Frontend for developers
- 1. Frontend for Developers HTML for WebApps
- 3. Web Browsers The most important ones. • Internet Explorer • Chrome • Firefox • Safari • Opera
- 4. Web Browsers Chrome is bigger than Internet Explorer. • Chrome • Internet Explorer • Firefox • Safari • Opera
- 5. Rendering engine How it works? 1. Parses HTML to construct the DOM tree 2. Renders tree construction 3. Creates layout of the render tree 4. Paints the render
- 6. Web Browser’s parts retrieves resources from the server and visually presents them.
- 7. The DOM is a language-independent API.
- 8. The DOM is implemented in JavaScript in the browser.
- 9. The DOM is the object presentation of the HTML document. html head body title h1 p h2 ul div li li span img p
- 10. The DOM is the interface of HTML elements to the outside world.
- 11. Rendering engine by browser. Engine used by Firefox, SeaMonkey, Galeon, Camino, K-Meleon, Flock, Epiphany- Gecko gecko ... etc Presto Opera, Opera Mobile, Nintendo DS & DSi Browser, Internet Channel Trident Internet Explorer, Windows Phone 7 Safari, Chrome, Adobe Air, Android Browser, Palm webOS, Symbian WebKit S60, OWB, Stream, Flock, RockMelt
- 12. JavaScript engine by browser. Engine used by SpiderMonkey Mozilla Firefox Rhino Mozilla Carakan Opera Chakra Internet Explorer > 9 JScript Internet Explorer < 8 V8 Chrome Nitro Safari
- 14. Progressive Enhancement aims to deliver information to the widest possible audience. • sparse, semantic markup contains all content • end-user web browser preferences are respected
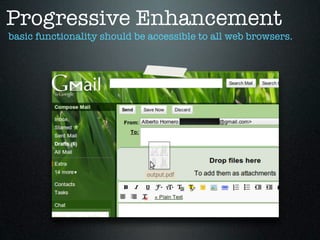
- 15. Progressive Enhancement basic content should be accessible to all web browsers.
- 16. Progressive Enhancement basic functionality should be accessible to all web browsers.
- 17. Progressive Enhancement enhanced layout is provided by externally linked CSS.
- 18. Progressive Enhancement enhanced behavior is provided by unobtrusive JavaScript.
- 19. Polyfills is a feature detection technique for regressive enhancement.
- 20. Frontend Its parts. • The Web Browser • The User Experience • The Content Layer • The Visual Layer • The Behavior Layer
- 22. What is HTML • HyperText Markup Language • Markup language is not programming language • The web is published in HTML • It’s maintained by the W3C
- 23. Elements Types of elements according to the tag. <p>It’s the content</p> Open tag & close tag. Element with content. <img /> Unique tag. Element without content.
- 24. Attributes Syntax. <p id=”paragraph”>It’s the content</p> Open tag & close tag. Element with content. <img src=”/image.jpg” alt=”It has a book.” /> Unique tag. Element without content.
