Fish Biodiversity and Conservation
- 1. Seminar on Fish Biodiversity and Conservation. ASHISH SAHU
- 2. Content 1.What is biodiversity ? 2.Fish biodiversity resources of India 3.Fish biodiversity resources of up 4.Fish biodiversity of India 5.Fish biodiversity of U.P. 6.Types of fish biodiversity i- Marine water fish biodiversity ii- Brackish water fish biodiversity iii- Fresh water fish biodiversity 7. Threats of fish biodiversity 8. Fish biodiversity conservation 9. Reference
- 3. What is biodiversity Father of biodiversity in - E.O. Wilson. Define Biodiversity “Biodiversity include of the particular area may be living organisms ( plant and animal ) called biodiversity ”. Define Fish biodiversity “Fish species diversity is define as the number of spp. And abundance of each spp. that live in a particular location ” .
- 4. Distribution of Biodiversity Flora and fauna diversity depends on – Climate. Altitude. Soils. Presence of other spp. Most of the biodiversity concentrated in tropical region. Biodiversity hotspot A region with high biodiversity with most of spp. being endemic. India have to biodiversity hotspot . Himalayan region. Western Ghat, Indo-Burma. Sundaland.
- 5. Eastern Himalayas Tropical Asia-East of the Ganges-Brahmaputra lower lands, excluding Malesian region. Covers an area of 2,373,000 sq.km.
- 6. Western Ghat The Western Ghat (Sahyadri Hills) is formed by the Malabar Plains and the chain of mountains running parallel to Indias western coast. Travers the states of Gujrat, Maharashtra Goa, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu. Cover an area of about 138,600 km.
- 7. Total fish biodiversity: World harbours total of 33059 spp, 4258 genera , 442 families. About 58 % marine, 41 % fresh water, 1 % migrants. In India, 3231 fishes spp 113 Brackish water 2443 are marine water951 fresh water From - CMFRI 2017
- 8. Total FISH BIODIVERSITY FISH spp. In uttar pradesh: TOTAL FISH BIODIVERSITY FISH SPP. IN FAIZABAD 126 FISH SPECIES IN U.P. 63 Species in faizabad 9 order 45 genera 20 family
- 9. State fish uttar pradesh: State fish of Uttar Pradesh - Chitala chitala Family: Notopetridae Also known as, Indian featherback, Kinfe fish. Endangered spp. In U.P.
- 10. Fisheries resources of India 1. RIVER 45000 Km 2. Coast line 8129 km 3.EEZ( Exclusive Economic Zone) 2.O2 million km 4.Reservoirs 3.15 million km 5. Estuaries 0.3 million km 6.Lakes 0.72 million km 7.Back water &lagoons 0.9 million km 8.Flood plain wetland 0.2 million km From – CMFRI 2017
- 11. FISHERIES RESOURCES OF U.P Uttar Pradesh being a land locked state having vast fresh water recourses. 1. Pond and tanks 2.25 million hac 2. Bheels and derelict 1.3 million hac 3. Leas and has channel 2.9 million hac 4. Irrigational canal and channel 1.2 lakh / km 5. Rivers and canals 7.20 lakh / km 6. Large medium reservoirs 1.38 lakh / km 7. Lakes 1.33 lakh / km 8. Only ponds 1.61 lakh / km From – NBFGR Lucknow 2017
- 12. types of fish biodiversity- 1- Marine fish diversity. 2- Brackish water fish diversity. 3- Fresh water fish diversity. Marine Fish Diversity The sea water surrounding east and west coast of the country with salinity more 30 ppt.decignated as marine water. India has a long coast line more than 8129 km. Its marine resources are spread over in the Indian ocean. Arbian Sea ,and Bay of Bengal.
- 13. The Andaman and Nicobar island and the coral island of Lakshadweep represents one of the richest ripositories of biodiversity in the whole of south Asia These resources comprising 1368 taxa including the commercially important Pelagic and Demersal species diversity. Commercially important species:- Shark Spp Perches fishes Carcharhinus sorrah Lethrinus spp. C. dussumieri Epinephilus spp. C. Gangeticus Silver bellies S. Sorrahkowah Secutor muconius Bombay duck Seer fish Harpadon nehereus Scomberomorous guttatus Oil sardine Mackerel Sardinella longiceps Rastrelliger kanagurta S. Fimbriatus Tuna S. Gibbosa Auxis thazard S .albella Pomfrets Pampus argentius and so other fishes .
