Facility Planning for Fire extinguisher
- 1. Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering Production Engineering Department 3rd Year 2nd Semester (2014/2015) Facility Planning Group Members ﺍﻻﺳﻢ ﺍﻟﻔﺼﻞ ﺍﻟﺮﻗﻢ ﺃﻣﺎﻥ ﺭﺷﺎﺩﻋﺜﻤﺎﻥ ﺭﺷﺎﺩ 3 59 ﻣﺤﻤﺪ ﺯﻛﻲ ﺍﻟﺪﻳﻦ ﻋﻼء ﻣﺎﺯﻥ5 90 ﻣﺤﻤﺪ ﺇﺳﻤﺎﻋﻴﻞ ﻣﺤﻤﺪﺇﺳﻤﺎﻋﻴﻞ 5 94 ﺃﺣﻤﺪ ﺣﺴﺎﻥ ﺃﺣﻤﺪ ﻣﺤﻤﻮﺩ6 117 ﺃﺣﻤﺪ ﻓﺮﺝ ﻣﺤﻤﺪ ﻣﺤﻤﻮﺩ6 124 ﺃﺣﻤﺪ ﻣﺤﻤﺪ ﻣﺤﻤﻮﺩ ﻣﺼﻄﻔﻰ7 138 Final Report Group ID : 20 Group project : Fire extinguisher
- 2. 1 | P a g e Facilities planning Report 1 Fire extinguisher Table of Contents Introduction ............................................................................................................................ 4 Task 1 ...................................................................................................................................... 4 Detailed design of product component .............................................................................. 4 1‐Body of control valve.............................................................................................................................................4 2‐Swivel.....................................................................................................................................................................4 3‐Locking nut (2) .......................................................................................................................................................5 4‐Swivel nut...............................................................................................................................................................5 5‐handle ....................................................................................................................................................................6 6‐Trigger....................................................................................................................................................................6 7‐Check valve spring .................................................................................................................................................7 8‐Check valve ............................................................................................................................................................7 9‐Locking nut (1) .......................................................................................................................................................8 10‐Powder tube ........................................................................................................................................................8 11‐Fire extinguisher body .........................................................................................................................................9 12‐ Fire extinguisher horn.........................................................................................................................................9 13‐Locking pin.........................................................................................................................................................10 14‐Pressure gauge...................................................................................................................................................10 Exploded assembly drawing .............................................................................................. 11 Parts List ............................................................................................................................ 12 Bill of material ................................................................................................................... 13 Route sheet ....................................................................................................................... 