Deposition
- 2. C. DEPOSITION The _____________ of particles and fragments. It is also called ___________________
- 3. The agents of deposition are: ____________________ ____________________ ____________________
- 4. RATES OF DEPOSITION DEPEND ON: 1. Particle size: ________ particles (clay,silt) settle more slowly than larger particles.
- 5. ________ do not settle out of solution unless the solution becomes _______________ _____________& __________ are the ions that come out of solution.
- 6. 2. Particle shape: ____________ between water and the surface of particles _______ settling. As the surface area ___________ the time it takes to settle __________
- 7. 3. Particle Density: ____________ particles settle faster.
- 8. What is the relationship between settling rate and particle size? Complete the graphs: label each axis Settling rate Particle size
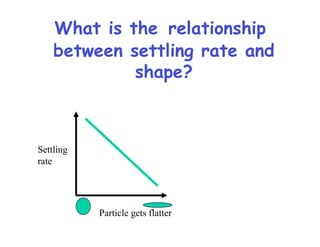
- 9. What is the relationship between settling rate and shape? Settling rate Particle gets flatter
- 10. What is the relationship between settling rate and density? Settling rate density
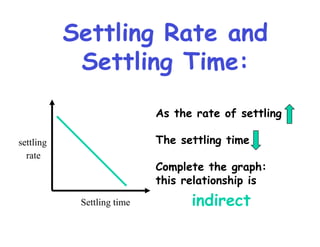
- 11. Settling Rate and Settling Time: As the rate of settling settling The settling time rate Complete the graph: this relationship is Settling time indirect
- 12. VELOCITY OF TRANSPORTING MEDIUM: The slower the velocity of the water the ________ particles will settle. It takes longer for particles to settle in ___________ water.
- 13. SORTING OF SEDIMENTS: Horizontal Sorting: a gradual change in the size,shape and density (of deposited particles) when a stream slows down
- 14. Horizontal Sorting boulders cobbles Roundest pebbles and sand densest Precipitation …………… silt ……………. Ions in ……………. (colloids) clay ……………. solution Smallest flattest least dense
- 16. Nile River Delta
- 18. Graded Bedding: Each layer represents a single event of deposition Largest at bottom smallest at top
- 19. EROSIONAL -DEPOSITIONAL SYSTEM: ___________ or ___________ are examples of this kind of system.
- 20. Within a stream system energy transforms from ____________ to ____________ energy.
- 21. Erosion _____________ _Will dominate in the steeper section and
- 23. Deposition ______________ In places of less gradient or slope.
- 25. Kinetic Energy depends on Slope- __________________ velocity increases Kinetic energy increases more erosion occurs
- 28. Potential Energy depends height on__________ not Slope energy is stored and deposition occurs
- 29. When the rate of erosion equals rate of deposition: Dynamic Equilibrium ___________________ is reached
- 30. Erosion occurs more often on land _______ And Deposition occurs in large bodies of water _______
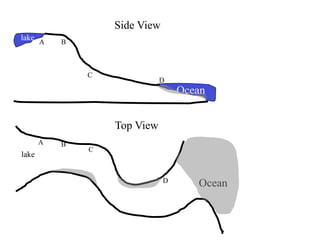
- 31. Side View lake A B C D Ocean Top View A B C lake D Ocean
- 32. Streams that flow over flat valleys may develop meandering paths because of erosion and deposition.
- 33. Glaciers
- 34. Sediments left by glaciers are: _______________
- 36. Glacial erratics are large rocks that have been transported by glacial ice without being broken into pieces
- 37. Some Glacial Features include: U-shaped valleys Moraines unsorted sediments drumlins kettle lakes Drumlins finger lakes outwash plains Kettle lakes erratics outwash plain
- 38. WIND:
- 39. Sediments left by wind are ________________
- 42. Sand dunes may form with a gentle slope facing into the wind ________________ Windward side And a steep slope on the opposite leeward side side___________
- 46. When wind direction changes sand dunes cross each other creating a feature known as Cross bedding ________________ Most sand dunes are well sorted ___________ layers in sloping ____________
- 47. Deposition on Coastlines by Ocean Waves and Currents:
- 48. The sand grains are rounded _____________ & frosted ______________
- 51. Waves move sand parallel __________ to the shore
- 53. Barrier beaches may form like Jones Beach or Fire Island
- 54. Wave action rounds sediments as a result abrasion of __________