Expt 2 ecm
- 2. BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus 2.Electro chemical machining (ECM) OBJECTIVE: (E2) Study and demonstration of Electro Chemical Machining (ECM)
- 3. BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus ECM is one of the recent and most useful machining process. In this process, electrolysis method is used to remove the metal from the workpiece. It is best suited for the metals and alloys which are difficult to be machined by mechanical machining process. Introduction ECM
- 4. BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus Faraday’s law of electrolysis : The Weight of the substance produced during electrolysis process is directly proportional to 1. The current which passes 2. The length of time of process 3. The equivalent weight of the material Two dissimilar metals are in contact with an electrolyte and anode loses metal to cathode Principle
- 5. BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus ECM Parameters
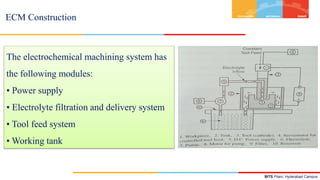
- 6. BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus The electrochemical machining system has the following modules: • Power supply • Electrolyte filtration and delivery system • Tool feed system • Working tank ECM Construction
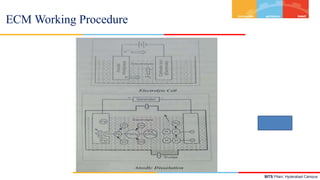
- 7. BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus The tool and the work piece are held close to each other with a very small gap (of 0.05 to 0.5mm) between them by using a servo motor. The electrolyte from the reservoir is pumped at high pressure and flows through the gap between the work piece and the tool at a velocity (of 30 to 60m/s). ECM Working Procedure
- 8. BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus A D.C voltage about 5-30 volts is applied between the tool and the work piece. Due to the applied voltage the current flows through the electrolyte with +ve charged ions and –ve charged ions. The +ve charged ions moves towards the tool (cathode) while –ve ions moves towards the work piece (anode). The electro chemical reaction takes place due to the flow of ions and it causes the removal of metal from the work piece. ECM Working Procedure
- 9. BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus Electrolysis: D.C voltage of about 5-30V is applied between the tool and work piece. So the current in water flows through the electrolyte (solution of NaCl) with charged ions. Many chemical reactions occurs at the cathode and the anode. ECM Working Procedure
- 10. BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus ECM Working Procedure
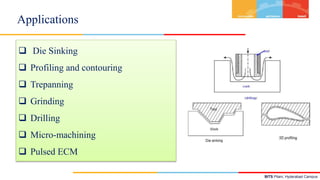
- 11. BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus Die Sinking Profiling and contouring Trepanning Grinding Drilling Micro-machining Pulsed ECM Applications
- 12. BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus Advantages ECM is well suited for the machining of complex two-dimensional shapes Delicate parts maybe made Difficult-to machine geometries Poorlymachinable materials may be processed Little or no toolwear Advantages and disadvantages
- 13. BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus Disadvantages o Initial tooling can be timely and costly Environmentally harmful by-products o Complicated tool design o Large power consumption