Fitration
- 1. Filtration By Yogeshwary Bhongade Assistant Professor Gondia college of Pharmacy, Gondia
- 2. UNIT-IV 1- Filtration • Objectives, applications, Theories & Factors influencing filtration, filter aids, filter medias. • Principle, Construction, Working, Uses, Merits and demerits of – Plate & frame filter, Filter leaf, Rotary drum filter, Meta filter Cartridge filter, Membrane filters & Seidtz
- 3. Filtration • It is the process of separation of particle from fluid by passing slurry through a permiable membrane. Slurry- Suspention of particle in Liquid Filter Medium-Medium through which slurry passed Residue- Separated solid on medium Filtrate- Clear liquid passing through medium
- 4. Objectives • For clarification • Cake filtration • Sterile Filtration • Ultra filtration
- 5. Applications • Fitration of bacteria and particulate contamination • Sterilization of heat labile solution • Separation of bulk product from reaction mixture • purification of water • Removing of solid or suspended olis from aqueous solution • Separation of alcohol from fermentation reactor • Treatment of waste liquid
- 6. Mechanism of filtration 1. Staining 2. Impringment 3. Entanglement 4. Electrostatic force
- 7. Filter Media • It is the medium through which slurry is passed to get filtrate or • The surface on which solids are retained after filtration process is called as Filter Medium.
- 8. Properties of Ideal Filter Media • Sufficient Mechanical Strength • Chemically inert • Minimum resistance to flow filtrate • High retention power • Should allow easy removal of cake • Should not absorb dissolved material • Not swell in contact with filtrate
- 9. Selection of Filter Media • Selection of Filter Media Depends on following • Size of Particles to be filtered • Nature of Product to be filtered • Amount of liquid to be filtered
- 10. Filter Media 1. Woven Mendia - Cotton Cloth -Nylon Cloth - Woven wire cloth 2. Non Woven Media 3.Membrane filter 4. The depth type Media - Fibrous Medium - Porous Medium - Bed of Granular solid
- 11. Filter Aid • Special type of filter medium, which form a fine surface deposite that form porous, non- compressible cake over filter medium, thus reducing resistance to flow • Act as depth filter • Maintain Flow
- 12. Ideal Filter Aid • Should form porous cake • Suitable particle size • Impurities free • Free from moisture • Should be innert • Should maintain suspended Precoating Body Mix
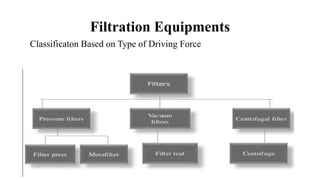
- 13. Filtration Equipments Classificaton Based on Type of Driving Force
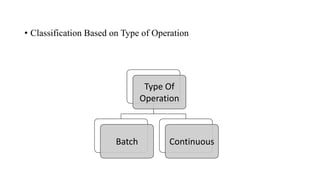
- 14. • Classification Based on Type of Operation Type Of Operation Batch Continuous
- 15. • Classification Based on End Product Based on End Product Filter Cake Clarifying Filter
- 16. • Choice of filter govern by specific requirement 1. Properties of Liquid eg. Viscosity 2.Objectives of Filtration eg. Recovery of solid/ sterilization/clarification 3.Properties of solid eg. Particle size, shape, compressibility 4.Whether Cake is to be washed 5.Operating Temperature and Pressure 6. Desired flow rate
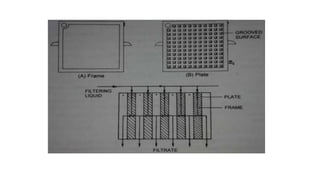
- 17. Plate & frame filter Principle • Based upon surface filtration • the slurry enters the frame by pressure and flows through the filter medium. • The filtrate is collected on plates and sent to outlet • surface area increased with the help of plate and frames then large volume of slurry can be proceed • The Filter press is made of two types of units, plate and frames.
