Data security
- 2. Objectives of this project To understand various threats to data security. To know the background of these threats. To know about the various techniques to defense these threats.
- 3. Introduction Data is the raw form of information, which stored in our databases, network servers, personal computers and some other places. But all data or information is not accessible for all. Some data or information is personal, as well as implicit for its own purpose. In that case some people or organizations can try to capture those ‘not accessible information’. So “Data Security” has come into focus.
- 4. What is Data According to Webster’s Third New International Dictionary, Data is “something given or admitted; facts or principles granted or presented; that upon which an inference or argument is based, or from which an ideal system of any sort is constructed”.
- 5. Classification of data Public Data ----- Open to all users and no security measures are necessary Limited-Access Data ----- Only authorized users have access to this type of data Private Data ----- This data is open to a single user only, the owner of that particular data
- 6. Physical Storage of Data Mechanical (Paper, punched card, film, gramophone record, etc.) Magnetic Storage (Magnetic tape, floppy disk) Optical Storage (Photographic paper, microform, optical disc) Electrical (Semiconductor used in volatile RAM chips, etc.)
- 7. What is Security Security is the protection of information, systems and services against disasters, mistakes and exploitation, so that the probability of incidents is minimized.
- 8. What is Data Security Data security is the means of ensuring that data is kept safe from corruption and that access to it is suitably controlled. Thus data security helps to ensure privacy. It also helps in protecting personal data. That means protection of data from unauthorized (that may be accidental or intentional) access, modification and destruction.
- 9. Why Data Security Access Controls: Access controls regulate the reading, copying, changing and deletion of data and programs. Flow Controls: Flow controls can prevent a service program from leaking the customer’s confidential data. Inference Controls: A method of preventing data about specific individuals from being inferred from statistical information in a data base about groups of people.
- 10. Various threats to a computer system Accidents and Natural Disasters: Natural disasters such as flood, wind or earthquake, and accidents such as fire, power failure, and breakdown of electrical systems create threats to the organizations computer High risk factor from Computer Abuse: High Vulnerability Violation of the principle of separation of duties Easy manipulation of large amount of data. Impersonal nature of systems
- 11. Various threats to a computer system Human Initiated Hackers Unaware Staff Dissatisfied Staff Spy
- 12. Technology Available for Computer Security Cryptography Biometric Systems Malicious Code and Anti Virus Solutions Firewall Intrusion Detection System (IDS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) PKI and Digital Certificates SSH Encryption SSL Encryption
- 13. Cryptography Cryptography is the “Practice of the enciphering and deciphering of messages in secret code in order to render them unintelligible to all but the intended receiver.” It is a high-level encryption technique that is being used to ensure privacy in the digital world. Encryption is “the mechanism of coding data transmitted by various telecommunication systems so that only authorized user may have access to it;”
- 14. Biometric Systems Biometrics is the application of any biological characteristics, such as pattern formed by the fingers, retinas, irises, hands etc. used for user authentication. Various biometric technologies: (a) Fingerprint verification (b) Hand geometry (c) Retinal scanning (d) Signature verification (e) Voice verification (f) Facial recognition
- 15. Malicious Code and Anti Virus Solutions The malicious code includes Computer viruses, Worms, Trojan horses, Back doors/trap doors, Logic bombs, Bacteria, etc.
- 16. Malicious Code and Anti Virus Solutions (contd…) Computer Viruses: Computer program designed to copy itself into other programs, with the intention of causing mischief or damage. Different Types of Viruses: Boot Sector viruses File infectors Macro viruses Polymorphic viruses
- 17. Malicious Code and Anti Virus Solutions (contd…) Spyware: Spyware is a type of malware that can be installed on computers, and which collects small pieces of information about users without their knowledge. The presence of spyware is typically hidden from the user, and can be difficult to detect. Typically, spyware is secretly installed on the user's personal computer.
- 18. Malicious Code and Anti Virus Solutions (contd…) Worm: In a computer, a worm is a self replicating virus that does not alter files but resides in active memory and duplicates itself. Worms use parts of an operating system that are automatic and usually invisible to the user. Trojan Horse: Trojan horse is a program in which malicious or harmful code is contained inside apparently harmless programming or data in such a way that it can get control and do its chosen form of damage.
- 19. Malicious Code and Anti Virus Solutions (contd…) Back Doors/Trap Doors: These are codes written into applications to grant special access to programs bypassing normal methods of authentication. Logic Bombs: Logic bombs are programmed that hidden in commonly used software for an extended period of time until they are activate. They come embedded with some programs. Bacteria/Rabbit: These codes do not damage files. Their purpose is to deny access to the resources by consuming all processor capability/memory/disk space by self-replicating.
