Dwm ppt
- 1. 1
- 2. WHY DAILY MANAGEMENT Thing do not stay there, they deteriorate IF NOT MANAGE IN ADEQUATE MANNER 2
- 3. LEVEL-1 Worker Work for Rentention/Maintt. LEVEL-2 Engg./Sup. Work for Cont. Imp. LEVEL-3 CEO Work for Breakthrough LEVEL-3 LEVEL-2 LEVEL-1 3
- 4. TQM To ensure the right input to achieve the desired output. DWM 5’S T Q POLICY DEPLOYMENT M CUSTOMER FOCUS TOTAL EMPLOY INVOLVEMENT 4
- 5. D A STANDARDIZATION I L Y W EXACTNESS O R K M A SIMPLIFICATION N A G E M E VISUAL MANAGEMENT N T 5
- 6. STANDARDIZATION Prepare standard for operational parameters based on past performance. It should not be a wish list but actual capability. Example – If m/c continuously perform at constant rate like 100 wls/hr from last three or six month then only it can be standardize. That shows m/c are capable for producing 100wls/hr 6
- 7. STANDARDIZATION A S C D A P l eve L A S C D C D A P A S C D C D Time Revision of Standard A S Enactment of Standard C D Review of Job Result Execution of Standard Job 7
- 8. EXACTNESS Do exactly what standard says. Example – If standard says run the m/c at 20wls/min then its speed can’t be changed 8
- 9. SIMPLIFICATION Communication between the different level should be simple & understood to each & everyone Example – Work instruction or standards should be in regional languages so that it is understood by concern person. 9
- 10. VISUAL MANAGEMENT Understand by seeing the thing Example – Way of working should have pictorial view so that one can understand by seeing the picture (to avoid the language gap). 10
- 11. MANAGEMENT BY WALKING AROUND DO’S DON’T 1. Pick some abnormalities in your area 1. Not discuss that issue in shop 2. Discuss the issue with concern floor at that moment. person in your daily meeting 11
- 12. MANAGEMENT BY WALKING AROUND DIRTY DIFFICULTY DANGEROUS 12
- 13. ABNORMILITIES When Man, Machine, Method, Material is not as per Standard. Operator should have the capability to detect the abnormal situation as soon as possible then only its come in ideal operator. Example – Machine have lot of noise/leakage problem which normally not happened 13
- 14. PURPOSE OF DAILY WORK MANAGEMENT Eliminate the Variance 100 % Employee involvement Continual Improvement 14
- 15. VARIANCE When input or output is not 100% identical SPORADIC CHRONIC 15
- 16. TYPE OF NATURE RESPONSIBILE VARIANCE Sudden behavior Or Man, Method, M/c, SPORADIC Occurrence Material CHRONIC Not Challenge Human Nature 16
- 17. Levels Worker Supervisor Manager Character Expectation Follow the std or Assure 100% Do Improvement W.I. compliance Kaizen Participate Motivate to do so Align the kaizen with company Goals Focus Activity base Ensure the end Process goal at their Improvement concern area Abnormality Early Detection Find the root Take firm action causes against that (Preventive action) 17
- 18. Criteria Between Duration Topic Of Levels Discussion Level - 1 Supervisor & 5 Mins Last Day Line Worker Issue or customer complaints Level - 2 Supervisor of 15 ~ 20 Mins Issues between different different department department at supervisor level Level - 3 HOD’s of different 60 ~ 90 Mins Overall department performance of the company 18
- 19. Sample DWM Log sheet Operation M/c Operator Productio Rejection Rework Gap Respons Target Status Pts. name No. Name n Analysis ibility Date S.No. S A S A S A 19
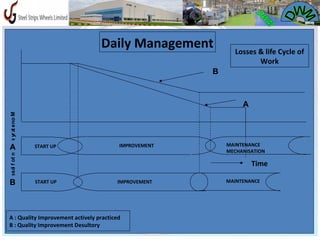
- 20. Daily Management Losses & life Cycle of Work B A ss o f ot nuo m yr a e no M a t IMPROVEMENT MAINTENANCE A START UP MECHANISATION Time l B START UP IMPROVEMENT MAINTENANCE A : Quality Improvement actively practiced B : Quality Improvement Desultory 20
- 21. DAILY MANAGEMENT CHANGE CONTROL Whenever there is a change in Man/Machine/ Material/Method/Measurement, the change must be managed according to standards, or new standards established Example – 1. New Operator 2. New Material 3. Method change 4. Commissioned after maintenance 5. New Instrument introduced 21