Mutual Funds
- 1. MUTUAL FUNDS PRESENTED BY: •Dering Naben •Aditi Thakur •Harshita Sehgal •Devi Kumari •Sakshi Sharma •Ekta Uniyal
- 2. Executive Summary Concept – Mutual Fund What is Mutual Fund ? History Structure of Mutual Fund Terminologies Types of Mutual Fund Benefits Drawbacks How and Why to invest in Mutual Fund? Latest Data Terminologies Disclaimer
- 3. What is Mutual Fund? A mutual fund is a professionally managed type of collective investment scheme that pools money from many investors and invests in stocks, bonds, short-term money market instruments and other securities.
- 4. Example: If one has Rs.1000 to invest, it may not fetch very much on its own. But, when it is pooled with Rs.1000 each from a lot of other people, then, one could Create a Big Fund large enough to invest in various shares and debentures. This is called Mutual funds.
- 5. History • • • • • First Phase – 1964-87 UTI was established in 1963 Unit scheme 1964 : The first and the largest scheme ULIP : launched in 1971 Second Phase-1987-1993 (Entry of Public Sector Funds) Entry of public sector mutual funds First Public sector mutual fund: State bank of India in 1987 Third Phase-1993-2003(Entry of Private Sector Funds) • Emergence of private funds
- 6. Continued--- • • Fourth Phase – since February 2003 SEBI regulation for mutual funds Dividends exempted from income tax from 1999
- 7. Structure Of Mutual Fund
- 8. Types Of Mutual Fund Schemes Structure Investment By Objective Income Fund Open Ended Growth Fund Close Ended Balance Fund Taxation Fund Money Market Fund
- 9. Continued--- By Structure By Investment Objective Open-Ended – anytime enter/exit Close-Ended Schemes – listed on exchange, redemption after period of scheme is over. Equity (Growth) – only in Stocks – Long Term (3 years or more) Debt (Income) – only in Fixed Income Securities (3-10 months) Liquid/Money Market – Short-term Money Market (Govt.) Balanced/Hybrid – Stocks + Fixed Income Securities (1-3 years) Other Schemes Tax Saving Schemes Special Schemes ULIP
- 10. Why Mutual Funds? Diversification No Entry Load Tax Benefit Professional Management Affordability Transparency Regulations
- 11. De-merits : Mutual Funds Exit load No control over costs No tailor-made portfolio No assured Returns Management Risk
- 12. How To Invest In Mutual Funds? Identify your Investment needs Choose the right mutual fund Select the ideal mix of schemes Invest regularly Keep your taxes in mind Start early Get in touch with your mutual fund or your advisor and start investing
- 13. Why Invest? Human Life Cycle Phase I Phase II Phase III Child’s Marriage Child’s Education Housing Child birth Marriage 38 yrs 22 yrs 10- 20 yrs Earning Years Education Age- 22 yrs Post Retirement Years Age- 60 yrs
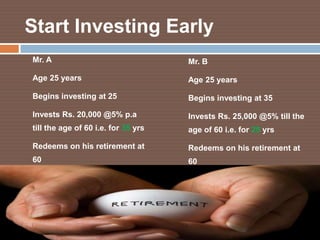
- 14. Start Investing Early Mr. A Mr. B Age 25 years Age 25 years Begins investing at 25 Begins investing at 35 Invests Rs. 20,000 @5% p.a Invests Rs. 25,000 @5% till the till the age of 60 i.e. for 35 yrs age of 60 i.e. for 25 yrs Redeems on his retirement at Redeems on his retirement at 60 60
- 15. Who has more? Is it Mr. A, who invested Rs. 20,000 for 35 years? OR Is it Mr. B, who invested Rs. 25,000 for 25 years? 2000000 Earnings at the age of 60 1500000 1000000 500000 0 Mr.A Mr.B
- 16. MUTUAL FUND DATA FOR THE MONTH ENDED - AUG 31 , 2012 ( IN CRORES) Category No. of new schemes launched during the month Sales New Redemption Existing schemes Total Total as on Aug 31 , 2012 as on Jul 31 , 2012 Inflow/ Outflow schemes B Bank Sponsored 0 0 113605 113605 110618 0 0 0 C Institutions 0 0 3047 3047 2254 0 0 0 Private Sector & Joint Venture : Indian 503 236747 237250 232666 0 0 0 Predominantly Indian 15 1129 248620 249749 241233 0 0 0 Predominantly Foreign D 9 0 0 20533 20533 19020 0 0 0 Grand Total (B+C+D) 24 1632 622552 624184 605791 0R 0 0
- 17. Buying Mutual Funds Contacting the Asset Management Company directly Agents/Brokers Locate one on AMFI site Financial planners Web Site Request for agent Bajaj Capital etc. Insurance agents Banks Net-Banking Phone-Banking ATMs Online Trading Account ICICI Direct Motilal Oswal, Indiabulls- Send agents
- 18. Terminologies o o o o o AMC- Asset Management company SEBI- Securities Exchange Board Of India UTI- Unit Trust Of India ULIP- Unit Linked Insurance plan AMFI- Association of Mutual funds In India
- 19. Disclaimer Mutual fund investments are subject to market risks. Please read the offer document carefully before taking an investment decision.
- 20. HAPPY INVESTIN G