Funding Options
- 1. Funding Op*ons: Find Your Path to Funding September 24, 2015
- 2. Today’s Panel Jess McLear: Launchpad Venture Group Pete McDonald: Silicon Valley Bank Kathryn Carlson: Buca Boot Melissa Withers: BetaSpring Eric Ahlgren: Bessemer Venture Partners Christopher Mirabile: Launchpad Venture Group
- 3. What Type of Company Are You? Before you can get funded, you have to know where to look Before you know where to look, you need to understand what you are
- 4. What Type of Company Are You? • The type of company you have will shape the type of funding available to you • Consumer mobile social so8ware company vs Chemistry-‐based life science technology product vs Equipment for emergency deployment in disaster zones • Changes in business model can change the funding required • IP licensing of new baFery technology to exisHng players vs build a baFery distribuHon company with outsource manufacturing or build a manufacturing company with, or without distribuHon
- 5. NORMAL GROWTH COMPANY HIGH GROWTH COMPANY EXTREME HIGH GROWTH COMPANY SOCIAL VENTURE COMPANY • Includes all service businesses • ExploiLng a local market need • Team has ‘great jobs’ • Growth by adding resources one by one • Exit will be based on value of cash flow (mature biz.) • Growth profile ultra-scalable • Team focus is exit • Revenue $40M+ with lots of room for growth (5 yr.) • Based on $20M+ investment • Exit targeted to IPO or by ‘large’ M&A event • Goal is to fulfill a social need • Has mission orientaLon • Team needs to support mission • Growth profile oWen one resource at a Lme • Exit …much harder to find fit • Company can grow fast (on-line) or has a scalable system • Team often motivated by exit • $7-10M revenue in 4-5 yrs & market size allows significant additional growth • Capital efficient total investment $2-4M • Exit by M&A What Type of Company Are You?
- 6. What Kind of Funding NORMAL GROWTH COMPANY HIGH GROWTH COMPANY EXTREME HIGH GROWTH COMPANY SOCIAL VENTURE COMPANY • Friends, family, founders • Debt, Bank, and other • (Future) Crowd funding (portal style) Early on • Accelerators • Individual Angels • Micro Cap VCs • Seed from VC Later stages • Venture Funds • Strategic VCs • Angel Syndication • Friends family, founders • Charity$$ • Crowd funding (Kickstarter, etc) • Impact Angels • (Future) Crowd funding (portal style) • Angels • Angel Groups • Angel Group Syndication • Angel List • Micro-cap Funds • (Future) Crowd funding (portal style) • Increasingly Strategic Corporate VCs
- 7. Capital Sources: Size & Cost Investment Size TradiLonal VC Micro VC Equipment Financing Angel Groups Angels Equity Crowdfunding Angel List, Circle Up, etc Corporate / Strategic Venture Customers Jobs Bill Portals Vendors Founder Friends & Family Crowdfunding: etc. Grants Venture Debt Bank Loans Personal Loans Private Equity B’Plan CompeLLon Accelerators Investment “Cost”
- 8. Capital Sources DiluLve Non-‐DiluLve Equity • ConverLble Note • Stock • Friends, Family Investors • Common vs Preferred Revenue Debt • Bank • Friends/Family • Non-‐converLble note Customer/Vendor/Partner • Prepaid product purchases from customers • Pay later services from vendors • Non-‐recoverable engineering costs from partners Grants • SBIR • Business compeLLons
- 9. Capital Sources Size of Capital Raise: High Time High Risk Low Risk Crystallize Ideas Demonstrate Product Early Scaling Growth Sustained Growth Market Entry Size of Capital Raise:Low As you develop your company, you reduce risk for your financial partners
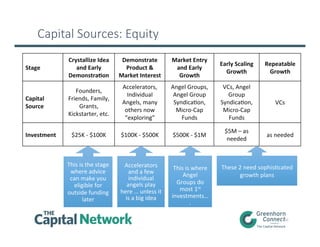
- 10. Capital Sources: Equity 10 Stage Crystallize Idea and Early DemonstraLon Demonstrate Product & Market Interest Market Entry and Early Growth Early Scaling Growth Repeatable Growth Capital Source Founders, Friends, Family, Grants, Kickstarter, etc. Accelerators, Individual Angels, many others now “exploring” Angel Groups, Angel Group SyndicaLon, Micro-‐Cap Funds VCs, Angel Group SyndicaLon, Micro-‐Cap Funds VCs Investment $25K -‐ $100K $100K -‐ $500K $500K -‐ $1M $5M – as needed as needed These 2 need sophisLcated growth plans This is the stage where advice can make you eligible for outside funding later Accelerators and a few individual angels play here … unless it is a big idea This is where Angel Groups do most 1st investments… .
- 11. Equity: VC vs Angel VC Funds • Invest other people’s money (pension funds, …) • Have mulL-‐million $ funds they need to put to work • Invest big and must get big returns for their investors • 7+ year outlook for exit returns (10-‐year funds) Angels • Invest their own money • MoLvated to help entrepreneurs, stay engaged • But Return on Investment is sLll the controlling metric • Likes big returns but will oWen be happy with more modest returns in a shorter amount of Lme3-‐5 year outlook on investments unless VCs get involved
- 12. Equity: VC vs Angel VCs • $48B in 2014,~ 4,000 investments • 1/2 in California alone Angels • $23B in 2013, 300,000 investors, ~ 71,000 investments • Types of angels • Individuals • Organized: Funds: 16%; Network: 63% (avg 10 deals / year) • AngelList • Informal networks & one-‐Lme-‐investors • Family offices • Mostly invest locally Angel Syndicates (relaLvely new) • Individual angels, or several angel groups invesLng as a unit • AngelList syndicates • VC-‐backed syndicates
- 13. Debt Capital Debt Capital • Funding based on a set schedule of principal and interest payments that provide a fixed return for the lender. • Availability may be based on asset value or cash flow or personal guarantee. • MUST be paid back. Not “speculaLve” cash. Sources: • Personal Loans – Friends/Family • Bank Loans • SBA Loans • Expect debt classes from Jobs Bill crowd funding portals • Credit Cards • Venture Debt (usually linked to equity & later stage)
- 14. Alternate Sources Crowd Funding • Kickstarter, Indiego-‐go • Usually associated with “product” companies • Can come with drawbacks Accelerators • Many incubators across the country • May focus on specific types eg. LearnLaunch for EdTech • Many different models • Non-‐profit, equity stake, revenue, loan • Can be very helpful but be wary of being of the “accelerator circuit” too long
- 15. Non-‐Dilu*ve Funding SBIR + STTR = 3% -‐ 3.6% of federal R&D Budget Best for research … need other commercial $$ Pros: • It is a contract/grant – non diluLve Cons: • Long SolicitaLon Process • March-‐in Rights • Work with universiLes for experLse • Best to incorporate (but more acceptance of LLCs) • AccounLng systems must be compliant with the government • Very compeLLve in some agencies
- 16. Conclusion • Educate yourself about all of your funding opLons • hups://www.sbir.gov • hup://nvca.org • hup://www.angelcapitalassociaLon.org • hup://www.thecapitalnetwork.org • Non-‐diluLve funding is always great but not always the easiest to get • It’s all about the numbers for equity investors • Network, Network, Network • hup://www.greenhornconnect.com