14 Part (1) Control valve ..............................................................................................................................................14 Part (5) Handle........................................................................................................................................................15 Part (6) Trigger ........................................................................................................................................................15 Part (8) Check valve.................................................................................................................................................16 Part (11) Fire extinguisher body..............................................................................................................................16 Assembly chart .................................................................................................................. 18 Operation Process chart .................................................................................................... 19 Task2 ..................................................................................................................................... 20 List of machines required to produce the product ........................................................... 20 Annual demand for part and its components ................................................................... 20
- 3. 2 | P a g e Annual demand for part..........................................................................................................................................20 Annual demand for the components......................................................................................................................20 Scrap estimate ................................................................................................................... 21 Worker efficiency and reliability of each machine ............................................................ 21 Number of machines required of each type ..................................................................... 22 1‐CNC (Machining) ..................................................................................................................................................23 2‐Power hacksaw (Cutting).....................................................................................................................................23 3‐Induction furnace (Melting).................................................................................................................................23 4‐Mechanical and hydraulic press (Drawing)..........................................................................................................23 5‐Automatic sandblast equipment (Finishing)........................................................................................................23 6‐Capstan lathe (Machining)...................................................................................................................................23 7‐Center lathe (Machining).....................................................................................................................................24 8‐Screw press (Drawing) .........................................................................................................................................24 Task3 ..................................................................................................................................... 24 Approximate number of employees in the production area ............................................ 24 Task4 ..................................................................................................................................... 25 Name of departments in the production area .................................................................. 