Female Foeticide in India
- 1. FEMALE FOETICIDE Made By Jaskaran S. Kohli X| - B
- 2. WHAT IS FEMALE FETICIDE? It is defined as aborting a female foetus after sex determination test. Ultra-sonography and Foetoscopy helps determine abnormalities in the fetus. But it is misused to find out sex of the fetus and abortion is done if it is a girl.
- 3. CAUSES OF FEMALE FETICIDE Obsession for Son. Fear of dowry by many poor class families. Girls are considered as financial obligation by many parents. Advancement in technology , nowadays parent determines the sex of a child before birth. Some of the doctors do this heinous act to fulfill their money desire. *Vicious Cycle of Female Feticide
- 4. CONSEQUENCES OF FEMALE FETICIDE Decrease in the female population. Adverse effect on women's health physically , mentally and emotionally. Women are abused and sexually exploited. Leads to women trafficking . Women are kidnapped , bought and sold for marriage. Suicide rates in women will increase .
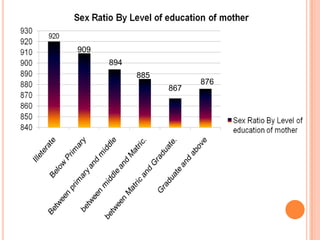
- 5. FEMALE FETICIDE IN INDIA The child sex ratio has dropped from 945 females per 1000 males in 1991 to 927 females per 1000 males in 2001. Estimated that 50 million girls and women are ‘missing’ from India’s population because of termination of the female foetus. Female foeticide in India increased by 49.2%.
- 7. SEX RATIO – AGE GROUP (0-6 YRS) 750 800 850 900 950 1000 960 933 880 850 846 820 Females per 1000 males
- 9. Dowry (known as Dahej ) is a payment of cash or gifts from the bride's family to the bridegroom's family upon marriage. Groom demands the bride’s father to provide money for his daughter’s maintenance as she is now a financial ‘burden’ on him. When the dowry amount is not considered sufficient the bride is often harassed , abused and even killed. It is estimated that a dowry death occurs in India every 93 minutes. EVIL OF DOWRY
- 11. LEGAL INITIATIVES The Prenatal Diagnostic Test Act (PNDT Act) The Medical Termination Of Pregnancy Act The Dowry Prohibition Act
- 12. THE PRENATAL DIAGNOSTIC TEST ACT (PNDT ACT) OF 1994 This Act was enacted in the year 1994 in all of the states in India , but it came into force in the year 1996. Through this Act the use of pre-natal diagnostic techniques is prohibited and regulated. PNDT Act was amended in 2003 with its main aim to to ban the use of sex-selection techniques as well as the misuse of pre-natal diagnostic techniques for sex- selective abortions . More than 21,600 centres conducting pre-natal diagnostic procedure have been registered.
- 13. THE MEDICAL TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY ACT, 1971 Was enacted by the Indian Parliament in the year 1971 and came into force in 1972 . As per India’s abortion laws only qualified doc stipulated conditions, can perform abortion on a woman in an approved clinic or hospital. The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act of India clearly states the conditions under which a pregnancy can be ended or aborted . Year 1972 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2003 2007 2010 Number of abortions reported 24300 214197 388405 583704 581215 570914 723142 1229937 1895721 2529979
- 14. THE DOWRY PROHIBITION ACT, 1961 Prohibits the request, payment or acceptance of a dowry, demanded or given as a precondition for a marriage. Asking or giving of dowry can be punished by an imprisonment of up to six months, or a fine of up to Rs. 5000. Indian government has modified property inheritance laws and permitted daughters to claim equal rights to their parental property.
- 15. MY VERDICT We as well educated and aware citizens can bring a change. The government should implement stern policies against this by removing the child sex recognizing centers and banning their licenses. The family who are involved in this act sholud be fined with some cash amount and sent to the jail for a minimum of 2 years. Higher status should be provided to women by involving them in the high profile jobs and including special reservation policies for women. Higher education should be provided to women so that they can take decisions for themselves.