Differentiated learning 2
- 4. PERHATIKAN BAIK-BAIK BAGAN TUGAS YG DIBERIKAN PADA ANDA. PILIH SALAH SATU YANG SESUAI DGN GAYA BELAJAR ANDA. PADA WAKTU YG DITENTUKAN, SILAKAN DIBUAT UNTUK KEMUDIAN DITAMPILKAN.
- 5. AKRONIM LAGU (1 menit) GERAK DAN TARI (1 menit) PUISI GAMBAR / KOMIK
- 9. Foundational to Transformational Concrete to Abstract Simple to Complex
- 10. Dependent to Independent • Students vary on the amount of independence they are ready for Structured to Open-ended • Some students are ready to improvise while others still need more straight forward guidelines to follow Slow to fast • Some students will move quickly through one part of a topic but then need to move more slowly in other areas
- 11. • Assigning work on the same topic at different degrees of difficulty • The students are getting the same type of information but in a way that is geared towards their individual ability. • The teacher should aim to provide work that is just a little too hard • This pushes students out of their level of comfort and allows the teacher to help them reach a new level of understanding
- 12. Enhancing motivation to learn Helping students to Using realize that familiar there is a ideas as a connection way to between introduce school and less familiar their own ideas interests
- 13. “Sidebar” Studies • Students study the aspects of a topic that interest them • Example- A student might like music and decide to focus on the music of the 1950s for a history class. Interest groups • Students who have similar interests form a group to do an in-depth study on one particular topic that they find most interesting
- 14. • Find a way to link a student interests with the curriculum • Teachers should make sure that students are acquiring the skills that the curriculum specifies. • Guide students to success by providing structure • Teachers should set goals and time-lines to guarantee that students are getting the most out of their learning.
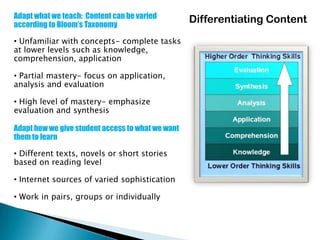
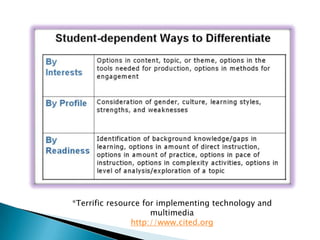
- 16. Adapt what we teach: Content can be varied Differentiating Content according to Bloom’s Taxonomy • Unfamiliar with concepts- complete tasks at lower levels such as knowledge, comprehension, application • Partial mastery- focus on application, analysis and evaluation • High level of mastery- emphasize evaluation and synthesis Adapt how we give student access to what we want them to learn • Different texts, novels or short stories based on reading level • Internet sources of varied sophistication • Work in pairs, groups or individually
- 17. Concept Based Teaching • Avoid rote memorization of long lists of facts • Focus instead on key concepts and principles, which are the building blocks of meaning • Make connections between subjects and facets of a single topic • Relate ideas to the student’s lives • Identify patterns and help student’s to use these to deal with future learning
- 18. Stage 3: Collaboratively • Create a challenging learning design a project for the environment student to engage in • Guarantee proficiency in basic while others focus on curriculum the general lesson • Buy time for enrichment and Stage 2: Note gaps in acceleration knowledge and define plan to address these Curriculum Compacting Designed to help Stage 1: Identify candidates advanced learners and assess their understanding of a particular subject or lesson maximize the use of their time for learning
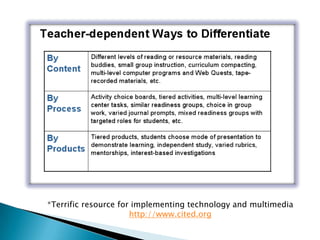
- 19. Using varied texts and resource materials • Build a classroom library that includes texts of various levels, magazines, brochures, internet files, videos etc. • A rich array of materials ensures that content is meaningful to learners of all levels • Computer programs can present different levels of challenge and complexity Learning contracts • Can contain both skills and content components • Combine a sense of shared goals with individual appropriateness and autonomy Mini-lessons • Some students may not fully grasp newly taught material • Meet with these students to revisit these concepts to extend their understanding and skill
- 22. Process refers to how a student comes to understand and assimilate facts, concepts and skills Allows students to learn based on what method is easiest for them, or alternatively, what will challenge them the most • A learning style inventory may help to identify this • http://www.personal.psu.edu/bxb11/LSI/LSI.htm • Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences to guide appropriate methodology Students make sense of ideas and information most effectively when classroom activities are: • Interesting • Involve high level thinking • Use key skills to understand key ideas
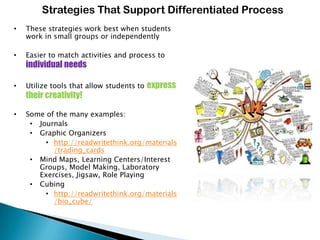
- 23. Strategies That Support Differentiated Process • These strategies work best when students work in small groups or independently • Easier to match activities and process to individual needs • Utilize tools that allow students to express their creativity! • Some of the many examples: • Journals • Graphic Organizers • http://readwritethink.org/materials /trading_cards • Mind Maps, Learning Centers/Interest Groups, Model Making, Laboratory Exercises, Jigsaw, Role Playing • Cubing • http://readwritethink.org/materials /bio_cube/
- 24. Products represent the student’s application and understanding of what they have learned • Typically a long term assignment • May supplement or replace a more traditional written test as an assessment of knowledge and understanding • Has the advantage of allowing a more flexible approach to student evaluation, accounting for multiple learning styles How to design an effective product • Decide on format • Clearly define core expectations • Decide on necessary scaffolding (brainstorming, rubrics, timelines, critiquing and revising • Coach for success and quality Benefits • Encourages students to engage using their strengths and interests • Student are intrinsically motivated as this is their chance to “own” the curriculum
- 26. Traditional grading system is designed to 1. Provide rank you within your two grades classroom cohort (Traditional and Personal) Not all work has to be 2. Traditional letter graded, especially if grades with a numeric intellectual risk taking superscript to indicate is the goal! 3below, 2at or 1above grade level 3. Supplemental The goal of normed grades differentiated with more individualized instruction is help you grades as it relates develop as a learner…it to a portfolio of can be more work individualistic
- 28. *Terrific resource for implementing technology and multimedia http://www.cited.org
- 29. *Terrific resource for implementing technology and multimedia http://www.cited.org
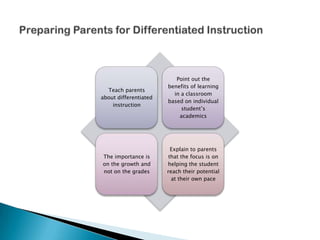
- 30. Point out the benefits of learning Teach parents in a classroom about differentiated based on individual instruction student’s academics Explain to parents The importance is that the focus is on on the growth and helping the student not on the grades reach their potential at their own pace
- 34. Twitter : @GuruInspiratif E-mail : rendraprihandono@gmail.com Pin BB : 294D9885