Energy and chemical change
- 1. 1 Everything Science www.everythingscience.co.za 12. Energy and chemical change Chemistry Grade 11
- 2. 2 Everything Science www.everythingscience.co.za Energy changes in chemical reactions When a reaction occurs, bonds in the reactants break and new bonds in the products form. These changes involve energy. When bonds break, energy is absorbed and when new bonds form, energy is released. The bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. It is the amount of energy (in kJ·mol−1 ) that is needed to break the chemical bond between two atoms. Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a chemical system for a given pressure and is given the symbol H.
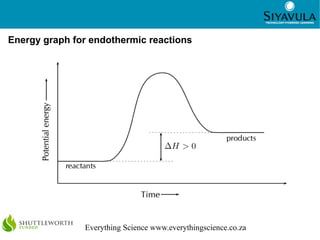
- 3. 3 Everything Science www.everythingscience.co.za Endothermic and exothermic reactions If the energy that is needed to break the bonds is less than the energy that is released when new bonds form, then the reaction is exothermic. The energy of the products is less than the energy of the reactants. An exothermic reaction is one that releases energy in the form of heat or light. Combustion reactions and respiration are both examples of exothermic reactions. If the energy that is needed to break the bonds is more than the energy that is released when new bonds form, then the reaction is endothermic. The energy of the products is greater than the energy of the reactants. An endothermic reaction is one that absorbs energy in the form of heat or light. Photosynthesis and the thermal decomposition of limestone are both examples of endothermic reactions.
- 4. 4 Everything Science www.everythingscience.co.za Heat of reaction The difference in energy between the reactants and the product is called the heat of reaction and has the symbol ∆H. ∆H is calculated using: ● In an endothermic reaction, ∆H is a positive number (greater than 0). ● In an exothermic reaction, ∆H will be negative (less than 0). Δ H=Eprod − Ereact Type of reaction Exothermic Endothermic Energy absorbed or released Released Absorbed Relative energy of reactants and products Energy of reactants greater than energy of products Energy of reactants less than energy of products Sign of ΔH Negative Positive
- 5. 5 Everything Science www.everythingscience.co.za Energy graph for exothermic reactions
- 6. 6 Everything Science www.everythingscience.co.za Energy graph for endothermic reactions
- 7. 7 Everything Science www.everythingscience.co.za Activation energy The activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that is needed to start a chemical reaction. The activated complex (or transition state) is the complex that exists as the bonds in the products are forming and the bonds in the reactants are breaking. This complex exists for a very short period of time and is found when the energy of the system is at its maximum. The two examples below show how the activated complex is drawn:
- 8. 8 Everything Science www.everythingscience.co.za Energy graph for exothermic reactions
- 9. 9 Everything Science www.everythingscience.co.za Energy graph for endothermic reactions
- 10. 10 Everything Science www.everythingscience.co.za For more practice see: www.everythingscience.co.za Shortcode: ESBQS