Earthquake engineering
- 1. EARTHQUAKE
- 2. Definition: • An Earthquake is a sudden and rapid shaking of the ground due to passage of vibrations beneath caused by transient disturbance of elastic or gravitational equilibrium of rocks. • The scientific study of earthquakes is called Seismology. • Earthquakes are measured using observations from seismometers. • Seismic waves are recorded on instruments called seismographs. • The time, locations, and magnitude of an earthquake can be determined from the data recorded by seismograph stations.
- 4. RICHTER MAGNITUDE SCALE: • The Richter magnitude scale was developed in 1935 by Charles F. Richter. • Earthquakes with magnitude of about 2.0 or less are usually called micro earthquakes; are generally recorded only on local seismographs. • Events with magnitudes of about 4.5 or greater, are strong enough to be recorded by sensitive seismographs all over the world. • Great earthquakes have magnitudes of 8.0 or higher. • On the average, one earthquake of such size occurs somewhere in the world each year.
- 6. CAUSES : Natural Causes of Earthquake: • Tectonic Movement • Volcanic Activity • Pressure of gases in the interior • Landslides and avalanches • Faulting and folding in the rock beds are responsible for causing minor earthquakes.
- 7. Man-made Earthquakes: • The impounding of large quantities of water behind dams disturbs the crustal balance. • The shock waves through rocks set up by the underground testing of Atom bombs or Hydrogen bombs may be severe to cause earthquake.
- 8. EFFECTS: Destructive Effects: • Earthquake causes dismantling of buildings, bridge and other structures at or near epicenter. • Rails are folded, underground wires broken. • Earthquakes originate sea waves called Tsunamis. • Earthquakes result in the formation of cracks and fissures on the ground formation. • The earthquakes cause landslides. • Landslide due to earthquake may block valleys to form lakes.
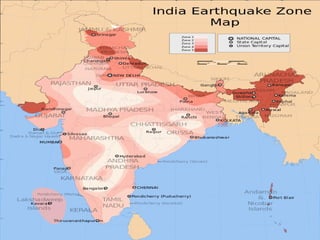
- 9. SEISMIC BELT: • Narrow geographic zone on the Earth's surface along which most earthquake activity occurs. • The outermost layer of the Earth (lithosphere) is made up of several large tectonic plates. There are three main seismic belts in the world : 1. Circum-Pacific seismic belt 2. Alpine-Himalayan seismic belt 3. Ridge seismic belt