- 25. Attributes The common attributes for the HTMLElement. • title • id • class • lang • dir • data-*
- 27. Reserved Characters cannot be used inside the document. • < can be mixed with tags • > can be mixed with tags • “ the quotes start an attribute • & the ampersand is also reserved
- 28. Entities are used to implement reserved characters. < --------- < > --------- > & --------- & “ --------- "e;
- 29. Entities examples. 10 < 20 <p> 10 < 20 </p> 20 > 10 <p> 10 > 20 </p> He said: “Don’t do it” <p>He said: "Don’t do it" </p> Company & Co. <p> Company & Co. </p>
- 30. The Structure html, head & body
- 31. The doctype is required to do cross browser. <!doctype html> <html> <head> <title>MercadoLibre</title> </head> <body> <p>The basic content</p> <!-- Comment --> </body> </html>
- 32. The html element is the root of the document. <!doctype html> <html> <head> <title>MercadoLibre</title> </head> <body> <p>The basic content</p> <!-- Comment --> </body> </html>
- 33. The head element is a collection of metadata. <!doctype html> <html> <head> <title>MercadoLibre</title> </head> <body> <p>The basic content</p> <!-- Comment --> </body> </html>
- 34. The body element is the place for the content. <!doctype html> <html> <head> <title>MercadoLibre</title> </head> <body> <p>The basic content</p> <!-- Comment --> </body> </html>
- 35. The DOM It’s the interface of HTML elements to the outside world
- 36. The DOM interface of a image element. interface HTMLImageElement : HTMLElement { attribute DOMString alt; attribute DOMString src; attribute DOMString crossOrigin; attribute DOMString useMap; attribute boolean isMap; attribute unsigned long width; attribute unsigned long height; readonly attribute unsigned long naturalWidth; readonly attribute unsigned long naturalHeight; readonly attribute boolean complete; };
- 37. Practices The best of them
- 38. Comment the code. <!doctype html> <html> <head> <title>MercadoLibre</title> </head> <body> <p>The basic content</p> <!-- Comment --> </body> </html>
- 39. Attributes must always be between quotes. <img width=”50” height=”90” alt=”Iphone Image” />
- 40. Attributes must always be between quotes. <img width=”50” height=”90” alt=”Iphone Image” />
- 41. JavaScript functions should never go in event attributes. <p onclick=”hideDiv();”></p>
- 42. JavaScript functions should never go in event attributes. <p onclick=”hideDiv();”></p> not recommended
- 43. JavaScript functions should never go in event attributes. <p id=”overview”></p> <p onclick=”hideDiv();”></p> not recommended
- 44. JavaScript never goes in head element. <!doctype html> <html> <head> <title>MercadoLibre</title> <script> function greet(){ alert(“hello world!”); } </script> </head> <body> <p>The basic content</p> <!-- Comment --> </body> </html>
- 45. JavaScript never goes in head element. <!doctype html> <html> <head> <title>MercadoLibre</title> <script> function greet(){ not recommended alert(“hello world!”); } </script> </head> <body> <p>The basic content</p> <!-- Comment --> </body> </html>
- 46. JavaScript never goes in head element. <!doctype html> <html> <head> <title>MercadoLibre</title> </head> <body> <p>The basic content</p> <!-- Comment --> <script> function greet(){ alert(“hello world!”); } </script> </body> </html>
- 47. CSS rules should never go inline. <p style=”color:#ffffff;”></p>
- 48. CSS rules should never go inline. <p style=”color:#ffffff;”></p> not recommended
- 49. CSS rules should never go inline. <p class=”featured”></p> <p style=”color:#ffffff;”></p> not recommended
- 51. The head element the place for metadata. <head> </head>
- 52. The title element represents the document’s name and identifies it out of context. • Required • Unique • ~ 64 characters
- 53. The title element represents the document’s name and identifies it out of context. <head> <title>MercadoLibre Argentina</title> </head>
- 54. The link element allows you to link the current document to other resources. <link /> • rel • href • media • type
- 55. The rel attribute adds meaning to the external resources. • alternate • nofollow • author • noreferrer • bookmark • prefetch • help • prev • icon • search • license • stylesheet • next • tag