25 Appropriate layout (cellular layout) .................................................................................. 25 Guide.......................................................................................................................................................................26 Final layout..............................................................................................................................................................27 Material flow diagram within the area ............................................................................. 28 The production area layout ............................................................................................... 29 Labels ......................................................................................................................................................................30 The required production area ........................................................................................... 30 Task 5 .................................................................................................................................... 30 Employee parking .............................................................................................................. 30 Food service ...................................................................................................................... 32 Locker rooms ..................................................................................................................... 32 Layout ................................................................................................................................ 33 For workers who need to change their clothes ......................................................................................................33 For workers who don't need to change their clothes.............................................................................................34 Health Services .................................................................................................................. 34 Restroom ........................................................................................................................... 34 Final layout ........................................................................................................................ 36 Task 6 .................................................................................................................................... 37
- 4. 3 | P a g e First from raw material or bought parts storage to the plant ........................................... 37 List of raw material and parts needed....................................................................................................................37 List of bought parts needed....................................................................................................................................37 Second flow of product parts in the plant ......................................................................... 39 In each department: ...............................................................................................................................................39 Between the departments:.....................................................................................................................................39 Third flow of final product from the plant to the warehouse and inside it ....................... 40
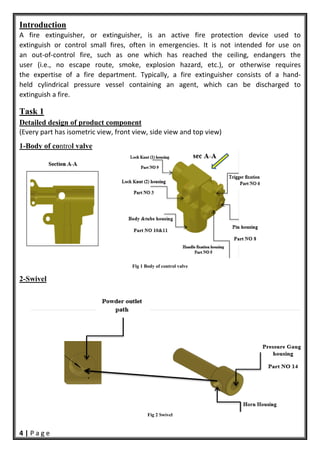
