Exp design water notes 2014
- 1. The Importance ofThe Importance of Science and ResearchScience and Research
- 2. The Importance of ScienceThe Importance of Science There have been many scientists that have made contributions to science that have changed our lives: Nicholas Copernicus = The Sun is at the center of our solar system. Sir Isaac Newton = Laws of motion and more Marie Curie = Created a theory of radioactivity Louis Pasteur = Bacteria is killed by heat and disinfectants. Rosalind Franklin = Discovered the structure of DNA
- 3. If Science was notIf Science was not Around…Around… • We would still think that the world was flat. • The light bulb wouldn’t have been invented. • We wouldn’t have landed on the Moon. • We wouldn’t have the cure for many diseases. • We wouldn’t have cell phones or computers. • We wouldn’t have tires, engines, heating and cooling for homes, or electricity.
- 4. If Science was not Around,If Science was not Around, What Else Would We notWhat Else Would We not Have?Have? Think about how research and science have affected your life. List five objects or ideas that are now available in our life-time that affect you. (Please do not include television, computers, or cell phones- think beyond these obvious choices.)
- 5. Scientific Method – StartScientific Method – Start with an Ideawith an Idea • Scientists start with an idea that can be researched to learn more about the topic. • Scientists then develop their findings into a problem for experimentation. • Your assignment: Topic: Water Filtration Research water filtration. Acquire enough information to develop a problem for experimental research. Create a hypothesis based on your research. Design an experiment to test your hypothesis.
- 6. Materials • Keep an accurate list of all materials and equipment used. Include: ▫ Correct name of materials and equipment ▫ Quantity, volume, and size of materials and equipment
- 7. Procedures • You will be following some steps as you work on your experimental design. • All of the steps are not completed in order- sometimes, you’ll need to cycle back to an earlier step. • You will write your own procedures specific to your experiment. • Be thorough and exact!
- 8. DataData •Collect data in your lab notebook. •A data table is an organized way to record information about your results. •Graphs are generated from the information in your data table.
- 9. Conclusion • Tell about what you learned. • Did your experiment go the way you thought it would? Was your hypothesis supported? Why or why not? • What would you do differently next time? Were there errors in your experiment? • What impact could your findings have on others?
- 10. Lab Write-Up •You will complete a lab report to share your results with others. •Take good notes as you experiment!!!
- 11. Why does it matter? Water FiltrationWater Filtration SystemsSystems
- 12. • Are you concerned about the quality of the water coming out of your faucet? • Do you ever really think about water quality? • According to the Environmental Protection Agency, more than 90% of the water supply in the United States is safe to drink.
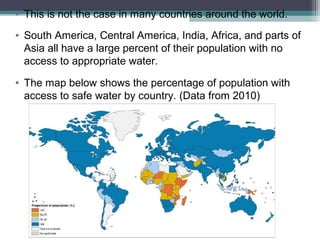
- 13. • This is not the case in many countries around the world. • South America, Central America, India, Africa, and parts of Asia all have a large percent of their population with no access to appropriate water. • The map below shows the percentage of population with access to safe water by country. (Data from 2010)
- 14. • What might cause water to be unsafe to drink? • Are there some countries that are more susceptible to pollution than others? • Why?
- 15. • How do you think a filter works? • On a very basic level, the process of filtration involves the flow of water through a granular bed of sand, or another suitable media, at a low speed. • The media retains most solid matter while permitting the water to pass. • The permeability of the material determines how quickly or efficiently the water will pass. Permeability is the capability of a porous rock or sediment to permit the flow of fluids through its pore spaces. • More porous materials have the ability to retain greater quantities of sediment due to their ability to hold water. What does a water filter do?
- 16. • Water’s viscosity allows it to pass quickly through the medium, removing solid particles from the solutions you will make in class. • Percolation is usually repeated through several layers to reduce the number of total suspended solids - TSS. • Water that is filtered several times will be less turbid than water filtered only once, although you may need a microscope to see the particles. What does a water filter do?
- 17. • TDS –Total dissolved solids refers to the total amount of all inorganic and organic substances – including minerals, salts, metals, cations or anions – that are dispersed within a volume of water. • Purified water has been mechanically filtered or processed to be cleaned for consumption. • The filters you will design and use in class will not make the water potable. What does a water filter do?
- 18. • What are some ways you can think of? • Which of these uses would require the water to have gone through some type of filtration? • Which use do you think requires the highest level of purity? • Human consumption • Washing clothes or dishes • Bathing • In a garden • Washing a car • For industrial use • For medical use Why do we need to filter water? Think about ways water is used on a daily basis.
- 19. • Reflect for a moment on what you have learned about physical properties. • Which of the physical properties are important to consider? • Physical properties include, but are not limited to: color, size, shape, texture, density, flexibility, conductivity, magnetism, opacity, mass, odor, melting point, boiling point, solubility, polarity, and state. What are the physical properties of a material that would make it useful as a filter?
- 20. • Your team will be working cooperatively, collaborating to design and test a water filtration system. • You will use your knowledge of science and math with your creativity to design a water filtration system that can clean contaminated water by removing particulate matter and color. It also needs to filter the water in a reasonable amount of time (efficiently). What now?
Editor's Notes
- Image courtesy Clip Art
- Image courtesy Clip Art
- Images courtesy of clip art
- Source: WHO World Map Gallery at http://gamapserver.who.int/mapLibrary/Files/Maps/ phe_Global_water_2010.png,
- Images courtesy of clip art
- Image courtesy of Ontario Ministry of the Environment and Earth (http://www.earthrangers.com/wildwire/take-action/filtered-water-please/)
- Image courtesy clip art
- Pause after students have read this slide. Facilitate a discussion about physical properties. If students are already sitting with their team members, allow about five minutes for them to begin discussing this topic to come up with a preliminary list of properties that are considered important.
- Image courtesy clip art