EAM
- 1. Drive maintenance best practices Eng. Baker Khader Abdallah, PMP, MBA Oracle EBS Consultant
- 2. Oracle eAM… Drives maintenance best practices and improve your organization’s performance Empowers all workers with easy to use self-service (web and mobile) applications Manages the full asset lifecycle with a complete view of your assets and equipment Replaces costly standalone maintenance systems with Oracle’s integrated solution
- 3. eAM Functionality Assets Management Asset Activities Management Work Management and Execution Preventive and Condition Based Maintenance Planning and Scheduling Maintenance Cost Management Integration with Other Modules
- 5. Assets Management Define your Assets (Equipment and Machines) Categorize similar assets in Asset Groups Define Asset Bills of Materials Define Asset Hierarchies Track Assets cost and work history Define Rebuildable Items Attach Reference Documents like Instructions documents and wiring diagrams to your assets
- 6. Define Asset Groups Assets that have similar physical configurations and maintenance requirements should belong to a single Asset Group Examples include Trucks, Pumps, Towers, Buildings, Storage Tanks, and Turbines.
- 7. Define Your Assets (Asset Numbers) A unique number that represents an asset or piece of equipment on which maintenance will be performed. An example of an asset number would be a Pump-101, or Toyota Truck 01. Truck 001
- 8. Asset Routes A "virtual asset" that enables multiple assets to be associated to a single work order. It eliminates the need for creating multiple work orders for the same activity.
- 9. Asset Bills of Material A bill of material (BOM) is used to list all items and components that make up a particular asset, and is defined for each Asset Group. Truck 001
- 10. Asset Hierarchy A parent/child relationships of assets It provides information that enables a user to quickly identify the relationship via an Asset Navigator that displays appropriate asset details. Truck 001 (Parent) Crane 001 (Child)
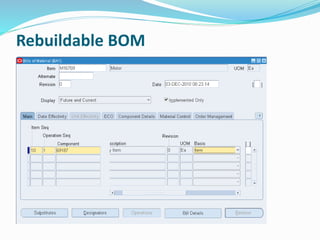
- 11. Rebuildable Items Items that are installed, removed, and refurbished Examples of Rebuildable Items include motors and computer boards. Rebuildable Items are inventory items and can be serialized
- 12. Rebuildable Items Serial Numbers
- 13. Rebuildable BOM
- 15. Asset Activities Management Define Standard Maintenance Operations Define Asset Activities (Standard Maintenance Jobs) Define Maintenance Jobs BOM Define Maintenance Routings
- 16. Maintenance Operations Identifies a single maintenance task
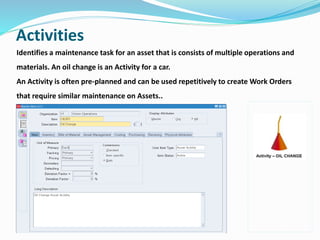
- 17. Activities Identifies a maintenance task for an asset that is consists of multiple operations and materials. An oil change is an Activity for a car. An Activity is often pre-planned and can be used repetitively to create Work Orders that require similar maintenance on Assets..
- 18. Asset-Activity Association Associate the Activities with assets and or Rebuildable. Streamline the creation of Activities and associations using an Activity Association Template.
- 19. Activity Workbench Using the Activity Workbench, you can view, create query, and manage all of your Activities.
