Evolution part1
- 1. Diversity and Evolution SC.912.L.151 SC.912.L.15.10 SC.912.N.1.3 SC.912.N.2.1 SC.912.L.15.8
- 2. Origins of Life on Earth
- 3. Original Conditions on Primitive Earth to make life…. • Presence of liquid water • Moderate temperature range • Free oxygen in the atmosphere • Adequate sunlight • Absence of toxic substances in atmosphere • Absence of lethal radiation
- 4. Volcanoes Play a BIG Role • Water vapor (eventually condensed and fell as RAIN) • Methane • Hydrogen • Nitrogen • Ammonia • Carbon Dioxide (we now have oxygen b/c of photosynthetic bacteria) • Carbon Monoxide
- 5. Earth History • Evolution is studied using concepts about earth history. The earth is between 4.3 and 4.5 billion years old. • Approximately 3.9 billion years ago, the surface was likely cool enough for water vapor to condense and form oceans • Geological evidence suggests that cells similar to modern bacteria were common 3.8 billion years ago.
- 6. How did life on Earth begin? Until the 1700’s people believed that living things could come from nonliving substances, spontaneous generation.
- 7. Spontaneous generation: Pasteur’s experiment • Experiment: Pasteur filled a flask with broth with a long S shaped neck. He boiled it to kill all life. It was open and exposed to air, but anything in the air got stuck on the curves of the neck. • Conclusion: Spontaneous generation was disproved and biogenesis theory was substantiated. Contamination came from other microorganisms, not “air”. QUESTIONS • What was the hypothesis? What was the experimental group? The control group? The constants? The variable?
- 8. Theory of Chemical Evolution “Primordial Soup Theory” • Conditions on the early Earth were very different. • The atmosphere had no oxygen • Energy sources, such as lightning, volcanic activity, and ultraviolet sunlight (no ozone layer)
- 9. Chemical Evolution • Earth’s early atmosphere: HCN, CO2, CO, N, H, S, H2O • “Life arose from the oceans” • He believed that energy from lightning and the sun can spark chemical reactions to create AMINO ACIDS that made proteins.
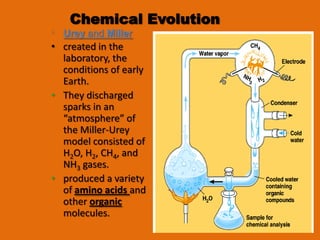
- 10. Chemical Evolution Urey and Miller • created in the laboratory, the conditions of early Earth. • They discharged sparks in an “atmosphere” of the Miller-Urey model consisted of H2O, H2, CH4, and NH3 gases. • produced a variety of amino acids and other organic molecules.
- 11. Chemical Evolution • Alternate sites proposed for the synthesis of organic molecules include • submerged volcanoes and deep-sea vents where hot water and minerals gush into the deep ocean.
- 12. Prokaryotes • Prokaryotes were the earliest organisms on Earth and evolved alone for 1.5 billion years. • two prokaryotic domains: Bacteria and Archaea
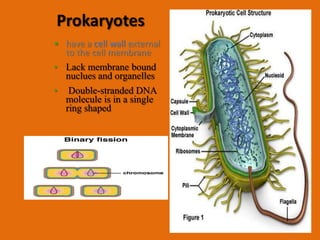
- 13. Prokaryotes • have a cell wall external to the cell membrane • Lack membrane bound nuclues and organelles • Double-stranded DNA molecule is in a single ring shaped
- 14. OXYGEN ATMOSPHERE The evidence of oxygen gas formation can be seen in rocks • Remember the atmosphere of early when layers of iron oxide on the Earth was made up of nitrogen, bottoms of oceans stopped carbon dioxide, water vapor, but no forming when oxygen appeared. free oxygen • Oxygen comes from photosynthesis when leaving oxygen gas. • About 2 billion years ago, the oxygen level in the atmosphere started to rise. Cyanobacteria created the oxygen in the atmosphere. • Aerobic metabolism, much more efficient than anaerobic, became possible. Question What are the reactants in photosynthesis? The products?
Editor's Notes
- Experimental group: Exposed for 1 year, no microorganismsControl Groups : Removed “S” curve and exposed it for 1 day and microorganisms grewConclusion: Spontaneous generation was disproved and biogenesis theory was substantiated. Contamination came from other microorganisms, not “air”.