- 5. 4 | P a g e Introduction A fire extinguisher, or extinguisher, is an active fire protection device used to extinguish or control small fires, often in emergencies. It is not intended for use on an out‐of‐control fire, such as one which has reached the ceiling, endangers the user (i.e., no escape route, smoke, explosion hazard, etc.), or otherwise requires the expertise of a fire department. Typically, a fire extinguisher consists of a hand‐ held cylindrical pressure vessel containing an agent, which can be discharged to extinguish a fire. Task 1 Detailed design of product component (Every part has isometric view, front view, side view and top view) 1-Body of control valve Fig 1 Body of control valve 2-Swivel Fig 2 Swivel
- 6. 5 | P a g e 3-Locking nut (2) Fig 3 Locking nut 2 4-Swivel nut Fig 4 Swivel nut
- 7. 6 | P a g e 5-handle Fig 5 handle 6-Trigger Fig 6 Trigger
- 8. 7 | P a g e 7-Check valve spring Fig 7 Check valve spring 8-Check valve Fig 8 Check valve
- 9. 8 | P a g e 9-Locking nut (1) Fig 9 Locking nut (1) 10-Powder tube Fig 9 Powder tube
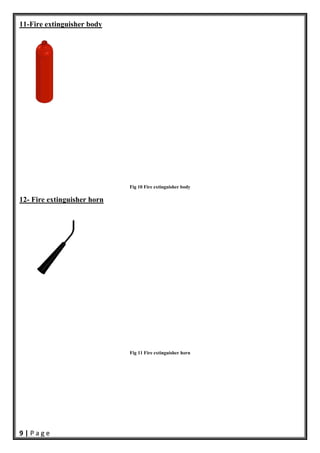
- 10. 9 | P a g e 11-Fire extinguisher body Fig 10 Fire extinguisher body 12- Fire extinguisher horn Fig 11 Fire extinguisher horn
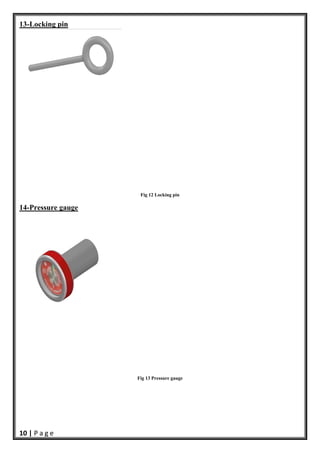
- 11. 10 | P a g e 13-Locking pin Fig 12 Locking pin 14-Pressure gauge Fig 13 Pressure gauge
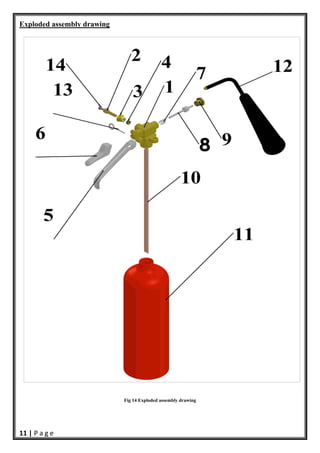
- 12. 11 | P a g e Exploded assembly drawing Fig 14 Exploded assembly drawing Part Number PART NAME 1 Body of control valve 2 Swivel 3 locking Knut (2) 4 swivel Knut 5 Handle 6 Trigger 7 Check valve spring 8 Check valve 9 locking Knut (1) 10 powder tube 11 fire extinguisher body 12 fire extinguisher horn 13 locking pin 14 pressure gauge
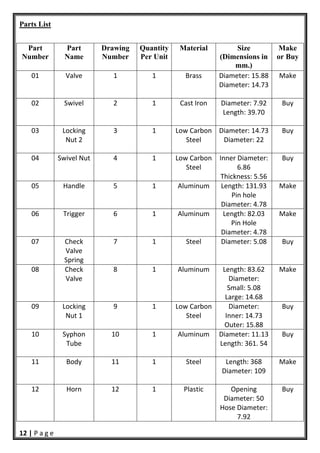
- 13. 12 | P a g e Parts List Part Number Part Name Drawing Number Quantity Per Unit Material Size (Dimensions in mm.) Make or Buy 01 Valve 1 1 Brass Diameter: 15.88 Diameter: 14.73 Make 02 Swivel 2 1 Cast Iron Diameter: 7.92 Length: 39.70 Buy 03 Locking Nut 2 3 1 Low Carbon Steel Diameter: 14.73 Diameter: 22 Buy 04 Swivel Nut 4 1 Low Carbon Steel Inner Diameter: 6.86 Thickness: 5.56 Buy 05 Handle 5 1 Aluminum Length: 131.93 Pin hole Diameter: 4.78 Make 06 Trigger 6 1 Aluminum Length: 82.03 Pin Hole Diameter: 4.78 Make 07 Check Valve Spring 7 1 Steel Diameter: 5.08 Buy 08 Check Valve 8 1 Aluminum Length: 83.62 Diameter: Small: 5.08 Large: 14.68 Make 09 Locking Nut 1 9 1 Low Carbon Steel Diameter: Inner: 14.73 Outer: 15.88 Buy 10 Syphon Tube 10 1 Aluminum Diameter: 11.13 Length: 361. 54 Buy 11 Body 11 1 Steel Length: 368 Diameter: 109 Make 12 Horn 12 1 Plastic Opening Diameter: 50 Hose Diameter: 7.92 Buy
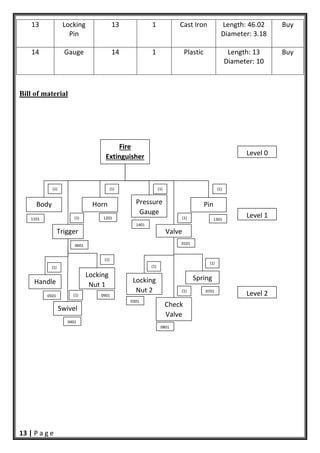
- 14. 13 | P a g e 13 Locking Pin 13 1 Cast Iron Length: 46.02 Diameter: 3.18 Buy 14 Gauge 14 1 Plastic Length: 13 Diameter: 10 Buy Bill of material Pin Spring Fire Extinguisher Body Handle Locking Nut 2 Check Valve Swivel Valve Pressure Gauge Locking Nut 1 Horn Trigger Level 0 Level 1 Level 2 (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) 0901 0401 0501 0301 0801 0701 1101 0601 0101 1201 1401 1301
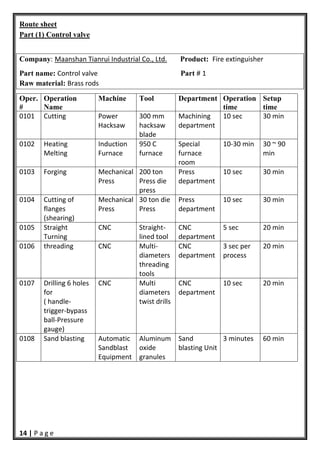
- 15. 14 | P a g e Route sheet Part (1) Control valve Company: Maanshan Tianrui Industrial Co., Ltd. Product: Fire extinguisher Part name: Control valve Part # 1 Raw material: Brass rods Oper. # Operation Name Machine Tool Department Operation time Setup time 0101 Cutting Power Hacksaw 300 mm hacksaw blade Machining department 10 sec 30 min 0102 Heating Melting Induction Furnace 950 C furnace Special furnace room 10‐30 min 30 ~ 90 min 0103 Forging Mechanical Press 200 ton Press die press Press department 10 sec 30 min 0104 Cutting of flanges (shearing) Mechanical Press 30 ton die Press Press department 10 sec 30 min 0105 Straight Turning CNC Straight‐ lined tool CNC department 5 sec 20 min 0106 threading CNC Multi‐ diameters threading tools CNC department 3 sec per process 20 min 0107 Drilling 6 holes for ( handle‐ trigger‐bypass ball‐Pressure gauge) CNC Multi diameters twist drills CNC department 10 sec 20 min 0108 Sand blasting Automatic Sandblast Equipment Aluminum oxide granules Sand blasting Unit 3 minutes 60 min