- 14. Species composition of some major Demersal spp. Elasmobranch – In india there are about 110 spp of elasmobranch which incudes 66 spp of sharks. Sharks- The dominant spp of sharks are Chiloscyllium indicum (slender bamboo shark ) ,C.griseum (grey bamboo shark ),Rhincodon typus (whale shark) etc.
- 15. Whale shark Rhincodon typus is slow moving filter feeding carpet shark and largest known extant fish spp. The largest confirmed individual had a length of 12.65 m and weight about 21.5 t. The Whale shark is the largest non-cetacean animal in the world . Whale shark in habits all tropical and warm temprate sea .
- 16. Brackish water fish diversity of India The Brackish water habitats are considered as the transition zone between fresh water of rivers and marine water of seas. The salinity of brackish water ranges from 0.5 -30 ppt. The major estuarine systems are Hoogly- Matlah, Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, Cauvery, Narmada, Tapti etc . Chilka and Pulicat lake also support brackish water biodiversity of fishes. There are 113 spp of brackish water fishes are recorded from Indian waters.
- 17. Fresh water fish diversity of India There are about 951 species of fresh water fishes are recorded from Indian waters . In India there are 14 major river systems and 44 medium river which supports a number of diversity of fishes. Fresh water species Some commercially important carps of India are Catla catla, Labeo rohita, Cirrhinus mrigala, L.calbasu, L.fimbriatus ,L. bata, Cirrhinus cirrhosa, C. reba . Some important catfishes are Mystus seenghala , M. aor,Wallago attu , Pangasius pangasius , Silonia silondia , Bagarius bagarius etc . Fresh water farming is mainly focused on Indian major carps .
- 18. Threats of fish biodiversity Over exploitation of fish . Water pollution Unsustainable fishing Global climate variation Divers of river beds for urbanization Destructive natural events ( flood ,tsunami, cyclone, disease, Earthquakes ) etc . Over exploitation of fish Unsustainable fishing Water pollution Global climate variation
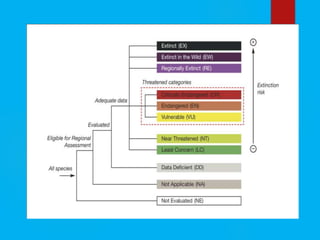
- 19. IUCN Categories of threatened species:- Extinct (ex) A taxon is Extinct when these in no reasonable doubt that the last individual has died. Ceritically endangered (CR)- Reduction of at least 80% over at least 10 years or 3 generation. Endangered (EN)- Reduction of at least 50% over a least 10 years of 3 generations. Vulnerable – Reduction of at least 2o% over at least 10 years or 3 generations.
- 21. List of Indian fishes in threatened category: Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) was the first who compiled a list of 21 vulnerable fishes- 4 Endangered Barilius bola Puntius chilinoides Semoplotus semiplotus Enobarbicheilus maculatus 17 Threatened species Notopterus chitala, Acrossocheilus hexagonolepis,Cirrhinus cirrhosa,Labeo fimbriatus,Labeo potali,Labeo kontius,Puntius carnaticus, P.curmuca, P.jerdoni, Tor khudree, T.putitora,T.tor, Schizothorax richardsonii, Schizothoraichthys progestus, Silonia children,Pangasius pangasius and Bagarius bagarius).
- 22. Techniques of conservation of biodiversity In-situ conservation:- It is the process of protecting an endangered species in its natural habitat Ex. - National park, sanctuary. Ex-situ conservation :- It is the process of protecting an endangered species outside its natural habitat ex – gene bank ,seed bank .
- 23. Reference Book - Handbook of fisheries and aquaculture ( Chapter No – 2, Page no-33, 34, 35 36) S. Ayappan Internet (https://www.en.m.wikipedia.org ). Ichthyofaunal diversity of Faizabad District - Uttar Pradesh ( Article January 2013) https://www.researchgate.net Authors – Dr. Jitendra Kumar (GADVASU - Punjab) Dr. A. K. Pandey (NBFGR – Lucknow) Dr. Mahesh V Sagar (CMFRI – Cochin, Kerala)