Evolutionary process models se.ppt
- 1. Evolutionary Process Models Prepared By : Ankita V. Kalola (150013107004). Ashvini A. Bhadja (140010107005).
- 2. ü What you mean by Evolutionary model Evolutionary process models are iterative type models. Using these models the developer can develop increasingly more complete versions of the software. Following are the examples of Evolutionary Process Model. 1)The Prototyping paradigm. 2)The spiral model. 3)The concurrent development model.
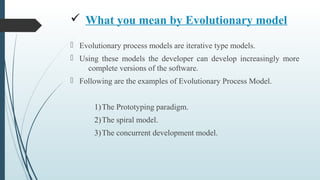
- 3. ü The Prototyping paradigm
- 4. Often, a customer defines a set of general objectives for software, but does not identify detailed requirements for functions and features. In this case Prototyping is best suited Prototyping can be used together with other models for elicitation of requirements The prototype can serve as “the first system.” Some prototypes are “Throw Away” while others also evolve and become part of the actual system. Both customers and developers like the prototyping paradigm. 1) Customer/End user gets a feel for the actual system 2) Developer get to build something immediately.
- 5. Ø Advantages: 1. Since in this methodology a working model of the system is provided, the users get a better understanding of the system being developed. 2. Errors can be detected much easier. 3. Quicker user feedback is available leading to better solution. 4. Missing functionality can be identified easily. Ø Disadvantages: 1. Software maintainability need more. 2. Software quality is not that much good as spiral model. 3. There is no guarantee of software quality in this type of model. 1.
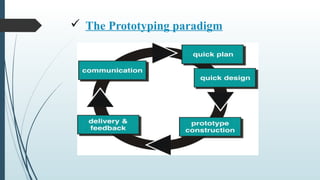
- 7. It was originally proposed by Barry Boehm, the spiral model is an evolutionary software process model that couples the iterative nature of prototyping with the controlled and systematic aspects of the waterfall model. It provides the potential for rapid development of increasingly more complete versions of the software. The spiral model can be adopted to apply throughout the entire lifecycle of the application from concept development to maintenance. The spiral model is divided into set of framework activities defined by software engineering team. The initial activity is shown from centre and developed in clockwise direction.
- 8. Ø Advantages: 1. In this approach, the project monitoring is easy and more effective compared to other models. 2. It reduces the number of risk in software development before they become serious problem. 3. Suitable for very high risk. 4. Schedule and cost is more realistic. 5. Risk management is in-built in the spiral model. 6. Changes can be accommodated in the later stages of development.
- 9. Ø Disadvantages: 1. If major risk is not discovered in early iteration of spiral, it may become a major risk in the later stages. 2. Each iteration around the spiral leads to more completed version of software. But it’s difficult to convince to the customer that the model is controllable. 3. Cost of this approach is usually high. 4. Not suitable for low risk management. 5. Rules and protocols must be followed very strictly to implement the approach.
- 10. ü The Concurrent Development Model
- 11. Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) software components, provide targeted functionality with well- defined interfaces that enable the component to be integrated into the software that is to be built. The component-based development model incorporates many of the characteristics of the spiral model. The modeling activity is one of the states and other activities like communication or construction can also be represented in an analogous manner.
- 12. Ø Advantages: 1. 2. The concurrent development model is applicable to all types of software development processes. 3. Gives very clear picture of current state of the project. 4. Easy to use and easy to understand. 5. Flexible and number of releases determined by the development team. 6. New functionalities as elicited by the client can be accommodated late in the project. 7. It has immediate feedback from testing.
- 13. Ø Disadvantages: 1. Since all the stages in the concurrent development model works concurrently, any change in the requirement from the client may halt the progress. This may happen due to dependent components among different stages and it lead to more longer development cycles as compared the planned cycles. 2. It requires excellent and updated communication between the team members. This may not be achieved all the time. 3. The SRS must be updated at regular intervals to reflect the changes.