EARTHS MOVEMENTS AND CHANGING LANDFORMS- 1.pptx
- 1. Which natural landforms can you spot in the image given above? Are all the landforms of the Earth similar? How do the natural forces and landforms impart a dynamic character to the Earth?
- 2. EARTHS MOVEMENTS AND CHANGING LANDFORMS LO: 1. To classify the movements of the earth. 2. To explain why and how earthquakes occur. 3. To explain how volcanoes are formed.
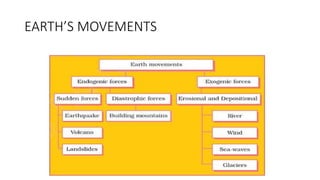
- 3. ENDOGENIC AND EXOGENIC FORCES The movements of the earth can broadly be divided into two on the basis of forces that cause them . The internal or endogenic forces originate within the Earth's crust create • slow Earth movements that form continents, ocean beds, mountains, plateaus and plains. • sudden Earth movements such as volcanic emptions, earthquakes and landslides. • The external or exogenic forces which originate outside the Earth 's crust cause changes on the surface of the Ea1th. For example, through erosion and deposition by natural agents such as wind, water, and so on.
- 4. FORMATION OF LANDFORMS BY INTERNAL PROCESSES •According to the Theory of Plate Tectonics, the Earth's lithosphere is divided into several Iarge and small irregularly shaped plates, called lithospheric or tectonic plates. It is believed that these plates are 'floating' on the molten mantle or the asthenosphere and a.re in a state of constant motion. These movements take place mainly due to the heat generated within the interior of the Earth. The movement of the lithospheric plates causes changes to the surface of the Earth.
- 6. Can You Remember What’s Under Your Feet? Mark the layers of the earth
- 7. HOW WERE THE SEVEN CONTINENTS FORMED? CAN YOU EXPLAIN IT?
- 8. THE THEORY OF CONTINENTAL DRIFT Today we observe millions of geological changes on the face of the earth. To explain the current position of the continents and the oceans, several scientists put forth different theories. The foremost attempt was made by Alfred Wegener in 1912. He was a German meteorologist. He tried to explain the present division of the continents and the oceans. According to his theory, a supercontinent called Pangaea broke into different continents 200 million years ago and the continents drifted to their present locations. This theory is called the Continental Drift theory.
- 9. THE THEORY OF CONTINENTAL DRIFT Movements of the plates occur due to the various forces acting upon it. Two broad categories of these forces are the endogenic and exogenic. Endogenic forces act in the interior of the earth. Exogenic forces work on the surface of the Earth. Endogenic forces produce slow as well as sudden movements like earthquakes and volcanoes which cause mass destructions over the surface of the earth. Horizontal and vertical movements are also produced by them, which result in variety of relief features like mountain building. Erosional and depositional works are done by exogenic forces like rivers, wind, glaciers and sea waves.
- 11. What do you see?
- 12. The Earth’s Plates The Earth’s plates are always moving. They move so slowly that we usually can’t feel it. The edges of plates are called faults. Faults can rub together, push toward each other, or pull away from each other. Have a look at the Earth’s plates. What do you notice about where New Zealand is?
- 13. The tectonic plates are constantly Rubbing together Moving towards each other Moving away from each other This kind of movement causes earthquakes.
- 14. An earthquake is the sudden and sometimes violent shaking of the Earth’s crust. It can have devastating effects on the land and areas on the surface as a result of the shock waves from the energy built up underground. What is an Earthquake?
- 15. The place of origin of an earthquake is called FOCUS. The point on the earth’s surface which is vertically above the focus is called the EPICENTRE. The vibrations of an earthquake spread out in concentric waves from the focus. These vibrations are called seismic waves. The effect or intensity of an earthquake is most at the epicenter. The surface of the earth can shake due to the movements of the lithosphere plates, volcanic eruptions or even bomb explosion.
- 16. How Are Volcanoes Made? Pressure builds up inside the Earth. This then affects the Earth’s crust, so that magma can sometimes erupt through it. The lava and ash that has erupted through the crust build up to form the classic volcano cone shape over time. This process is happening all the time!
- 17. Watch the video about volcanoes. • https://youtu.be/lAmqsMQG3RM
- 18. What’s It All Called? magma chamber eruption cloud crater conduit/main vent Secondary vent lava
- 19. Mark the parts of a volcano.
- 20. Types of Volcanoes active A volcano that erupts frequently and throws out ashes, gases, lava and rocks.- Etna and Stromboli in Italy, Kilauea in Hawaii dormant A volcano that has erupted and is quiet now. They don’t show signs of erupting in the near future, but may erupt again. Vesuvius in Italy, extinct A volcano that hasn’t erupted in the last 10 000 years, and isn’t expected to erupt again. Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania.
- 21. Where Are Most Volcanoes Located? Distribution of volcanoes The circum – pacific Belt: It encircles the pacific ocean. It is also known as Pacific “.Ring of fire” Most volcanoes are located in the red area, which is named “Ring of Fire”. Most of the volcanoes are located in the Andes of S.America and th Rockies of N.America Why do you think it is called that?
- 22. A second belt of volcanoes is found along the Mediterranean Sea. • It is called the Mid World Mountain Belt. • It mostly has dormant and extinct volcanoes.