Essential Questions Charts
- 1. Essential Questions Charts Katie Mallette Fall 2011
- 2. Source: Galileo.org - Essential Questions Site Information Own Words What I Learned •Provide fundamental organizing •Essential questions allow for learners •Through this website, I gained a nice principles to guide development. to gain assistance in organization and introduction to the idea of E.Q. •Key Components assist them in completing tasks. •The key components are a guide of 1. Learn more about the world we •E.Q. contains specific components to understanding for this philosophy. live in. explain. •I found it interesting that E.Q. 2. Invite perspective 1. Questions arise from curiosity contains so many different ideas such 3. Answer essential questions since the beginning of history. as imagination, history, knowledge, 4. Explore what knowledge is 2. Questions can have different mystery, perspective, and 5. Poised at the boundary of the meanings and contexts. commitment. known and unknown. 3. Answering E.Q. allows people to •These ideas are often included in 6. Embedded in ideals of freedom, build in community and learn questioning, but not all at once. strength, and possibility to about their surroundings and permit people know. environment. 7. Engages the imagination in 4. E.Q. allows people to see significant ways. changes in knowledge. 5. E.Q. encourage exploration and mystery. 6. E.Q. can form from the ideas that people can make a difference. 7. Imagination is key in E.Q.
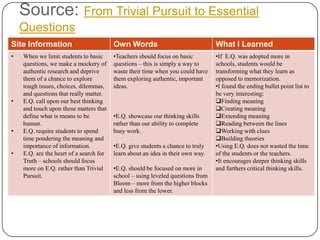
- 3. Source: From Trivial Pursuit to Essential Questions Site Information Own Words What I Learned • When we limit students to basic •Teachers should focus on basic •If E.Q. was adopted more in questions, we make a mockery of questions – this is simply a way to schools, students would be authentic research and deprive waste their time when you could have transforming what they learn as them of a chance to explore them exploring authentic, important opposed to memorization. tough issues, choices, dilemmas, ideas. •I found the ending bullet point list to and questions that really matter. be very interesting: • E.Q. call upon our best thinking Finding meaning and touch upon these matters that Creating meaning define what is means to be •E.Q. showcase our thinking skills Extending meaning human. rather than our ability to complete Reading between the lines • E.Q. require students to spend busy work. Working with clues time pondering the meaning and Building theories importance of information. •E.Q. give students a chance to truly •Using E.Q. does not wasted the time • E.Q. are the heart of a search for learn about an idea in their own way. of the students or the teachers. Truth – schools should focus •It encourages deeper thinking skills more on E.Q. rather than Trivial •E.Q. should be focused on more in and furthers critical thinking skills. Pursuit. school – using leveled questions from Bloom – more from the higher blocks and less from the lower.
- 4. Source: Framing Essential Questions Site Information Own Words What I Learned • E.Q. reside at the top of Bloom’s •E.Q. is not simply researching a •Through this source, I learned that Taxonomy – students “Evaluate”, topic, but using the more complex E.Q. strongly encourage critical “Synthesize”, or “Analyze”. level Bloom’s Taxonomy. thinking skills among students. • E.Q. spark our curiosity and •E.Q. make us want to learn and find •E.Q. is useful in all content areas, not sense of wonder. and understanding. just Math or Science. • Answers to E.Q. cannot be •E.Q. inspire students to create the •Strengthens the idea of using found, they must be invented and answers to their own questions, Bloom’s Taxonomy when planning may take a life time to find. despite the effort and time table. lessons, discussions, and projects for • E.Q. engage students in real life •E.Q. teach students to develop students. problem solving and stretch to critical thinking skills for future multidisciplinary investigations. dealings within many different content areas.
- 5. Source: Filling the Tool Box Site Information Own Words • A primary goal of education is to develop •Education teaches students how to be curios and ways to autonomous but interdependent thinkers. Students ask questions so they can be meaningful to the learning deserve frequent opportunities to shape and direct experience. classroom inquiry. •It is important to show students (at any age) that being • To fuel this inquiry, it is also essential that we curious it a positive aspect of learning. validate the importance of curiosity in the process of •Begin a unit with brainstorming about the topic – good learning. time to incorporate the K-W-L chart • Try starting a new unit by thinking of questions that What do I know could be asked about the topic (Students need to be What to I want to know taught to ask the right kind of questions.) What did I learn • There are 4 rules to brainstorming •Brainstorming has a process and students need to be • Questions need to be categorized (group the taught that process – they just do not know it. questions) •Brainstorming before a unit allows the students to • Questions add intrinsic motivation for finding become more interested in the topic since they came up answers since they come from the students. with the investigative questions. • Questions strategies can be added to these topics: •Several topics and content areas can benefit from Homework learning the appropriate ways to ask questions, Interview/Media brainstorm, and categorize. Book Reports •Assignments, tests, and projects also benefit from the Writing strategies as well. Arts Projects and Test Taking skills
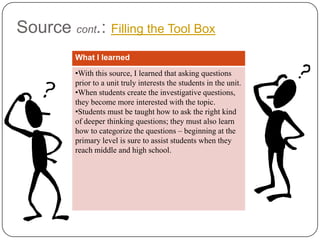
- 6. Source cont.: Filling the Tool Box What I learned •With this source, I learned that asking questions prior to a unit truly interests the students in the unit. •When students create the investigative questions, they become more interested with the topic. •Students must be taught how to ask the right kind of deeper thinking questions; they must also learn how to categorize the questions – beginning at the primary level is sure to assist students when they reach middle and high school.
