E commerce
- 1. Presented By – Anand S Iyer
- 2. What is Commerce and e-Commerce? ‘Commerce’ is a division of trade or production which deals with the exchange of goods and services manufacturer to final consumer. It is commonly known as electronic marketing. ‘e- Commerce’ is the purchasing, selling & exchanging goods and services over internet through which transactions or terms of sale are performed electronically.
- 4. Different types of e-Commerce Business-to-Business (B2B) Business-to-Consumer (B2C) Business-to-Government (B2G) Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) Government-to-Consumer (G2C) Government-to-Business (G2B)
- 5. What is B2B e-Commerce? Business-to-Business (B2B) e-Commerce is simply defined as the sale of goods and services between businessess via an online sales portal. For Example – Intel selling microprocessor to Dell. Delmonte selling ketchup to Burger King.
- 6. Process of B2B e-Commerce
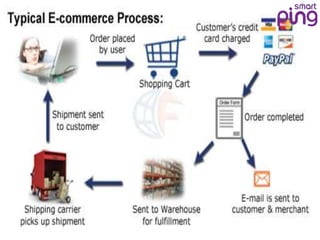
- 7. What is B2C e-Commerce? Business-to-Consumer (B2C) e-Commerce, or commerce between companies and consumers, involves customers gathering information; purchasing physical goods or receiving products over an electronic network. For Example – Purchasing laptop/mobile phone from Amazon.in. Sony Bravia TV purchased from Croma site.
- 8. Process of B2C e-Commerce
- 9. What is B2G e-Commerce? Business-to-Government (B2C) e-Commerce is generally defined as commerce between companies and the public sector. It refers to use to public procurement, licensing procedures and other government related operations. For Example – Business pay taxes, sell goods and services to Govt. agencies. Manufacturer selling Military defense equipments to Govt. Process of B2G e-Commerce
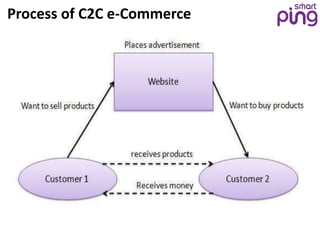
- 10. What is C2C e-Commerce? Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) e-Commerce is the commerce between private individuals or consumers. For Example – Peter buying an iPod from Prathap on eBay. Bhaarath selling a car to Vikhar on OLX.
- 11. Process of C2C e-Commerce
- 12. What is G2C e-Commerce? Government-to-Consumer (G2C) e-Commerce is where the government is provides goods and effective services to each citizens. This model is also a part of ‘e-governance’. The Government provides the facilities to the citizens through website. Different welfare schemes. Process of G2C e-Commerce
- 13. What is G2B e-Commerce? Government-to-Business (G2B) e-Commerce is a business model that refers to government providing services or information to business organization. The Government uses B2G model website to approach business organizations. Such websites support auctions, tenders and application submission functionalities. Process of G2B e-Commerce
- 14. Advantages and Disadvantages of e-Commerce Advantages – Faster buying/selling procedure, as well as easy to find products. Buying and selling 24/7. More reach to customers, there is no theoretical geographic limitations. No need of physical company set-ups. Customers can easily select products from different providers without moving place to place. Disadvantages – Unable to examine products personally. Not everyone is connected to the internet. There is possibility of credit card number theft. Mechanical failures can cause unpredictable effects on total processes.