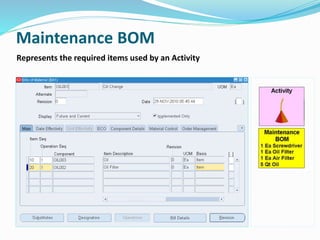
- 20. Maintenance BOM Represents the required items used by an Activity
- 21. Maintenance Routing The step-by-step operations you perform to perform the maintenance activity. Each routing can have any number of operations. For each operation you determine the resources you may use for it
- 23. Work Management Overview Work Requests Work Orders Operations and Tasks Work Order Relationships Work Transactions Work Order Planning
- 24. Work Management Work orders define what resources and items are needed to conduct the work. Work orders can be created manually or automatically based on preventive maintenance schedules
- 25. Work Requests Created to report asset problems within your organization Linked to Work Orders Work Request Life Cycle:
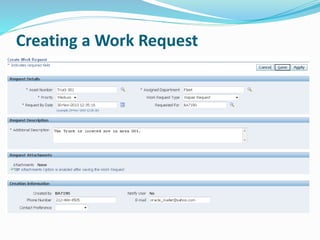
- 26. Creating a Work Request Asset Management Home Page > Create Work Request Easy –to-use self service web page for creating and following work requests
- 27. Creating a Work Request
- 28. A plan that defines the resources and material equipment needed to conduct work, and then associated start and end dates. Created against asset and Rebuildable inventory items Defined manually or automatically based on a scheduled activity Work Orders When an activity is attached to the work order, all its attributes such as maintenance BOM, maintenance route, will be added automatically
- 29. Work Orders Life Cycle
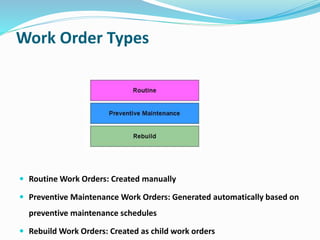
- 30. Work Order Types Routine Work Orders: Created manually Preventive Maintenance Work Orders: Generated automatically based on preventive maintenance schedules Rebuild Work Orders: Created as child work orders
- 31. Creating a Work Order
- 32. Attaching Documents to Work Orders You can attach existing documents to a Work Order, and create text to associate with a work order
- 34. Preventive Maintenance Preventive Maintenance Overview Meters: Readings of Operating Conditions Preventive Maintenance (PM) Schedule
- 35. Overview of Preventive Maintenance eAM generates Work Orders automatically based on meter readings, runtime and or calendar days. An example of meter-based preventive maintenance is your car's oil changes.
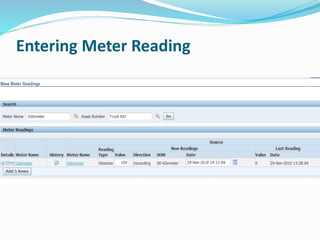
- 36. Meters Meters are used to measure asset usage and periodically service the asset, based on the measurement
- 37. Meter Definition
- 38. Meter Association Meter Association creates the relationship between the meter definition and the Asset Number
- 40. Preventive Maintenance Scheduling Scheduling of Activity for an Asset, Rebuildable item or asset route. The Preventive Maintenance (PM) Scheduler process creates suggested Work Order dates based on these rules. A planner can then view these forecasted Work Orders, and generate them as necessary.
- 42. PM Scheduling Rules Options Date Rules: PM will be performed based on days interval Meter Rules: PM will be performed based on Meter readings
- 43. Generating Work Orders After establishing PM schedule definitions, you can generate work orders
- 45. eAM Planning and Scheduling Overview eAM Planning. eAM Scheduling
- 46. Overview Cost savings and work management efficiencies are achieved by generating future planned work activities, and then using a planning process to balance the work load for resource management.
- 47. eAM Planning Based on Material Requirements Planning (MRP) The material requirements for maintenance work orders are calculated based on: The master schedule bills of material scheduled receipts on-hand inventory balances lead times order modifiers
- 48. eAM Scheduling Using the schedule workbench to schedule work orders and operations Scheduler workbench enables a planner to graphically view and reschedule work orders
- 49. Scheduler Workbench Schedule work orders and operations Expand and collapse work orders and operations, using a tree hierarchy Display both firmed and unfirmed work orders View and update start and end date for each resource
- 51. eAM Cost Management Overview eAM Cost Estimation Asset Cost Rollup
- 52. Overview Costs generate as maintenance work is executed and completed. These costs roll up through the Parent/Child hierarchies, and can roll up to any level within an asset hierarchy Labor, Material, and Equipment charges further classify into several maintenance cost categories.
- 53. eAM Cost Estimation Estimating the cost of maintenance work orders is necessary for planning and assessing purposes A Work Order's estimated and actual costs might differ because all materials or resources, associated with a Work Order, might not actually be used when the Work Order executes The Work Order Cost Estimate Processor can continually execute or launch manually Work Order Cost Estimation Life Cycle
- 54. Work Order Cost Estimation
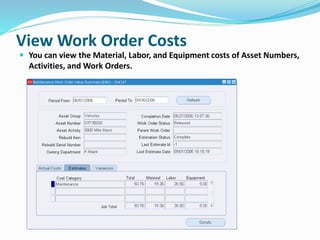
- 55. View Work Order Costs You can view the Material, Labor, and Equipment costs of Asset Numbers, Activities, and Work Orders.
- 56. Asset Cost Rollup You can optionally roll a child asset's costs into its parent asset, for reporting purposes
- 58. Direct Items Procurement Direct items are either non-stock or description-based. Non-Stock Direct Items can represent items that are not stocked in inventory, or services that need to be purchased from a supplier A planner can procure Direct Items from the Maintenance Workbench Purchase requisitions and purchase orders of such items capture the Work Order for which they are required
- 60. eAM Reports