- 18. • Usually made of aluminium alloy. • Sometimes, these are also lacquered for protection against corrosive chemicals and made suitable for steam sterilization.
- 21. Frame • It contains a open space inside wherein the slurry reservoir is maintained for filtration and an inlet to receive the slurry. • It is indicated by two dots in description. Slurry inlet Handle to rest on rod • Frames of different thickness are available. • It is selected based on the thickness of cake formed during filtration. • Optimum thickness of frame should be chosen.
- 22. Plate • The plate has a studded or grooved surface to support the filter cloth and an outlet. It is indicated by one dot in description. Through channels Filtrate outlet • Plate supports the filter medium, receiving the filtrate and outlet. • The filter medium usually cloth is interposed between plate and frame. • Plate, filter medium, frame, filter medium and plate are arranged in sequence and clamed to a supporting structure. • It is normally described by dots as 1.2.1.2.1 so on. • A number of plates and frames are employed so that the filtration area is as large as necessary. • ts controlled by valves.
- 23. • Number of filtration units are operated in parallel. • Channels for slurry inlet and filtrate outlet can be arranged by fitting eyes to the plates and frames, these join together to form a channel. • In some types only one inlet channel is formed, while each plate is having individual outle
- 24. Working of filter press • Working can be divided into two steps- 1. Filtration operation 2. Washing operation Filtration operation
- 25. Advantages: 1- Construction is very simple and a wide variety of materials can be used. 2- It provides a large filtering area in a relatively small floor space. 3- It is versatile, the capacity being variable according to the thickness of the frames and the number used. 4- The construction permits the use of considerable pressure difference. 5- Efficient washing of the cake is possible. 6- Operation and maintenance is straightforward , because there no moving parts, filter cloths are easily renewable and, because all joints are external, any leaks are visible and do not contaminate the filtrate.
- 26. Disadvantages: 1- It is a batch filter, so it is a time consuming. 2- The filter press is an expensive filter, the emptying time, the labour involved, and the wear and tear on the cloths resulting in high costs. 3- Operation is critical, as the frames should be full, otherwise washing is inefficient and the cake is difficult to remove. 4- The filter press is used for slurries containing less about 5 % solids 5- In view of the high labour costs , it is most suitable for expensive materials.e.g.the removal of precipitated proteins from insulin liquors.
- 27. Filter leaf • It is the simple form of batch filter consisting of dranage canal converted with filter cloth Principle • Surface filtration Construction • It consist of grooved metal frame work over which filter cloth is fixed. • The groved frame encloses drainage screen. • The outlet for filtrate connected to inside the frame.
- 28. Working • The filter leaf is placed in a vessel containing the liquid to be filtered. • When vacuum is applied , the pressure inside the leaf is decreased. • Due to the difference in external and internal pressure inside the leaf, the liquid moves inside the filter through the filter cloth. • The filtrate is collected in the receiver , and cake gets collected on outside of the cloth.
- 29. Advantages: Liquid can be filtered from any vessel . Filter cake can be removed simply by washing or blowing air. It is very economical . Disadvantages : It is not effective when solid content in the liquid is more than 5%.
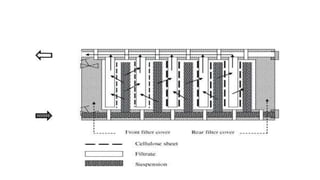
- 30. Meta filter Also known as Edge filter Principle • It fuction as surface filter and separate the particle by staining through the tappering channels formed by series of ring with semicircular projection. Construction • It is made up of a series of metal ring made of ss packed on grooved rod. • ring have internal diamete 15 mm and external diameter 22mm
- 32. Working • The entire assembly is placed inside a pressure vessel , containing the liquid to be filtered. • When vacuum applied, liquid will flow from outside to inside. • The clear liquid is collected in to a receiver from the top. • The pack of rings acts as a base on which the true filter medium is supported.
