Family apiaceae
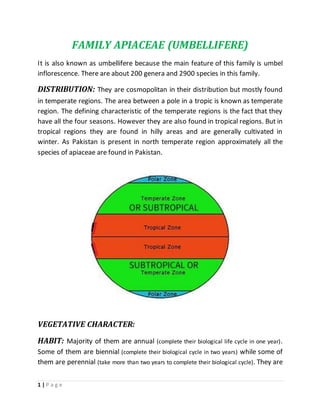
- 1. 1 | P a g e FAMILY APIACEAE (UMBELLIFERE) It is also known as umbellifere because the main feature of this family is umbel inflorescence. There are about 200 genera and 2900 species in this family. DISTRIBUTION: They are cosmopolitan in their distribution but mostly found in temperate regions. The area between a pole in a tropic is known as temperate region. The defining characteristic of the temperate regions is the fact that they have all the four seasons. However they are also found in tropical regions. But in tropical regions they are found in hilly areas and are generally cultivated in winter. As Pakistan is present in north temperate region approximately all the species of apiaceae are found in Pakistan. VEGETATIVE CHARACTER: HABIT: Majority of them are annual (complete their biological life cycle in one year). Some of them are biennial (complete their biological cycle in two years) while some of them are perennial (take more than two years to complete their biological cycle). They are
- 2. 2 | P a g e generally herbs but sometime shrubs and under shrubs are also found. Under shrubs are dwarf shrubs which are woody at the base. Root: They have Tap and branched root. Daucus carota (carrot) is its typical example. Stem: stem is erect, rarely climbing, and herbaceous; nodes are swollen, usually fistular. Fistular is the stem which has hollow internodes. Leaf: They have alternate leaf. The leaf is extipulate (no stipule). Much dissected (contain many partitions). Rarely opposite as in Apiastrum i.e. Apiastrum angustifolium (mock parsley). FLORAL CHARACTERS: INFLORESCENCE: They have umbel inflorescence. The umbel may be simple as in Hydrocotyle (water pennywort) or it may be compound as in coriandrum sativum (coriander). In compound umbel an involucre of bract is present at the top of the main axis from where the umbel arises. At the base of each umbel involucel of bract is found and at the base of each flower bract is found.
- 3. 3 | P a g e FLOWER: Flower is hermaphrodite (bisexual). Sometime unisexual. The flower is small, actinomorphic (having radial symmetery), epigynous, pentamerous, pedicellate, bracteate, complete. CALYX: The calyx consist of 5 sepals. Which are very minute and fused. In some cases the calyx is absent i.e. foeniculum vulgare (aniseed or saunf). CORROLA: The corrola consist of 5 petals which are free. The petal is bifid (divided into two parts) as in coriandrum sativum. ANDROECIUM: Androecium consist of 5 stamens alternating with petals. They are free. Anther is bilobed which means having two lobes. Anthers are introse means facing inside. They may be basifixed (fixed to the stalk at base) or dorsifixed (fixed to the stalk at dorsal side).
- 4. 4 | P a g e GYNOECIUM: The gynoecium is bicarpellary. It is syncarpous (carpels are united). The ovary is epigynous (inferior) and bilocular (consist of two locules). Each loculus have single pendulous ovule (hanged ovule like a pendulum). Placentation is axile (ovule is present at the tip of placenta). FRUIT: Fruit is generally cremocarp which splits into two mericarp each containing a seed. SEED: The seed is endospermic. POLLINATION: Insects pollinating plants. FLORAL FORMULA: ⊕ k (5), C5, A5, G(2) FLORAL DIAGRAM:
- 5. 5 | P a g e ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE: SOURCE OF FOOD: Carrots (Daucus carota), celery (Apium graveolens), parsely (Petroselinum sativum) are used as vegetables and are source of food. FODDER: Many members of the family such as Heracleum species. (cow- parsnip), Angelica species. (Angelecas), carrots, wild parsely, etc are used as fodder plants for animals. Condiments: Ferula (Hing), Carum (Ajwain), Cuminum (Zeera), Foeniculum (Saunf) and coriandum (dhania) are used as condiments or carminatives. Bark, leaves and fruits of certain plants provides volatile oils, resins etc. SOURCE OF MEDICINES: Ligusticum (Lovage), Asafoetida (Hing), Foeniculum (saunf), Anetum (sowa) are used as drugs for digestive disorders. Hydrocotyle (Brahmi) is useful for brain work. POISONS: several members of the family such as conicum (Hemlock) contain an acrid watery juice which is more or less narcotic in its effect. Similarly species of Oenathe, Cicuta and Aethusa are poisonous and their roots are deadly to all kinds of live stock and also fatal to man.