Emotional Intelligence Workshop Chandramowly
- 1. H R D Dimensions
- 2. H R D Dimensions
- 3. H R D Dimensions
- 4. What Is Emotional Intelligence? “The capacity for recognizing our own feelings and those of others, for motivating ourselves, for managing emotions well in ourselves and in our relationships.” Daniel Goleman (1995/1998) H R D Dimensions
- 5. Balance H R D Dimensions
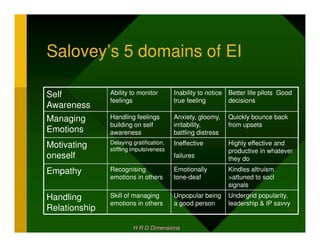
- 6. Salovey’s 5 domains of EI Self Ability to monitor Inability to notice Better life pilots Good feelings true feeling decisions Awareness Managing Handling feelings Anxiety, gloomy, Quickly bounce back building on self irritability, from upsets Emotions awareness battling distress Delaying gratification, Ineffective Highly effective and Motivating stiffling impulsiveness productive in whatever oneself failures they do Empathy Recognising Emotionally Kindles altruism emotions in others tone-deaf >attuned to socl signals Handling Skill of managing Unpopular being Undergrid popularity, emotions in others a good person leadership & IP savvy Relationship H R D Dimensions
- 7. The Five Parts of EI Empathy Managing 4 Self Relationships Motivation 5 3 1 2 Know what Manage you are your feeling feeling Self Awareness Self Regulation H R D Dimensions
- 8. LeDoux’s Research* Thalamus Visual Cortex Amygdala * Neuroscientist, Center for Neural Science at New York Fight or Flight response H R D Dimensions
- 9. Activity: Reading the Fuel Meter Importance Scale E F If each of your team member had a guage of importance you place on him/her, what would his/her indicator read? Write the name to on left and mark the level of ‘Importance’ you you give each person on the right Are you filling them up? Or are they running empty? H R D Dimensions
- 10. 1: My Ideal Self- Who do Practicing the I want to be? new behaviour Building new neural path- Ways through 2: My Real Self- to mastery Who am I? 5. Developing Trusting relationships That help, support and 4. Experimenting Encourage each My Strengths- With new behaviour, Step in the where my Ideal thoughts and feelings process & Real Self are Similar 3. My Learning Agenda- Building on My Gaps- my Strengths while where my Ideal reducing Gaps and Real Self differ 5 Discoveries H R D Dimensions
- 11. Developing leaders Personal Productivity Career Success Team Performance Motivation/Empowerment Difficult Clients / Teams Customer Satisfaction Creativity & Innovation Time Management Talent Retention Work/Life Balance Stress Reduction H R D Dimensions
- 12. E I Competencies Link to Career Architect Action Oriented Developing Direct Reports Organization Ability Approachability Drive For Results Patience Boss Relationships Fairness To Direct Reports Per Relationships Building Effective Teams Informing Perseverance Career Ambition Innovation Management Personal Learning Caring About Direct Reports Integrity And Trust Political Savvy Comfort Around Top Mgmt Interpersonal Savvy Priority Setting Command Skills Learning On The Fly Self Development Compassion Listening Self Knowledge Composure Managerial Courage Standing Alone Conflict Management Managing Diversity Strategic Agility Customer Focus Managing Vision & Purpose Time Management Dealing With Ambiguity Motivating Others Understanding Others Negotiating Work/Life Balance H R D Dimensions
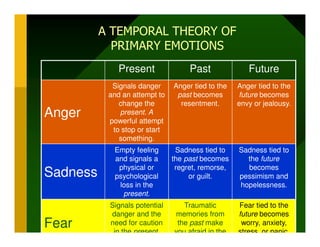
- 13. A TEMPORAL THEORY OF PRIMARY EMOTIONS Present Past Future Signals danger Anger tied to the Anger tied to the and an attempt to past becomes future becomes change the resentment. envy or jealousy. Anger present. A powerful attempt to stop or start something. Empty feeling Sadness tied to Sadness tied to and signals a the past becomes the future physical or regret, remorse, becomes Sadness psychological or guilt. pessimism and loss in the hopelessness. present. Signals potential Traumatic Fear tied to the danger and the memories from future becomes Fear need for caution the past make H R D Dimensions in the present. you afraid in the worry, anxiety, stress, or panic.
- 14. A TEMPORAL THEORY OF PRIMARY EMOTIONS Present Past Future Signals danger Anger tied to the Anger tied to the and an attempt to past becomes future becomes change the resentment. envy or jealousy. Anger present. A powerful attempt to stop or start something. Empty feeling Sadness tied to Sadness tied to and signals a the past becomes the future physical or regret, remorse, becomes Sadness psychological or guilt. pessimism and loss in the hopelessness. present. Signals potential Traumatic Fear tied to the danger and the memories from future becomes Fear need for caution the past make H R D Dimensions in the present. you afraid in the worry, anxiety, stress, or panic.
- 15. ABCDE approach Activating event Beliefs Consequences Source: Dr Albert Ellis - Rational Emotive Behaviour Therapy H R D Dimensions
- 16. ABC-DE Dispute • Evidence? • Alternatives? + Decatastrophise Effects H R D Dimensions
- 17. The 3Ps of Optimism Permanent: – Permanent vs temporary Pervasive: – Pervasive vs specific Personal: – Personal vs external H R D Dimensions