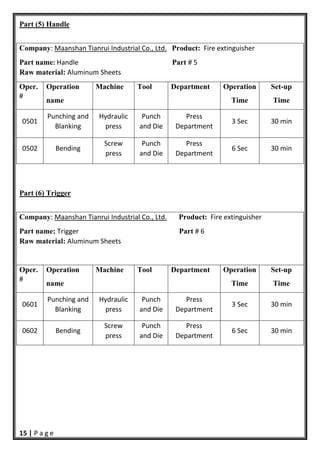
- 16. 15 | P a g e Part (5) Handle Company: Maanshan Tianrui Industrial Co., Ltd. Product: Fire extinguisher Part name: Handle Part # 5 Raw material: Aluminum Sheets Oper. # Operation name Machine Tool Department Operation Time Set-up Time 0501 Punching and Blanking Hydraulic press Punch and Die Press Department 3 Sec 30 min 0502 Bending Screw press Punch and Die Press Department 6 Sec 30 min Part (6) Trigger Company: Maanshan Tianrui Industrial Co., Ltd. Product: Fire extinguisher Part name: Trigger Part # 6 Raw material: Aluminum Sheets Oper. # Operation name Machine Tool Department Operation Time Set-up Time 0601 Punching and Blanking Hydraulic press Punch and Die Press Department 3 Sec 30 min 0602 Bending Screw press Punch and Die Press Department 6 Sec 30 min
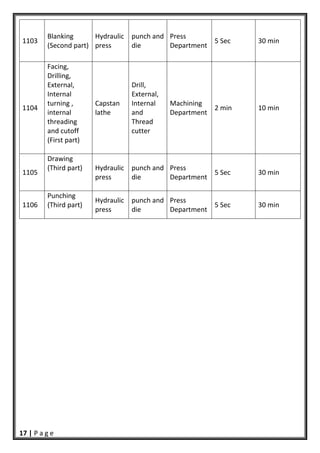
- 17. 16 | P a g e Part (8) Check valve Company: Maanshan Tianrui Industrial Co., Ltd. Product: Fire extinguisher Part name: Check valve Part # 8 Raw material: Aluminum Oper. # Operation name Machine Tool Department Operation time Setup time 0801 Facing Capstan Lathe spot facing tool Machining department 5 sec 10 min 0802 Straight turning (multi Sections) (5.08 &14.68 mm diameters) Capstan Lathe Straight‐ lined tool Machining department 2 min 10 min 0803 Cutoff Capstan Lathe 83.62 mm cut off Machining department 5 sec 10 min 0804 Straight turning (5.08 mm diameter) Center lathe Straight‐ lined tool Machining department 2 min 1 min Part (11) Fire extinguisher body Company: Maanshan Tianrui Industrial Co., Ltd. Product: Fire extinguisher Part name: Body Part # 11 Raw material: Steel Blanks Oper. # Operation name Machine Tool Department Operation time Set-up Time 1101 Drawing (Second part) Hydraulic press punch and die (109.72 mm) diameter Press Department 15 Sec 30 min 1102 Trimming (Second part) Hydraulic press punch and die Press Department 5 Sec 30 min
- 18. 17 | P a g e 1103 Blanking (Second part) Hydraulic press punch and die Press Department 5 Sec 30 min 1104 Facing, Drilling, External, Internal turning , internal threading and cutoff (First part) Capstan lathe Drill, External, Internal and Thread cutter Machining Department 2 min 10 min 1105 Drawing (Third part) Hydraulic press punch and die Press Department 5 Sec 30 min 1106 Punching (Third part) Hydraulic press punch and die Press Department 5 Sec 30 min
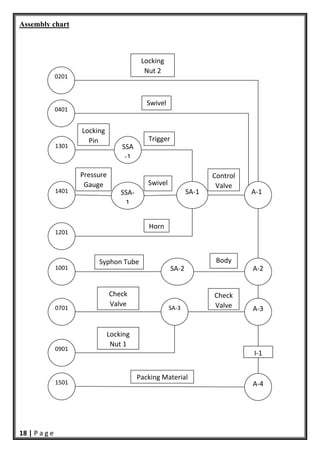
- 19. 18 | P a g e SSA‐ 1 SA‐2 SA‐1 0201 A‐3 A‐2 SA‐3 A‐1 A‐4 1501 0701 0901 1001 1201 1401 0401 Control Valve I‐1 Packing Material Check Valve Swivel Locking Nut 2 Body Syphon Tube Swivel Pressure Gauge Horn SSA ‐1 1301 Locking Pin Trigger Check Valve Locking Nut 1 Assembly chart
- 20. 19 | P a g e Operation Process chart
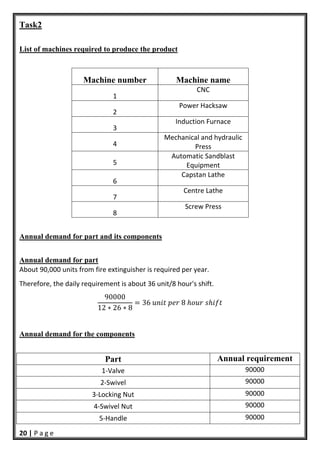
- 21. 20 | P a g e Task2 List of machines required to produce the product Machine number Machine name 1 CNC 2 Power Hacksaw 3 Induction Furnace 4 Mechanical and hydraulic Press 5 Automatic Sandblast Equipment 6 Capstan Lathe 7 Centre Lathe 8 Screw Press Annual demand for part and its components Annual demand for part About 90,000 units from fire extinguisher is required per year. Therefore, the daily requirement is about 36 unit/8 hour's shift. 90000 12 ∗ 26 ∗ 8 36 8 Annual demand for the components Part Annual requirement 1‐Valve 90000 2‐Swivel 90000 3‐Locking Nut 90000 4‐Swivel Nut 90000 5‐Handle 90000
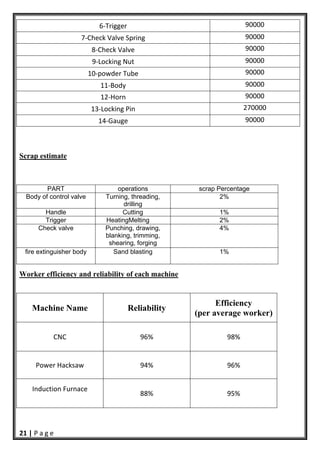
- 22. 21 | P a g e 6‐Trigger 90000 7‐Check Valve Spring 90000 8‐Check Valve 90000 9‐Locking Nut 90000 10‐powder Tube 90000 11‐Body 90000 12‐Horn 90000 13‐Locking Pin 270000 14‐Gauge 90000 Scrap estimate Worker efficiency and reliability of each machine Machine Name Reliability Efficiency (per average worker) CNC 96% 98% Power Hacksaw 94% 96% Induction Furnace 88% 95% PART operations scrap Percentage Body of control valve Turning, threading, drilling 2% Handle Cutting 1% Trigger HeatingMelting 2% Check valve Punching, drawing, blanking, trimming, shearing, forging 4% fire extinguisher body Sand blasting 1%