- 56. The rel attribute examples. <link rel=”stylesheet” type=”text/css” href=”/external.css” ... /> <link rel=”alternate” type=”application/rss+xml” ... /> <link rel=”prev” title=”Chapter 2” href=”/chapter-2” ... /> <link rel=”next” title=”Chapter 4” href=”/chapter-4” ... /> <link rel=”alternate stylesheet” title=”New Layout” ... />
- 57. The meta element represents various kinds of metadata. <meta /> • name • charset • http-equiv • content
- 58. The meta element The name attribute. <meta name=”author” content=”Hernan Mammana” /> <meta name=”copyright” content=”2011” /> <meta name=”description” content=”It’s the ... for HTML talk” /> <meta name=”generator” content=”gDocs” /> <meta name=”keywords” content=”html,talk,slideshow” /> <meta name=”robots” content=”all” />
- 59. The meta element The charset attribute. <meta charset=”utf-8” />
- 60. The Content Inside the body
- 61. The elements for text are used to give meaning to the content. • Headings • h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 • Paragraph • p • Inside Headings, Paragraph and List • strong, em, cite, sup, sub, acronym, a
- 62. Headings Examples from Home. <h1>MercadoLibre</h1> <h2>Clasificados</h2> <h2>Categorías</h2> <h2>Recomendados</h2> <h2>Más vendidos de la ... </h2> <h2>Destacados</h2> <h2>Más Compartidos</h2> <h2>Subastas desde $1</h2> <h2>Historial</h2> <h2>12 Cuotas sin interés</h2> <h2>Imperdibles del día</h2>
- 63. Headings Examples for VIP. <h1>Apple Ipod touch...</h1> <h2>Reputación del vendedor</h2> <h2>Medios de pago</h2> <h2>Medios de envío</h2>
- 64. Paragraph examples. <p>MercadoLibre no vende este artículo ... </p> <p>Local Palermo Fscomputers Dist Autorizado ... </p>
- 65. Inside paragraphs ... Examples. <p><strong>Elige el motivo de tu denuncia: </strong></p> <p><strong>$ 1.899<sup>99</sup></strong></p>
- 67. Ordered & Unordered Lists The most used lists on the web. • Ordered List To show rankings, prioritize tasks and search results • List Item To put anything inside the Ordered List • Unordered List To list anything without priorities • List Item To put anything inside the Unordered Lists
- 68. Ordered List is used to show rankings, prioritize tasks and search results. <ol> <li>Apple Ipod Touch 8 Gb 4ta Generaci... </li> <li>Apple Ipod Touch 32gb 4g 4ta Gener... </li> <li>Apple Ipod Nano 8gb 6g 6ta Genera... </li> </ol>
- 69. Unordered List is used to list anything without priorities. <ul> <li>Artículo nuevo </li> <li>208 vendidos </li> <li>Capital Federal </li> </ul> <ul> <li>Efectivo </li> <li>Visa American... </li> <li>Tu compra esta...</li> </ul>
- 70. Description List is used to make dictionaries, screenplays and key-value pairs. • It has three parts • Description List element • Description Term element • Description Definition element
- 71. Definition List Example. <dl> <dt>Condición:</dt> <dd>Artículo nuevo</dd> <dt>Ubicación:</dt> <dd>capital federal</dd> <dt>Vendidos:</dt> <dd>193 vendidos</dd> <dt>Finaliza en:</dt> <dd>Finaliza en 4d 2h</dd> </dl>
- 72. Table To organize the data
- 73. The table element and all its semantic elements. • The basic elements table, tr, td, th • The semantic elements caption, thead, tbody, tfoot, colgroup, col
- 75. The basic elements The semantic table elements. <table> <tr> <th>header</th> <th>header</th> </tr> <tr> <td>data</td> <td>data</td> </tr> </table>
- 76. The table element The global data container. <table> <tr> <th>header</th> <th>header</th> </tr> <tr> <td>data</td> <td>data</td> </tr> </table>
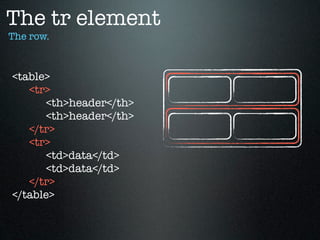
- 77. The tr element The row. <table> <tr> <th>header</th> <th>header</th> </tr> <tr> <td>data</td> <td>data</td> </tr> </table>
- 78. The th element The header data element. <table> <tr> <th>header</th> <th>header</th> </tr> <tr> <td>data</td> <td>data</td> </tr> </table>
- 79. The td element The content data element. <table> <tr> <th>header</th> <th>header</th> </tr> <tr> <td>data</td> <td>data</td> </tr> </table>
- 80. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. <table> <caption>It’s title of the table</caption> <thead> </thead> <tfoot> </tfoot> <tbody> </tbody> </table>
- 81. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. <table> <caption>It’s title of the table</caption> <thead> </thead> <tfoot> </tfoot> <tbody> </tbody> </table>