- 20. Malicious Code and Anti Virus Solutions (contd…) Creators of Virus Code: The malicious codes are written / created by dissatisfied employees, spies, experimenters, publicity hunter, political activists, etc. Damages Caused by Malicious Codes Loss of data services Leak of information Loss of reputation or legal penalty for software firm
- 21. Malicious Code and Anti Virus Solutions (contd…) Steps to protect the computer from viruses When installing new software, install it first on a non-critical system and test for bugs. Periodically review all system start-up and configuration files for changes. Turn off the automatic open on receipt feature from your e-mail software Before opening any attachments first scan it using updated anti-virus software. Regularly update anti-virus software engine and data files. Turn off visual basic scripting. When not in use turn off the workstation or disconnect it from the network. Take regular backup of critical data and system files.
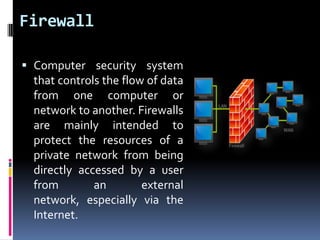
- 22. Firewall Computer security system that controls the flow of data from one computer or network to another. Firewalls are mainly intended to protect the resources of a private network from being directly accessed by a user from an external network, especially via the Internet.
- 23. Why Firewall? Prevent outside access except some special service like E-mail or HTTP IP addresses of the site can be protected from outside world by blocking DNS service. All incoming and outgoing traffic from the Internet can be logged to provide statistics about the network usage.
- 24. Intrusion Detection System (IDS) A device or software application that monitors network and/or system activities for malicious activities or policy violations and produces reports to a Management Station. Types: 1. Host Based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) 2. Network Based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS)
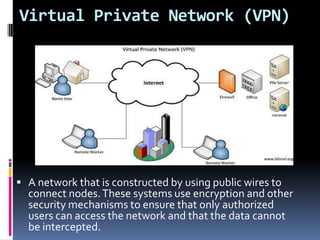
- 25. Virtual Private Network (VPN) A network that is constructed by using public wires to connect nodes. These systems use encryption and other security mechanisms to ensure that only authorized users can access the network and that the data cannot be intercepted.
- 26. PKI and Digital Certificates PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) is a process that enables users to implement public key cryptography. PKI offers various services related to authentication and access control, such as digital certificates to associate a user’s identity, certificate download, signing of certificate, confirm validity of certificate, terminate certificate, etc.
- 27. SSH Encryption Secure Shell (Developed by SSH Communications Security Ltd.), is a program to log into another computer over a network, to execute commands in a remote machine, and to move files from one machine to another.
- 28. SSL Encryption Secure Sockets Layer (Also known as TLS or Transport Layer Security) is a protocol developed by Netscape for transmitting private documents via the Internet.
- 29. Other security processes E-Mail Security File system security Disk Mirroring Backup UPS Personnel Security Auditing
- 30. Some Security Tips Encourage or require employees to choose passwords that are not common. Require employees to change passwords every 90 days. Make sure your virus protection subscription is current and update. Educate employees about the security risks of e-mail attachments. Assess your security posture regularly. When an employee leaves a company, remove that employee’s network access immediately. If you allow people to work from home, provide a secure, centrally managed server for remote traffic. Update your Web server software regularly. Do not run any unnecessary network services.
- 31. Acts for Data Security To protect data from various threats, a lot of act has been enacting. Some of these are The Privacy Act (1974), U.S. The Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (1986), U.S. The Computer Security Act (1987), U.S. The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA), 1998, U.S. Data Protection Act 1998, U.K. Swiss Federal Act on Data Protection (DPA), 1992 The Information Technology Act 2000, India
- 32. Data Security action in India In India, some Cyber Crime Enforcement Agency has been set up Cyber Crime Police Station, Bangalore Cyber Crime Investigation Cell of Mumbai Police Cyber Crime Police Station of Andhra Pradesh The Crime Branch of Criminal Investigation Department, Tamilnadu police In East India, Cyber Crime Cells have been set up by the Kolkata Police as well as the Criminal Investigation Department, West Bengal
- 33. Data Security Council of India Data Security Council of India (DSCI), a section 25 not-for-profit company, was setup as an independent Self Regulatory Organization (SRO) by NASSCOM, to promote data protection, develop security and privacy codes & standards and encourage the IT/BPO industry to implement the same.
- 34. Conclusion Due to hacking issue the popular British Tabloid “News of the World” has been banned. The Australian Internet activist Julian Assange has gone to the prison due to wikileaks. But hacking is not stopped. So, we must aware of data security. We have to adopt the latest technology for defending the various threats.
- 35. Thank You !