DoA
- 1. Objectives • Be able to define social norms • Be able to outline the Deviation from Social Norms definition • Be able to identify limitations of the DSN definition • Be able to apply DSN to Tourettes syndrome Some will be able to • Apply DSN to other disorders (e.g. Depression, schizophrenia)
- 2. Abnormality Definitions: Deviation from Social Norms Failure to Function Adequately Deviation from Ideal Mental Health
- 3. Deviation from Social Norms - Those who break the ‘rules/norms’ of society are abnormal Definitions Deviation from Failure to Function Ideal Mental Health Adequately - Those who lack - Those who characteristics of can’t cope with ideal mental daily life are health are abnormal abnormal
- 4. Deviation from Social Norms Recap: What are social norms? What are the 2 types? Social norms allow for the regulation of normal social behaviour. All societies have norms for appropriate behaviours and beliefs (expectations of how people should behave/think Examples: - A behaviour to suggest you are ‘normal’ e.g. Being quiet in the cinema - A behaviour to suggest you are ‘abnormal’ e.g. Talking loudly in the cinema
- 5. Deviation from Social Norms Deviation from Social Norms Someone is abnormal if they do not follow/break social norms
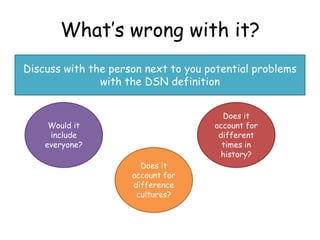
- 6. What’s wrong with it? Discuss with the person next to you potential problems with the DSN definition Does it Would it account for include different everyone? times in history? Does it account for difference cultures?
- 7. DSN – Limitations (A02) P – Social norms change over time and therefore a behaviour that broke social norms in the past wouldn’t now E – For example an unmarried mother in the 1940/50’s would have been breaking social norms and so would have been classed as abnormal E – This is a limitation because it brings into question that validity of this definition in terms of defining abnormality – society has changed not the individual
- 8. DSN – Limitations (A02) P – Social norms differ between cultures E – For example in British culture it is considered polite to finish the food on your plate, but in India to finish all food from your plate is a sign that you are still hungry E – This is a limitation because it means that the definition is different according to culture and the same criteria cannot be applied universally
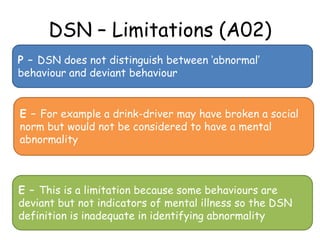
- 9. DSN – Limitations (A02) P – DSN does not distinguish between ‘abnormal’ behaviour and deviant behaviour E – For example a drink-driver may have broken a social norm but would not be considered to have a mental abnormality E – This is a limitation because some behaviours are deviant but not indicators of mental illness so the DSN definition is inadequate in identifying abnormality
- 10. Objectives • Be able to outline and identify DSN • Be able to list the 5 characteristics of the FFA definition • Be able to apply the characteristics of FFA to depression • Be able to identify limitations of FFA Some will be able to- • Be able to apply the characteristics of FFA to other disorders • Be able to explain limitations of FFA
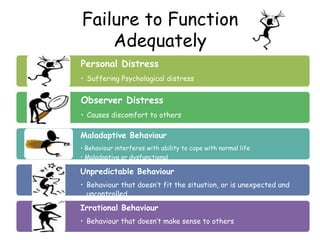
- 11. Failure to Function Adequately Failing to function is generally taken to mean that a person is unable to cope with everyday life. Their behaviour is seen to be maladaptive, disruptive (to work) and causing distress (self and others) Rosenham & Seligman (1989) suggested the characteristics It is the presence of these characteristics that indicate Psychological abnormality
- 12. Failure to Function Adequately Personal Distress • Suffering Psychological distress Observer Distress • Causes discomfort to others Maladaptive Behaviour • Behaviour interferes with ability to cope with normal life • Maladaptive or dysfunctional Unpredictable Behaviour • Behaviour that doesn’t fit the situation, or is unexpected and uncontrolled Irrational Behaviour • Behaviour that doesn’t make sense to others
- 13. What’s wrong with it? Discuss with the person next to you potential problems with the FFA definition Could there be other What if the reasons for behaviour is someone desirable? failing to function? Can people still function normally with an abnormality?
- 14. FFA – Limitations (A02) P – Failing to function does not always indicate the presence of a psychological abnormality E – For example in the current economic climate someone might struggle to hold down/get a job because of limited availability rather than a psychological abnormality E – This is a limitation because environmental factors beyond an individuals’ control may cause a failure to function rather than a psychological abnormality
- 15. FFA – Limitations (A02) P – The presence of an abnormality doesn’t always result in a failure to function E – For example an individual with depression may be able to keep a job and run a family successfully E – This is a limitation because it shows that this definition is inadequate in truly identifying behaviours that may be considered abnormal, as an abnormality might not always result in an inability to function
- 16. FFA – Limitations (A02) P – Behaviour that looks as if it’s a ‘failure to function’ may actually be desired/admired by society E – For example some political prisoners will go on hunger strike as part of their political protest will often be respected E – This is a limitation because although starving yourself may be seen as irrational, maladaptive and unpredictable (failing to function) but it is understandable in a certain context & not an indication of an abnormality
- 17. Deviation from Ideal Mental Health This defintion stands out because it doesn’t directly define abnormality, but it outlines ‘ideal mental health’ and considers someone with an abnormality will deviate from these characteristics Marie Jahoda (1958) created a list of characteristics indicating psychological health and therefore an absence of these characteristics suggests abnormality
- 18. Characteristics... Strong sense of self- • Individual should be in touch with their own identity identity and feelings • Individual should be resistant to stress and Resistant to stress it’s negative effects • Individual should be focussed on the future Self-actualisation and fulfilling their potential • Individual should be able to function Autonomy independently, recognising own needs with an accurate perception of reality • Individual should show understanding towards Empathy others
- 19. What’s wrong with it? Discuss with the person next to you potential problems with the DIMH definition Can you easily decide Anything what ‘normal’ else? is? Can anyone realistically fulfil all of the criteria?
- 20. DIMH – Limitations (A02) P – The criteria of this definition are too idealistic E – For example Maslow (1968) argued that very few people actually ever reach self-actualisation E – This is a limitation because if this definition is true many of us would be considered abnormal as the criteria for ideal mental health is set too high.
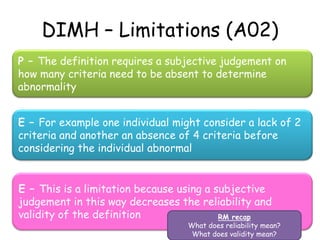
- 21. DIMH – Limitations (A02) P – The definition requires a subjective judgement on how many criteria need to be absent to determine abnormality E – For example one individual might consider a lack of 2 criteria and another an absence of 4 criteria before considering the individual abnormal E – This is a limitation because using a subjective judgement in this way decreases the reliability and validity of the definition RM recap What does reliability mean? What does validity mean?
- 22. DIMH – Limitations (A02) P – The criteria of this definition are based on Western culture – the definition is ethnocentric E – For example, Jahoda’s emphasis on personal growth and autonomy reflect Western individualistic culture rather than collectivist culture E – This is a limitation because it means that the definition is subjective, may therefore be biased and the same criteria cannot be applied universally.