Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP)
- 1. Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) Presentation by: Farman Ahmad ETP Engineer Nilar Pulp & Paper No. 59, U Shwe Bin Street, Industrial(1), Dagon Seikkan Township, Yangon, Myanmar. Tel: (95-1) 593 766,28,30,43 Fax: (95-1) 592 275 Email: farmankhan241@gmail.com +91 9058658402
- 2. What is an ETP ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant) is a process design for treating the industrial waste water for its reuse or safe disposal to the environment. ETP helps to make ecofriendly environment.
- 3. Influent: Influent is water that "flows in“ to ETP. This is the raw, untreated industrial waste water. Effluent: Effluent means to "flow out“ from ETP. This is the treated industrial wastewater. Effluent is defined by the United States Environmental Protection Agency as "wastewater - treated or untreated - that flows out of a treatment plant, sewer, or industrial outfall. Sludge: Solid part separated from waste water by ETP Thick, soft, wet mud or a similar viscous mixture of liquid and solid components, especially the product of an industrial or domestic waste water treatment plant.
- 4. To meet the Standards for emission or discharge of environmental pollutants from Industries set by the Government and avoid hefty penalties Why Need ETP?
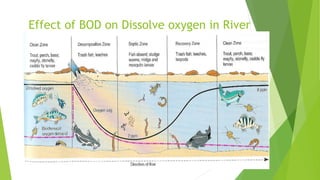
- 5. Hazards of wastewater? Wastewater is a big health issue, as it carries and transports a myriad of diseases and illnesses. It is believed that about 2.2 million people die each year (globally) from diarrhoeal disease. One child die on every 20 seconds due to water related disease (WHO, 2008). All ecosystems are connected and they all ultimately depend on water. This means careless wastewater discharge can have some serious ripple effect. If one part of the ecosystem chain is destroyed, it can upset its entire food chain. and whole nature become destroy.
- 6. Effect of BOD on Dissolve oxygen in River
- 7. Composition of ETP ETP Comprise four level of treatment and having four types of treatment. Level of Treatment Description Type of treatment Preliminary treatment Removal of large solid as rags, sticks, grits and grease etc. that may damaged equipment of ETP Physical Primary treatment Removal of floatable and settledable material such as suspended solid. Physical and chemical Secondary treatment Biodegradable organic material Biological Tertiary Treatment Removal of residual suspended solid, Dissolve solid and disinfection. Chemical, Physiochemical Solid Waste management Safe Disposal of solid waste Physical, Biological
- 8. Preliminary Treatment Purpose: Removal of floating and settleable materials such as suspended solids, organic matter and other inorganic solid. Preliminary treatment may be various type like as 1. Screening 2. Grit Chamber 3. Skimming Tank 4. Equalization Screening : This works like a watchman and cares the operation of ETP. Equalization : Flow rate, temperature, and contaminant concentrations varies widely. equalization helps in homogenization of all type of pollutants and equalized wastewater goes to downstream of ETP. Equalization needs 2 to 4 hour HRT and Air or mechanical mixing of waste water is must here to prevent deposition of solid and septicity.
- 9. Primary Treatment Primary treatment reduces the suspended solids and the B.O.D. of the wastewater. From the primary treatment tanks water is pumped to the secondary treatment system. Secondary treatment will further reduce the suspended solids and B.O.D. of the wastewater. Primary treatment may be different type such as- 1. Primary Clarifier 2. Primary sedimentation 3. DAF 4. Lamella Clarifier
- 10. Primary Clarifier Wastewater flow is slowed down and suspended solids settle to the bottom by gravity the material that settles is called sludge or biosolids Clear Supernant water is carry over to launder that go to Secondary treatment system for further treatment. Primary clarifier design in respect of Surface Loading Rate (SLR) and Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) Standard SLR for primary clarifier is 6.0 – 9.0 m3/m2/day for paper industry effluent and varied to effluent quality. Standard HRT for Primary clarifier is 4 -6 Hour for Paper industry effluent and varied to effluent quality.
- 12. Dissolve Air Flotation (DAF) Solid particles in liquid suspension become attached to microscopic air bubbles. Waste flow or a portion of clarified effluent is pressurized to 3.4 – 4.8 atm in the presence of sufficient air to approach saturation. When pressurized air-liquid mixture is released to atmospheric pressure, minute air bubbles are released from the solution. Agglomerate rise to the surface to join other particles and form a blanket that can be removed mechanically. Sludge flocs, suspended solids, oil globules are floated by the air bubbles. Air-solids mixture skimmed off from the surface Inorganic or heavy material collect from bottom that called rejected sludge. Clarified liquid removed from the middle A portion of the effluent recycled back to the pressure chamber.