- 7. Source: A Questioning Toolkit Site Information Own Words What I Learned • Questioning should begin as • Teaching the proper formation of • Within this source, I learned E.Q. early as Kindergarten so that questioning skills at an early age are helpful as early as kindergarten. It student can bring powerful allows students to be ready for high is never too early to teach students to questioning technologies and education levels. be curious. techniques with them to high • Again, teaching to question, school. brainstorm, and categorize helps • Most E.Q. are interdisciplinary in • E.Q. are not focused in one area. students from an early age and up. If nature; they cut across the lines They assist students in all areas in and these strategies are known, students created by school and scholars to out of school and help to define an are bound to be more determined, mark terrain of investigation of learning. focused, and successful. departments/disciplines. • E.Q. offer organizing focus for a •E.Q. help to build guidelines and unit. benchmarks for a new unit within a • Subsidiary Questions help us to content area. build answers to E.Q. • E.Q. and S.Q. help us to •S.Q. help to find the knowledge construct new knowledge. students are in search of within their E.Q.
- 8. Source: What Is an Essential Question? Site Information Own Words What I learned • Students have to think critically to •Students do not need to simple fact I found this source to be useful and answer an essential question – they questions; they need challenging, consistent with many of the other conduct research and create an evaluating questions. resources I have previously looked original answer. •The 7 qualities listed explain key at. It continues the idea of Provoke deep thought points of the Essential Question – establishing critical thinking and Solicit information each is key to this type of Q. provoking deeper thought. Results in an original answer •Students assist the teacher in this Conduct problem-related research learning process of E.Q. and vice I found this to be the first source Produce original ideas rather than versa – it is a joint learning which included information predetermined answers experience. regarding the Internet. I learned E.Q. May not have an answer •E.Q. assist in teaching students would be beneficial to teaching about Encourage critical thinking about credible and reliable Web reliable Web resources. •Students and teachers become resources. problem solvers together. •Student learn to research and create •E.Q. teach students how to use the their ideas from sources they can Internet without wasting time on trust. unproductive Web surfing. •Helps students to be more critical of Web resources and more discriminating about the information they use.
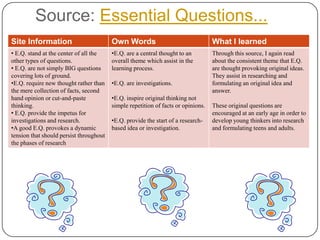
- 9. Source: Essential Questions... Site Information Own Words What I learned • E.Q. stand at the center of all the •E.Q. are a central thought to an Through this source, I again read other types of questions. overall theme which assist in the about the consistent theme that E.Q. • E.Q. are not simply BIG questions learning process. are thought provoking original ideas. covering lots of ground. They assist in researching and •E.Q. require new thought rather than •E.Q. are investigations. formulating an original idea and the mere collection of facts, second answer. hand opinion or cut-and-paste •E.Q. inspire original thinking not thinking. simple repetition of facts or opinions. These original questions are • E.Q. provide the impetus for encouraged at an early age in order to investigations and research. •E.Q. provide the start of a research- develop young thinkers into research •A good E.Q. provokes a dynamic based idea or investigation. and formulating teens and adults. tension that should persist throughout the phases of research
- 10. Final Summary on Essential Questions
- 11. Final Summary Essential Questions (E.Q.) are key to the learning experience. E.Q. assist students and teachers in the classroom and in life. E.Q. help with larger ideas and develop guidance within complex topics and/or units. When using E.Q. in the classroom, it is a good idea to match it up with the levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy. Students will be using the levels of Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation.
- 12. Sources From Blackboard: 1.http://www.galileo.org/tips/essential_questions.html 2.http://www.fno.org/feb01/pl.html 3.http://www.fno.org/sept96/questions.html 4.http://www.fno.org/toolbox.html 5.http://www.fno.org/nov97/toolkit.html Sources found on own: 1.http://questioning.org/mar05/essential.html 2.http://www.tnellen.com/alt/essential.html