E Business & E Commerce +
- 1. E-Business & E-Commerce Finishing Chapter 3
- 2. What is E-Business, e-commerce? Derived from the term e-commerce , is the conducting of business on the Internet, not only buying & selling, but also serving customers and collaborating with business partners e-commerce : is the buying and selling of goods & services over the Internet
- 3. e-Business Models Business-to-business (B2B) Businesses that buy and sell from each other over the Internet Business-to-consumer (B2C) Businesses that sell to consumers over the internet Consumer-to-business (C2B) Applies to any consumer that sells a product or service to a business over the Internet Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) Applies to sites that primarily offer goods and services to assist consumers interacting with each other over the Internet
- 4. B2B
- 5. Examples of B2C & C2B B2C: e-shops, e-stores, or e-tailer C2B
- 6. Online Auction Sites Electronic Auction : sellers and buyers solicit consecutive bids from each other & prices are determined dynamically Reverse Auction : an auction that buyers use to purchase a product or service selecting the seller with the lowest bid All Auction sites are electronic! Key point: they do not take title of goods being sold eBay Priceline & B2B : sellers compete to earn business Forward Auction : An auction that sellers use as a selling channel to many buyers & the highest bid wins
- 7. C2C Auction Sites: e-bay Online Communities: kazaa
- 8. How do companies use e-commerce? E-Commerce improves market efficiencies in a variety of ways, as this figure shows. Customers benefit from the first two, disintermediation and increased price information. Businesses benefit from increasing their knowledge of price elasticity. Take out the middleman! Measures the amount that demand rises or falls with price changes
- 9. Economic Factors that disfavor E-Commerce Channel conflicts that occur when a manufacturer competes with its traditional retail outlets by selling directly to the consumer. Price conflicts that may occur by a manufacturer selling directly to consumers and undercutting retailers’ prices. Logistics expenses increase when a manufacturer must process thousands of small-quantity orders rather than a few large-quantity orders. Customer-service expenses increase when a manufacturer must begin dealing directly with customers rather than relying on retailers’ direct relationships with customers.
- 10. Strategies for e-business: Marketing & Sales A series of online marketing and sales strategies exist and new innovations in sales & marketing arrive everyday Online Ads Pop-up and pop-under ads Mass customization Personalization (amazon.com uses personalization to create a unique portal for each of its customers)
- 11. Questions What is eBay's model and why do you think it has been so successful? What type of auction site is Priceline.com? How can amazon.com use m-commerce to influence its business?
- 12. Organizational Strategies To be successful in e-business, organizations must master the art of electronic relationships Traditional means of customer acquisition such as advertising, promotions and PR, are just as important with a website.
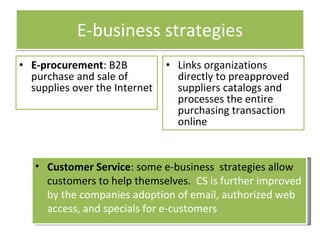
- 13. E-business strategies E-procurement : B2B purchase and sale of supplies over the Internet Links organizations directly to preapproved suppliers catalogs and processes the entire purchasing transaction online Customer Service : some e-business strategies allow customers to help themselves. CS is further improved by the companies adoption of email, authorized web access, and specials for e-customers
- 14. Web traffic is one metric, a better measure for e-business is how much revenue has been generated by web traffic, number of new customers, reduction of CS calls because of the web traffic…. E-business Metrics
- 15. techniques Cookie : a small file left on a consumers hard drive; allows websites to record the comings and goings of customers usually without their consent Click-through: tracks the number of users who visit a site and click on a ad Banner Ads: advertises the product or services of another dot com business
- 16. Added value but at what cost to consumers? The Internet has created a virtual market with a high number of buyers & sellers…. This is good! It also has made the collection of user information extremely easy with wide gaps in the area of transaction regulation….this can be bad!
- 17. Consumer Protection E-business organizations must consider how to protects its customers from security threats in an online environment Of most concern is the protection of consumer financial data online
- 18. Techniques for securing online transaction include; Encryption : scrambles information and requires a key or PW to decrypt Secure Socket layer (SSL): creates a private connection between client & server, encrypts info, transmits over the Internet Secure electronic transaction (SET): Much like the SSL but adds customer authentication
- 19. Security & Privacy of Consumer Information
- 20. Customer Issues with E-Commerce Distance has been shortened . Shoppers & merchants come together from anywhere in the world now Indirect contact between merchant & consumer Asynchrony in the accomplishment of transactions : there is usually a delay between the closure of a purchase and the reception of the product or service
- 21. E-business: why are security & privacy so important? Trust: consumer trust is crucial in order for web-based businesses to survive It is hard to establish trust when; They do not know how their PI is going to be used after the transaction When they receive unsolicited communication from related businesses and partners They don’t know how long their PI will be kept and where
- 22. Questions What different methods does an organization have available to access the Internet? What is the difference between disruptive and sustaining technologies? What metrics could Amazon use to assess the efficiency and effectiveness of its website?
- 24. Intranets Is an internalized portion of the Internet, protected from outside access, that allows an organization to provide access to information and application software only to its employees Hosts all kinds of company-related information such as; Benefits Schedules Strategic directions Employee directories
- 25. Intranets
- 26. Intranets & ROI By avoiding costs associated with print material, organizations experience a greater ROI with electronic publishing Impact on ROI & increased access to organizational information? Examples of Intranet Info systems in business: Windows SharePoint Services ( web-based) WebEx’s Web Office Considerable amount of opportunity for small business application developers
- 27. Extranet Is an Intranet that is available to strategic partners such as; Customers Suppliers Distributors Etc… Provides secured access to those groups of people (customer and / or suppliers) that provides a level of SCM Without incurring the responsibility of managing partner IT resources!!!
- 28. More ways to Access Internet Resources Portals Is a very generic term for what is in essence a technology that provides access to information A portal is a website that offers a broad array of resources & services such as email, discussion groups, search engines, etc… Examples Yahoo! Netscape Microsoft (Years ago we had the butterfly!) America Online How can portals provide a business solution?
- 29. Kiosks A kiosk is a publicly accessible computer system that has been setup to all interactive information browsing The computer’s operating system has been hidden from view, program runs in full screen mode that provides a few simple tools for navigation
- 30. Providing Internet Information Three common forms of internet service providers include; Internet Service Providers (ISP) Online Service Providers (OSP) Application Service Providers (ASP)
- 31. ISP’s ISP Provides individual and other companies with access to the internet along with other services Local ISPs (Big in the early 90’s) would lease line space WISP Wireless internet service provider allows subscribers to connect to a server at designated hotspots or access points using a wireless connection Examples of this provider is T-Mobile
- 32. OSP’s & ASP’s OSP Online Service Provider: uses their own browser to allow users access to the Internet. AOL is a good example of an OSP Early 2000’s MSN’s butterfly was another example of an OSP…. ASP Application service providers: offers organizations with access over the internet to systems and related services that would have otherwise have to located on personal or organizational computers ASP is essentially the outsourcing of part of a companies business logic