- 13. Dissolve Air Flotation (DAF)
- 14. Secondary Treatment System Secondary treatment system reduces COD, BOD, TSS, Turbidity etc. Secondary treatment system is two type different type- Aerobic treatment system Aerobic treatment process take place in the presence of oxygen by Prokaryotes and eukaryotes microorganism, and produces CO2, Hydrogen, Energy and reproduction itself by microorganism. Anaerobic treatment system Anaerobic treatment process take place in the absence of oxygen by the methanogen microorganism and produces Methan gas as end product.
- 15. Aerobic Treatment system Aerobic Treatment system may be different type 1. Activated Sludge process system 2. Extended Aeration system 3. Conventional aeration system 4. Sequence batch reactor 5. MBBR (Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor) 6. MBR (Membrane Bio Reactor) 7. Trickling filter 8. Oxidation ditch 9. Many more
- 16. Activated Sludge Process System
- 17. Activated sludge Process System Basic Equation is that-
- 19. Aeration Tank
- 20. Aerobic treatment system Pollution reduction efficiency BOD : 70- 95% COD : 60 – 90% TSS : 30 – 60% This type of treatment is applicable upto 3000 mg/l COD concentration. We can discharge aerobically treated effluent directly if Environmental norm does not violate. To remove colour and dissolve solid from the effluent tertiary treatment system is required for further treatment.
- 21. Anaerobic Treatment System Anaerobic Treatment System may by different kind 1. UASB Reactor (Upflow anaerobic sludge Blanket Reactor) 2. CSTR Reactor (Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor) 3. ECSB Reactor (External Circulation Sludge Bio Reactor) 4. IC Reactor (Internal Circulation Reactor) 5. ULRD (Low Retention Digester) 6. Many More
- 23. Anaerobic Treatment System Anaerobic treatment system works over high organic COD and BOD concentration. Anaerobic treatment produces Methan gas that can be used in Boiler by result save fuel. Its reduces the carbon emission and Green house effect. Its reduces the 70 - 85% BOD and 60-75% COD. Anaerobically treated effluent goes to aerobic treatment for further treatment. We can not discharge anaerobically treated water directly.
- 25. Tertiary Treatment System Final or advanced treatment consists of removing the organic load left after secondary treatment for removal of nutrients from sewage and particularly to kill the pathogenic bacteria and raise the effluent quality before it is discharged to the receiving environment such as sea, river, lake, ground, etc., or to raise the treated water quality to such a level to make it suitable for intended reuse. Advanced treatment system is of different type – 1. Nutrient Removal 5. Membrane Process 2. Disinfection 6. Filtration 3. Nitrification & DE nitrification 7. Carbon adsorption 4. Ion Exchange 8. Chemical Precipitation
- 26. Solid waste Management Sources Primary sludge usually have strong odors Secondary sludge have high concentration of microorganism Goals of treatments are: Reduce odors Remove water reduce volume Decompose organic matter. Untreated sludge are about 97 percent water Settling can reduce about 92 to 96 percent of water.
- 27. Solid waste Managment Solid waste management is of different kind.- 1. Digestion Anaerobic treatment 2. Incineration 3. Wet Oxidation 4. Dewatering 5. Composting 6. Drying 7. Many More
- 28. Solid waste Management Solid waste classified into two categories- 1. Hazardous waste 2. Non Hazardous waste If solid waste comes under hazardous waste categories then waste will be disposed off as per hazardous waste disposal regulation. While non hazardous waste can be disposed off by scientific way.
- 29. Basic Diagram of ETP
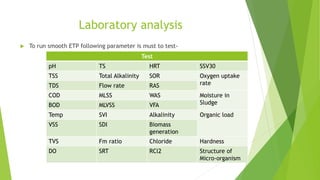
- 30. Laboratory analysis To run smooth ETP following parameter is must to test- Test pH TS HRT SSV30 TSS Total Alkalinity SOR Oxygen uptake rateTDS Flow rate RAS COD MLSS WAS Moisture in SludgeBOD MLVSS VFA Temp SVI Alkalinity Organic load VSS SDI Biomass generation TVS Fm ratio Chloride Hardness DO SRT RCl2 Structure of Micro-organism
- 31. Questions
- 32. Thank You