financial markets and services unit 1
- 1. A V V S PRASAD Assoc. Prof. MBA.,M.Phil.,Ph.D.
- 2. UNIT 1 Financial System in India: Introduction Evolution of Banking Phases of development RBI and the Financial System Committees on Banking Sector Reforms Prudential Banking RBI Guidelines and directions.
- 3. FINANCIAL SYSTEM:- System “a set of complex and closely connected or intermixed institutions, agents, practices, markets, transactions, claims, and liabilities in the economy”. Financial System is concerned about ○ Money –current medium of exchange ○ Credit –money returned normally with interest ○ Finance –monetary resources comprising debt and ownership funds
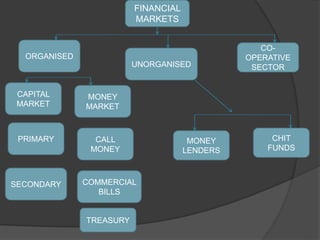
- 4. Financial System Financial Institutions Financial Markets Financial Instruments (Claims, Assets, Securities) Financial Services Regulatory Intermediaries Non- Intermediaries Others Banking Non- Banking Organized Unorganized Primary Secondary Short Term Medium Term Long Term Secondary Capital Markets Primary Money Markets Equity Market Debt Market Derivative Market
- 5. FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS REGYLATORY BANKING INTERMEDARIES OTHERS NON- INTERMEDARIES NON BANKING RBI NFBIS, UTI, LIC, GIC COMM. BANKS IDBI, NABARD
- 6. FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS Business organizations that act as mobilizes and depositories of savings, and as purveyors of credit or finance Intermediaries intermediate between savers and investors —lend money as well as mobilize savings —liability towards the ultimate savers —assets are from the investors or borrowers Intermediaries– all banking institutions, non- banking Financial intermediaries (NBFIs) –UTI, LIC, GIC Non-intermediary institutions --> do loan business but resources not directly obtained from the savers Non-intermediaries – IDBI, NABARD, IFC—also called non-banking statutory financial organizations(NBFSO)
- 8. FINANCIAL MARKETS Provide facilities for buying and selling of financial claims and services Primary and Secondary Markets Money and Capital Markets ○ Both perform same function of transferring resources to the producers ○ Distinction based on – differences in period of maturity of financial assets issued in these markets ○ Money market – short-term claims (<1 year) – T-bills, call money market, commercial bills ○ Capital market – long-term claims (>1 year) – stock market, govt. bonds market ○ Commercial banks belong to both
- 10. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS AND SERVICES Financial asset – represents a claim to the payment of a sum of money in the future and/or a periodic payment in the form of interest or dividend. Financial securities – primary and secondary
- 11. Financial services are the economic services provided by the finance industry, which encompasses a broad range of businesses that manage money, including credit unions, banks, credit- card companies, insurance companies, accountancy companies, consumer- finance companies, stock brokerages, investment funds, individual ...
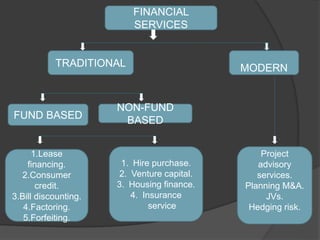
- 12. FINANCIAL SERVICES Project advisory services. Planning M&A. JVs. Hedging risk. MODERN NON-FUND BASED TRADITIONAL FUND BASED 1.Lease financing. 2.Consumer credit. 3.Bill discounting. 4.Factoring. 5.Forfeiting. 1. Hire purchase. 2. Venture capital. 3. Housing finance. 4. Insurance service
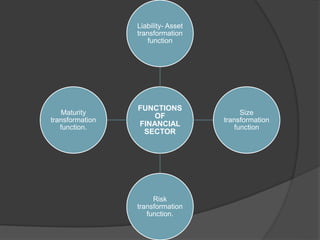
- 15. Liability- Asset transformation function Asset transformation is the process of creating a new asset (loan) from liabilities (deposits) with different characteristics by converting small denomination, immediately available and relatively risk free bank deposits into loans
- 16. size transformation function of financial system A type of transformation that is performed by banks and other depositary institutions whereby small deposits by different types of depositors are pooled in order to issue large loans to seekers of funds
- 17. risk transformation function of financial system Risk transformation is about how to mitigate risk and in parallel develop competitive advantages. ... Risk may include financial risk, security/safety- related risks, uncertainty, and risk through action or lack of action.
- 18. maturity transformation function of financial system Maturity transformation is the practice by financial institutions of borrowing money on shorter timeframes than they lend money out.
- 19. Equilibrium in Financial Markets Equilibrium in financial markets– usually determined by assuming perfect competition Financial markets are said to be perfect when A large number of savers and investors operate in markets The savers and investors are rational All operators in the market are well-informed and information is freely available to all of them There are no transaction costs The financial assets are infinitely divisible The participants in markets have homogenous expectations There are no taxes Under these ideal conditions, the financial markets attain equilibrium position when supply and demand are equal the interest rate at which the supply curve and demand curve intersect with each other
- 20. EQUILIBRIUM CONTD., The equilibrium in financial markets is established when the expected demand for funds (credit) for short-term and long- term investments matches with the planned supply of funds generated out of saving and credit creation. Supply of funds ○ Aggregate savings by household, business and govt. sectors
- 21. EQUILIBRIUM CONTD., Demand of funds ○ Investment in fixed and circulating (working) capital ○ Demand for consumer durables ○ Investment in housing ○ Current level of capital stock ○ Capacity utilization ○ Desired capital stock ○ Availability of internal funds ○ Cost of funds ○ Technological changes
- 24. Financial System and Economic Development 1.Finance is not important at all Ex: environment- friendly, appropriate technology. 2.Finance is very important. 3. Cautionary View: Economic Growth – growth results predominantly not from the increase in labor and capital but from the technical progress, which is external money and finance and the policies about them cannot contribute to the growth process.
- 25. A well developed financial system can contribute significantly to the acceleration of economic development through – Technical progress is endogenous ( human and physical capital are its important sources dependent on financial system) Good financial system rate of capital formation (finance available in time, in adequate quantity and on favorable terms) economic development Financial system enhances the efficiency of the function of medium of exchange helps in economic development.
- 26. k you…
Editor's Notes
- Purveyors = providers