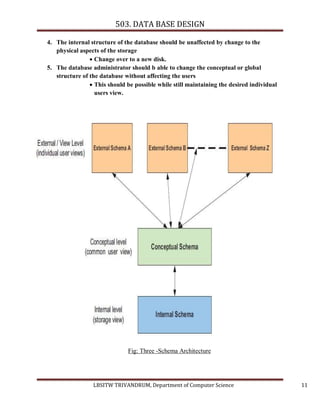
- 10. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN Physical schema : It describes data base design at physical level Logical schema : It describes data base design at logical level. Sub schemas : Database design at view level THREE -SCHEMA ARCHITECTURE Also known as 3-Level architecture of a DBMS or ANSI –SPARC Model ANSI_- American National Standard Institute SPARC-Standard Planning And Requirements Committee. Most modern commercial DBMS are based on this system OBJECTIVES 1. It allows independent customized user views: Each user should be able to access the same data, but have a different customized view of data. 2. It hides the physical storage details from user: Users should not have to deal with physical database storage details. They should be allowed to work with the data itself,without concern for how it is physically stored. 3. The database administrator should be able to change the database storage structure without affecting the user’s view: From time to time rationalization or other changes to the structure of an organization’s data will be required. LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 10
- 11. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN 4. The internal structure of the database should be unaffected by change to the physical aspects of the storage Change over to a new disk. 5. The database administrator should b able to change the conceptual or global structure of the database without affecting the users This should be possible while still maintaining the desired individual users view. Fig: Three -Schema Architecture LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 11
- 12. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 12
- 13. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN Detailed figure of Three schema architecture LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 13
- 14. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN DATA BASE USERS Mainly categorized into three main categories I. II. III. End user Application programmer Data Base Administrator LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 14
- 15. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN I. End user Deals only with the higher level of abstraction They may not be concerned with or even aware of the details of the DBMS The end users involved in updates to the database or queries on the database. Categories of end users are. Casual end user: Access database occasionally when needed. They need different information each time. Thy uses a sophisticated database query language to specify their request. Naïve or parametric users. Users who interact with the system by involving one of the application programs that have been written previously. They make up a large section of the end user population. These are the users who communicate with the database on regular period. Their job is to constantly querying and updating the database using the standard queries. This is called canned transaction. Ex: Bank teller, Reservation clerks etc. Sophisticated users These include business analyst scientist, engineers, and other thoroughly familiar with the system capacity. LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 15
- 16. 503. DATA BASE DESIGN LBSITW TRIVANDRUM, Department of Computer Science 16