- 82. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. <table> <caption>It’s title of the table</caption> <thead> </thead> <tfoot> </tfoot> <tbody> </tbody> </table>
- 83. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. <table> <caption>It’s title of the table</caption> <thead> </thead> <tfoot> </tfoot> <tbody> </tbody> </table>
- 84. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. <table> <caption>It’s title of the table</caption> <thead> </thead> <tfoot> </tfoot> <tbody> </tbody> </table>
- 85. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. <table> <caption>It’s title of the table</caption> <thead> </thead> <tfoot> </tfoot> <tbody> </tbody> </table>
- 86. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. table first name last name age purchase
- 87. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. table first name last name age purchase
- 88. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. table personal data purchase first name last name age
- 89. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. table personal data purchase first name last name age
- 90. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. <table> <caption>Title of the table</caption> <colgroup> <col /> <col /> <col /> </colgroup> <tfoot> ... </table>
- 91. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. table personal data age purchase first name last name
- 92. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. <table> <caption>Title of the table</caption> <colgroup> <col /> <col /> </colgroup> <col /> <tfoot> ... </table>
- 93. The semantic elements The semantic table elements. <table> <caption>Title of the table</caption> <colgroup id=”personalData”> <col class=”first-name” /> <col class=”last-name” /> </colgroup> <col class=”age” /> <tfoot> ... </table>
- 94. Yes, we can use tables! Only for data!
- 96. The a element allows you to link current document to other resources. • href • rel • target • title • type
- 97. The a element URL decomposition attributes. interface HTMLAnchorElement : HTMLElement { ... attribute DOMString protocol; attribute DOMString host; attribute DOMString hostname; attribute DOMString port; attribute DOMString pathname; attribute DOMString search; attribute DOMString hash; };
- 99. The img element allows you to insert an image. • src • alt • title • width • height
- 100. The img element allows you to insert an image. <img src=”/image.jpg” alt=”It has a book.” />
- 101. Forms Getting the user’s data
- 102. The form element establishes a relationship between the user and the organization.
- 103. The form element establishes a relationship between the user and the organization.
- 104. The form element establishes a relationship between the user and the organization.
- 105. The form element establishes a relationship between the user and the organization.
- 106. The form element establishes a relationship between the user and the organization.
- 107. The form element establishes a relationship between the user and the organization. • Component of a web page • They have form controls, like text fields & buttons • The user can interact with them • The user’s data can be sent to the server • No client side scripting is needed • An API is available. It augments the user experience
- 108. The form element example. <form method=”post” action=”/signup”> </form>
- 109. The form element The method attribute. <form method=”post” action=”/signup”> </form>
- 110. The form element The action attribute. <form method=”post” action=”/signup”> </form>
- 111. Semantic elements for the form. • fieldset is the element to group similar meaning controls • legend is the element to give a meaning to the fieldset • label is the element to give meaning to a control
- 112. Semantic elements for the form. <form method=”post” action=”/signup”> <fieldset> <legend>Regístrate</legend> <label>Nombre:</label> </fieldset> </form>
- 113. Form controls The elements inside the form. • input, It render very different control related to his type attribute. • select It render two list of options, single and multiple. • optgroup Semantic element to group similar options. • option It’s a option in the select list. • textarea It render a control to multiline text. • button It render a common button. Could be user outside the form tag.