- 23. 22 | P a g e Mechanical and Hydraulic Press 98% 97% Automatic Sandblast Equipment 94% 95% Capstan Lathe 98% 96% Center lathe 99% 96% Screw press 99% 98% Number of machines required of each type Number of units to be processed (Q) = Where P: percentage of scrap Machine Fraction (F) = Where F: Number of machine required per unit time Q: Number of units to be processed H: Amount of time available E: Worker efficiency R: Machine reliability S: Standard time per unit product
- 24. 23 | P a g e 1-CNC (Machining) Q = . =36.73 F = ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ . ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ = 0.066 =1 2-Power hacksaw (Cutting) Q = . =36.73 F = ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ . ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ = 0.076 = 1 3-Induction furnace (Melting) Q = . =36.73 F = ∗ ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ . ∗ . . ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ = 1.83 = 2 4-Mechanical and hydraulic press (Drawing) Q = . =73.11 F = ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ . ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ = 0.09 = 1 5-Automatic sandblast equipment (Finishing) Q = . =146.93 F = ∗ ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ . ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ = 1.15 = 2 6-Capstan lathe (Machining) Q = . =36.73
- 25. 24 | P a g e F = ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ . ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ = 0.04 = 1 7-Center lathe (Machining) Q = . = 36.73 F = ∗ ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ . ∗ . ∗ ∗ = 0.16 = 1 8-Screw press (Drawing) Q = . =75 F = ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ . ∗ . ∗ ∗ ∗ = 0.08 = 1 Task3 Approximate number of employees in the production area Machine number Machine name No of workers 1 CNC 2 2 Power Hacksaw 2 3 Induction Furnace 3 X 2 = 6 4 Mechanical and hydraulic Press 3 5 Automatic Sandblast Equipment 2 X 2 = 4 6 Capstan Lathe 3 7 Centre Lathe 3 8 Screw Press 3 Assembly number of workers = 10 2 2 6 3 4 3 3 3 10 36 .
- 26. 25 | P a g e We have another production area with the same layout, number of workers = 36 worker. For two production areas cleaners, number of workers = 10 worker. Security, number of workers = 10 worker. Administrative Officer = 20 worker. Cafeteria, number of workers = 8 workers. Store, number of workers = 10 workers. Number of engineers = 10 engineer. Total number of workers = 36+36+10+10+20+8+10+10=140 worker. Task4 Name of departments in the production area Department Symbol Machining department A Mechanical Press' department B Induction Furnace Room C Automatic Sandblast Equipment room D CNC Machines E Forging department F Assembly Process G Appropriate layout (cellular layout) We choose cellular layout because of cellular manufacturing is suitable for our product because of variety of fire extinguisher volumes.
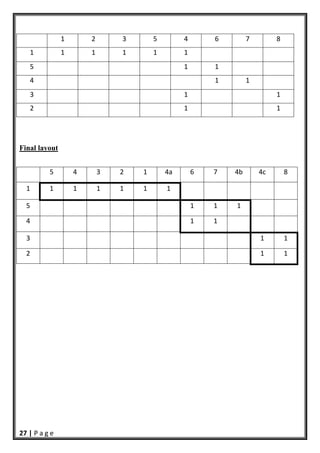
- 27. 26 | P a g e Guide Machine number Machine name Part number Part name 1 CNC 1 Control Valve 2 Power Hacksaw 2 Handle 3 Induction Furnace 3 Trigger 4 Mechanical and hydraulic Press 4 Check valve 5 Automatic Sandblast Equipment 5 Fire extinguish body 6 Capstan Lathe 7 Centre Lathe 8 Screw Press Machine number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Sum 1 1 1 1 1 1 5 2 1 1 2 3 1 1 2 4 1 1 2 5 1 1 2 sum 1 1 1 4 1 2 1 2 7 5 3 2 1 8 6 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 5 1 1 4 1 1 3 1 1 2 1 1 PartNumber
- 28. 27 | P a g e 1 2 3 5 4 6 7 8 1 1 1 1 1 1 5 1 1 4 1 1 3 1 1 2 1 1 Final layout 5 4 3 2 1 4a 6 7 4b 4c 8 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 5 1 1 1 4 1 1 3 1 1 2 1 1
