Diffractionncxcjhdcjnnjdcndkj New (1).pptx
- 1. CHAPTER 14 Lesson 1 DIFFRACTION THOUGHT OF THE DAY
- 3. DIFFRACTION Learning Objectives:- • Define Diffraction • Understand Huygens Principle of Diffraction. • Explain Single Slit Diffraction and its significance Class activity:- Demonstrate wave nature of light Observe interference pattern in single slit experiment
- 4. DESTRUCTIVE INTERFERENCE Review of Waves TERMS Overlapping of two waves to cancel each other COHERENT WAVES Waves having zero or constant phase difference and frequency TRANSVERSE WAVES All the particles of waves oscillate at right angles to the direction of wave CONSTRUCTIVE INTERFERENCE WAVEFRONT Overlapping of two waves with resultant larger amplitude wave Straight vertical lines representing crests or troughs
- 6. • Watch the video carefully https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4bCUTLWyicM • Understand the concept of diffraction • Raise your hands when you know the answer Bonus Point Goes 1. 2. 3.
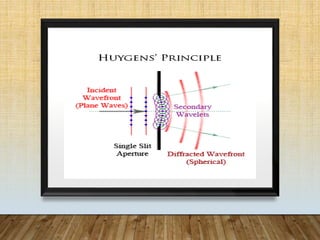
- 7. • Diffraction is the resultant of the wave-nature of light. • When light waves passes through the edges of obstacles or a narrow aperture, this causes the waves to bend and spread out. This phenomenon is called diffraction. • This bending results in formation of (bright and dark fringes) interference pattern which can be seen on the visualizing screen. • Wavelets (as in Huygens’ Principle) in a wavefront interfere with each other. WHAT IS DIFFRACTION????
- 10. Single Slit Diffraction Pattern • All the waves passing through the slit interfere to produce a diffraction pattern consisting of bright and dark fringes. • The bright fringes are due to constructive interference, and the dark areas are due to destructive interference. • A number “n” represents the order of the bright and dark fringes. • The intensities of the fringes consist of a central maximum surrounded by maxima and minima on its either side. • The central maximum is brighter than the other maxima. The maxima rapidly decrease as one moves further from the center.
- 12. 1. The divergence of light from its initial direction is called __________ 2._________discovered the wave nature of light. 3. Constructive interference causes dark fringes/ bands to form on the screen. True/False. 4. The intensity of central maxima increases if slit width is narrowed. True/False. 5. What do you mean by Huygen’s wavelets? 6. Can you explain Single slit Experiment?
- 13. By the end of the lesson all students should be:- Able to Define Diffraction. Understand Huygen’s Principle of Diffraction. Explain Single slit Experiment and its significance.