- 33. Advantage • It possess considerable strength and hence can withstand high pressure. • It is economical. • The corrosive liquids can be filtered without any problem. • Cake can be removed effectively without any difficulty. Use • Used mostly for clarification of syrups , elixirs and parenteral solutions .
- 34. Rotary drum filter • Rotary drum filter is continuous filter that can handle slurries with high proportion of solid, with simultaneously removal of cake. • It operate on vacuum Construction • It consist of hallow metal cylinder on which filter cloth is mounted with support of mesh. • the cylinder has five sections- 1.Pickup zone 2.Drainage zone 3. Washing zone 4. cake removal zone 5. Drying zone
- 36. Working • The drum rotate slowly and pickup slurry from the feed through (pickup zone). • The slurry is filtered under vacuum and the cake built on the filter cloth. • From the fewatering zone the water is completely removed from cake.
- 37. Advantages • Automatic and continuous • low labor cost • Can handle large ammount of slurry • Speed of drum can varry to control the thickness of cake Disadvantages • Difficult to maintain as it contain may moving part • Cake may crack due to vacuum, making washing difficult • Small pressure difference(liquid may boil) • not suitable for gelatinous solids.
- 38. Membrane filters Construction Membrane filters are made of thin and flat membranes of cellulose derivatives, such as cellulose acetate and cellulose nitrate. • Thickness: 50-150 µ • 400-500 million pores • Pores are uniform in size and occupy 80% of filter volume. • A membrane filter is fixed in a metallic holder before its use. • Selection of membrane filter depends on particles to be removed. • Pore size (in µ) Particles removed 0.2 All bacteria 0.45 All coliform group bacteria 0.8 All air born particles 1. • All Non living particles considered dangerous in I.V. Fluid. 5 All Significant cell from body fluid 4. Membrane Filters 12
- 39. Advantages • The processes can function effectively at low temperatures. • Energy requirements are low. • Processes are relatively simple to scale up. • Membranes can be manufactured in a uniform and highly precise manner. Disadvantages • It cannot be used for filtration of organic solvents, such as alcohols, ketones, esters and chloroform. • Pre-filtration is often required to avoid rapid clogging of a membrane. • Equipment cost can be high. • If the membrane manufacturing process is not precisely controlled, membranes with wide pore size distribution may result, giving poor separation performance. • Uses Mainly used for sterilisation of both aqueous and oily liquids
- 40. Cartridge filter Principle • The principle behind this filter is water is pushed through thin porous membrane in which pre-filter and membrane filter are combined into the single unit. • as a result the particals are retained on the surface Construction • it consist of cylindrical centrifugation having disposable filter media which are made up of platic or metal. • The filter consist of cartridge one of which act as prefilter while another one act as actual filter for filtration. • The cartridges are enclosed in holder. There is also provsion for slurry and filtrate outlet. • At the bottom discharge cake is collected which is removed from bottom.
- 41. Working • A slurry is pump into cartridge holder through the inlet. it passes through cartridge filter. • The filtration occures due to mechanism of staining. • The particle get attached to the surface while clear liquid passes to the centre • The filtrate ove up and collected through the outlet
- 42. Uses • Preparation of sterile solution(Parentral and opthalmic) • Water treatment plant
- 43. Advantages • Suitable for sterile preparation. • low contamination • easy to dissasemble • Filter media can be reused • cartridge with self cleaning devices are useful • cartridge are not brittle, whwn they dry. • Can use continuous
- 44. Disadvantages • To much cost
- 45. Seitz filter Principal • Filtration of asbestos pad filter disc Construction • Funnel like structure. • Upper part • Asbestos pad filter disc • Lower part
- 46. Working • Join parts then add slurry. Slurry deposit on asbestos pad filter disc and Filtrate will pass. Application • Serum sterilization. • Sterilization. Advantages • Contaminate filters • Simple to use • Useful for viscous solutions. Disadvantages • delicate
- 47. THANK YOU