- 29. 28 | P a g e Material flow diagram within the area
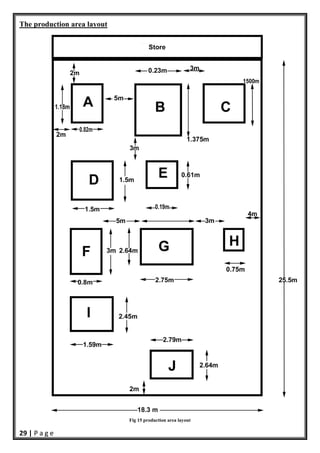
- 30. 29 | P a g e The production area layout Fig 15 production area layout
- 31. 30 | P a g e Labels Letter name A Hacksaw B Capstan lathe C Induction Furnace D Induction Furnace E Centre lathe F Sandblast unit (2) G Hydraulic press H Screw press I CNC J Hydraulic press The required production area 25.445 ∗ 17.55 446.55975 ~ 450 Task 5 Employee parking Cars Number= 140/1.25= 112 cars 1. Standard cars= 112*.55= 62 cars PW= 6’ W= 45’3’’ 2. Compact cars+ 112*.40= 45 cars PW= 5’40’’ W= 36’8’’ 3. Handicapped cars= 112*.05= 6 cars θ = 45˚ Y= 16*cos(45)= 11’19’’ Width= 160’ (Assumption) Total depth= (1*36’8’’) + (2*45’3’’)= 127’ Row 1: No. of spaces = (160‐11.31)/5.66= 26 spaces for compact cars Row 2:
- 32. 31 | P a g e No. of spaces = (160‐11.31‐15‐15)/5.66= 20 spaces (but 19 just 19 spaces are needed) Row 3: No. of spaces = (160‐11.31‐15‐15)/ 6= 19 spaces for standard cars Row 4: No. of spaces = (160‐11.31‐15‐15)/6= 19 spaces for standard cars Row 5: No. of spaces = (16011.31‐‐15‐15)/6= 19 spaces for standard cars Row 6: Total space= 160‐11.31=148.69’ Actual space = 5 standard cars + 6 HC= (5*6) + (6 *12) = 102’ < 148.69’ Fig 26 production area layout 127 160 26 Compact 19 Compact 19 Standard 5 Standard Cars + 19 Standard 15’ 26 19 Standard
- 33. 32 | P a g e Food service 140 workers will require 140 vending machines and a cafeteria 1 Vending Machine = 1 square feet Vending Machines Area = 140 square feet Cafeteria Area= 12 x 140 = 1680 square feet Total Area = 1680 + 140 = 1820 square feet = 169 m2 Locker rooms According to reference "Facilities Planning ‐Tompkins ‐ 3rd Edition" For workers who need to change their clothes Location for storage of personal belongings should be provided between the employee entrance and work area. In our case, we have 120 employees that need to change their clothes Number of workers in onr ptoduction line 2 2 6 3 4 3 3 3 10 36 worker. We have another production line with the same layout, number of workers = 36 worker. For two production areas cleaners, number of workers = 10 worker. Security, number of workers = 10 worker. Cafeteria, number of workers = 8 workers. Store, number of workers = 10 workers. Number of engineers = 10 engineer. Total number of workers = 36+36+10+10+8+10+10=120 worker. For workers who don't need to change their clothes They typically store lunches, briefcases, and purses at their place of work. Their storage location may be located in an adjacent to the employee entrance. In our case, we have administrative Officer = 20 worker. Common rules Locker rooms are provided for each sex even if clothes changing is not required. Each employee should be assigned a locker. For planning purposes, 6 should be allocated for each person using the locker room. If toilet facilities are to be included, they must be physically separated from the locker room area should lunches be stored in the lockers.
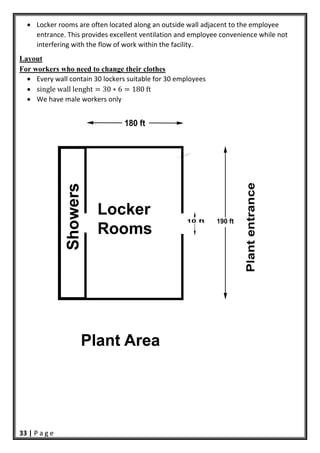
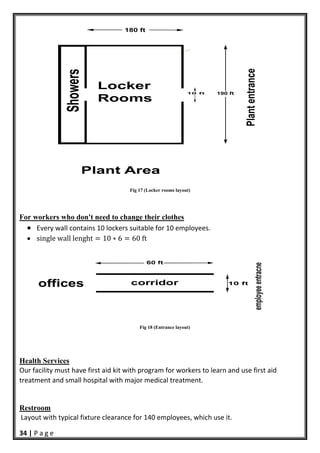
- 34. 33 | P a g e Locker rooms are often located along an outside wall adjacent to the employee entrance. This provides excellent ventilation and employee convenience while not interfering with the flow of work within the facility. Layout For workers who need to change their clothes Every wall contain 30 lockers suitable for 30 employees single wall lenght 30 ∗ 6 180 ft We have male workers only
- 35. 34 | P a g e Fig 17 (Locker rooms layout) For workers who don't need to change their clothes Every wall contains 10 lockers suitable for 10 employees. single wall lenght 10 ∗ 6 60 ft Fig 18 (Entrance layout) Health Services Our facility must have first aid kit with program for workers to learn and use first aid treatment and small hospital with major medical treatment. Restroom Layout with typical fixture clearance for 140 employees, which use it.