- 114. The input element It has many types. Each type has a different display. <input type=”{VALUE}” /> • hidden • month html5 • text • week html5 • search html5 • time html5 • tel html5 • datetime-local html5 • url html5 • number html5 • file • email html5 • range html5 • submit • password • color html5 • image • datetime html5 • checkbox • reset • date html5 • radio • button
- 115. The input element It has many types. Each type has a different display. <input type=”{TYPE}” name=”{NAME}” id=”{ID}” /> • accept • multiple • autocomplete • pattern • autofocus • placeholder • checked • readonly • disabled • required • list • size • max • src • maxlength • step • min • value
- 116. The type hidden represents a value that isn’t intended to be manipulated. <input type=”hidden” /> • name • value
- 117. The type text represents a one line text edit control for the element’s value. <input type=”text” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • maxlength • placeholder • readonly • required • size
- 118. The type text represents a one line text edit control for the element’s value. <input type=”search” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • maxlength • placeholder • readonly • required • size
- 119. The type tel represents a control for editing a telephone number. <input type=”tel” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • maxlength • placeholder • readonly • required • size
- 120. The type password represents a one line text edit control for the element’s value. <input type=”password” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • maxlength • placeholder • readonly • required • size
- 121. The type email represents a control for editing the e-mail addresses. <input type=”email” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • maxlength • multiple • placeholder • readonly • required • size
- 122. The type url represents a control for editing a single absolute URL. <input type=”url” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • maxlength • multiple • placeholder • readonly • required • size
- 123. The type file represents a list of selected files. <input type=”file” /> • accept • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • multiple • placeholder • readonly • required • size
- 124. The type date represents a control for setting a string representing a date. <input type=”date” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • max • min • placeholder • readonly • required • size • step
- 125. The type datetime represents a control for setting a global date and time. <input type=”datetime” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • max • min • placeholder • readonly • required • size • step
- 126. The type month represents a control for setting a string representing a month. <input type=”month” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • max • min • placeholder • readonly • required • size • step
- 127. The type week represents a control for setting a string representing a week. <input type=”week” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • max • min • placeholder • readonly • required • size • step
- 128. The type datetime-local represents a control for setting a local date and time. <input type=”datetime-local” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • max • min • placeholder • readonly • required • size • step
- 129. The type number represents a control for setting a string representing a number <input type=”number” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • max • min • placeholder • readonly • required • size • step
- 130. The type range represents a number, but the exact value is not important. <input type=”range” /> • autofocus • disabled • max • min • readonly • required • size • step
- 131. The type color represents a control for setting a string simple color. <input type=”color” /> • autocomplete • autofocus • disabled • placeholder • readonly • required • size
- 132. The type checkbox represents a two-state control. <input type=”checkbox” /> • checked • disabled • readonly • required • value
- 133. The type radio represents a mutually exclusive options control. <input type=”radio” /> • checked • disabled • readonly • required • value
- 134. The type image represents an button from which we can add some behavior. <input type=”image” /> • autofocus • disabled • readonly • required • src
- 135. The type submit represents a button that, when activated, submits the form. <input type=”submit” /> • autofocus • disabled • required • value
- 136. The type reset represents a button that, when activated, resets the form. <input type=”reset” /> • autofocus • disabled • required • value
- 137. The type button represents a button with no default behavior. <input type=”button” /> • autofocus • disabled • required • value
- 138. The select element represents a control for selecting amongst a set of options. <select> <option>Otros (Debes completar el comentario).</option> </select>
- 139. The select element Attributes. <select> ... </select> • autofocus html5 • multiple • size • required • readonly • disabled • name
- 140. The select element Examples. <select> <option value=”opt1”>value</option> </select> <select> <optgroup label=”Group One”> <option value=”opt1”>value</option> </optgroup> </select>
- 141. The textarea element represents a multiline plain text edit control. <textarea></textarea>
- 142. The textarea element is used for long inputs of text. <textarea></textarea> • autofocus • cols • dirname • disabled • maxlength • name • placeholder html5 • readonly • required • rows • wrap
- 143. Thanks