- 36. 35 | P a g e Fig 19 (Restroom layout)
- 37. 36 | P a g e Final layout
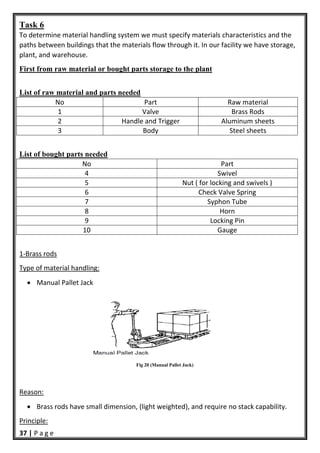
- 38. 37 | P a g e Task 6 To determine material handling system we must specify materials characteristics and the paths between buildings that the materials flow through it. In our facility we have storage, plant, and warehouse. First from raw material or bought parts storage to the plant List of raw material and parts needed No Part Raw material 1 Valve Brass Rods 2 Handle and Trigger Aluminum sheets 3 Body Steel sheets List of bought parts needed No Part 4 Swivel 5 Nut ( for locking and swivels ) 6 Check Valve Spring 7 Syphon Tube 8 Horn 9 Locking Pin 10 Gauge 1‐Brass rods Type of material handling: Manual Pallet Jack Fig 20 (Manual Pallet Jack) Reason: Brass rods have small dimension, (light weighted), and require no stack capability. Principle:
- 39. 38 | P a g e Ergonomic Principle (Fitting the job to the abilities of the worker reducing the weight of a load that the worker carries. 2.3 Aluminum and steel sheets (for Handle, Trigger, and body) Type of material handling: Forklift. Fig 21 (Fork lift) Reason: variable paths, with no restrictions on the area covered by the movement Insufficient (or intermittent) flow volume such that the use of a conveyor cannot be justified. Principle: Unit Load Principle( A unit load is one that can be moved or stored as a single entity at one time, regardless of the number of items in that load). For parts 4~10: Type of material handling: Wheel Handed Truck Fig 22 (Wheel Handed Truck) Reason: • Provide more flexibility in movement than conveyors and cranes.
- 40. 39 | P a g e • Move materials over variable (horizontal) paths with no restrictions on the area covered (i.e., unrestricted area). Principle: Standardization Principle(Less variety and customization in the methods and equipment employed). Second flow of product parts in the plant In each department: Conveyors. Since we need to transport a large number of products through a short distance from a machine to the other. Fig 23 (Conveyors) Between the departments: We use different types due to different reasons. Fork lift. Is used to transfer the heavier parts (Extinguisher Body) and the large number of parts for large distances to the assembling station. Fig 24 (Fork lift) Manual Hand Trucks.
- 41. 40 | P a g e As the “Shelf Economy Wire Cart” can also be used for the transportation of the less number of parts through the shorter distances. Fig 25 (Manual Hand Truck) Third flow of final product from the plant to the warehouse and inside it Product which will be handling is the final product (Fire extinguisher). The methods used and available:‐ Automatic Guided Vehicles. Fig 26 (Automatic Guided Vehicles) Reason:‐ 1‐Easy to use it for transport products inside the store and between the rows. 2‐Products will be heavy so use AGV. 3‐good for finish work quickly and high safety. 4‐Safe time. Principle:
- 42. 41 | P a g e Ergonomic Principle (Fitting the job to the abilities of the worker reducing the weight of a load that the worker carries. Fork Lift. Fig 27 (Fork lift) Reason: Variable paths, with no restrictions on the area covered by the movement Insufficient (or intermittent) flow volume such that the use of a conveyor cannot be justified. Principle: Unit Load Principle( A unit load is one that can be moved or stored as a single entity at one time, regardless of the number of items in that load).