fungal disease
- 1. WELCOME TO OUR PRESENTATION Topic: Common Fungal Diseases of Fish And Shrimp in Bangladesh
- 2. Contents Introduction Disease and Fungal disease Fungi Mode of Fungal infection Fungal Diseases of Fish Occur in Bangladesh Fungal Diseases of Shrimp Occur in Bangladesh Conclusion
- 3. Introduction Disease has become one of the major limiting factors in aquaculture production of Bangladesh. Especially with the recent increase of aquaculture practices in order to fulfill the protein deficiency of the rural people. Common disease of freshwater fishes are tail and fin rot, gill rot dropsy, protozoan, metazoan disease including fungal disease like EUS (Epizootic Ulcerative Syndrome), Aspergillomycosis, Saprolegniasis, Branchiomycosis, Ichthyophonus etc.
- 4. Disease and Fungal disease A disease is any condition which results in the disorder of a structure or function in a living organism that is due to external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions, particularly of the immune system etc. When diseases are caused by fungal infection, it’s known as fungal disease.
- 5. Fungi A fungus (plural: fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of unicellular, multicellular or syncytial spore producing eukaryotic organisms. It includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms
- 6. Mode of Fungal infection Most commonly seen in temperate regions. Poor water quality Poor hygienic condition Injury Decomposing organic materials.
- 7. Fungal Diseases of Fish Occur in Bangladesh 1.Epizootic Ulcerative Syndrome (EUS) EUS is a very serious disease of freshwater and some brackishwater fishes, external rapidly across South Asia over the past three decades,spread in sequential manner in Bangladesh(1988).
- 8. Continued… Casual agents: Aeromonas hydrophila, Asorbia (Freshwater),Vibrio angullarium (brackishwater),ect. Susceptible species: Carp,snakehead,catfish,smallfi shes,tilapia,mullets,etc wild fishes are much more susceptible.
- 9. Continued… Pathology: First sign is darker body then anorexia. Floating on surface, hyperactivity; large red or gray color shallow ulcers with brown ,necrotic. Prophylaxis: Liming and disinfections of pond bottom. Water at regular interval liming. Stocking of healthy and strong fish Destroying highly ulcerative fish Effective management practices. Treatment: Antibiotics with feed 500mg/kg body wt for 5-7 days. Potassium permanganate 2-3 ppm. Antibiotic injection 40ml body wt. for 5 days
- 10. Continued… 2. Saprolegniasis It is a fungal disease of fishes and fish eggs caused by various lower fungi of the family Saprolegniaceae of class Oomycete. Common Name Water mould, skin fungus, cotton wool disease. Casual Agents Saprolegnia parasitica, Achlya spp Susceptible Species Carp, catfish, fertilized eggs and hatchings in the hatchery, fry and fingerlings.
- 11. Continued… Etiology The Saprolegniaceae are characterized as having non-septate, multinucleate and unbranched or branched hyphae. Epizootiology All freshwater fish and their eggs can be infected. There is no correlation of fungal attack with season, fish with primarily injuries appear to be especially susceptible in cool temperature
- 12. Continued… Pathology Weak and lethargic movement . Ulceration of exfoliation of skin following haemorrhage. Prophylaxis Avoid rough handling. Avoid overcrowding and stress conditions. Treatment Salt 5% bath for 10 min. Malachite green 0.2 ppm bath for 5min.
- 13. Continued… 3. Branchiomycosis It is a gill disease of freshwater fish caused by phycomycete fungi of the genus Branchiomyces. Common name Gill rot. Causative agent Branchiomyes sanguinis, B. demigrans Susceptible species The most species of freshwater fishes are susceptible to Branchiomycosis.
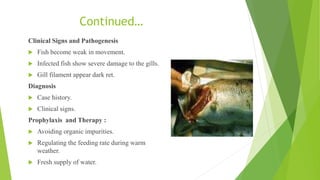
- 14. Continued… Clinical Signs and Pathogenesis Fish become weak in movement. Infected fish show severe damage to the gills. Gill filament appear dark ret. Diagnosis Case history. Clinical signs. Prophylaxis and Therapy : Avoiding organic impurities. Regulating the feeding rate during warm weather. Fresh supply of water.
- 15. Continued… 4. Ichthyophoniasis Ichthyophoniasis is a cosmopolitan systemic granulomatous fungal disease of economic significance. Common name Ichthyophonus disease sometimes referred to as ichthyophoniasis, Ichthyosporidium disease, and ichthyosporidiosis.
- 16. Continued… Causative agent: The causative agent of Ichthyophoniasis is Ichthyophonus hoferi Etiology: Most fungal diseases in pet fish and fish eggs are secondary Opportunistic infections that can be found in fish weakened by stress, epithelial injury, and bacterial, viral, or parasitic disease Pathology: First sign is darker body then anorexia. Floating on surface, hyperactivity;large red or gray color shallow ulcers with brown ,necrotic.
- 17. Continued… Prophylaxis: Liming and disinfections of pond bottom. Water at regular interval liming. Treatment: Antibiotics with feed 500mg/kg body wt for 5-7 days. Potassium permanganate 2-3 ppm.
- 18. Continued… 5.Aspergillomycosis Causative agent Aspergillus fumigatus, A.niger, A.sydowii, A.flavus and A.ter Host Aspergillomycosis infection has been reported from cultured tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) Isolation and Identification Isolated from fungal infected parts of fish body like liver, spleen, kidney, Intestine, swim bladder.
- 19. Continued… Epizootiology Olufemi et al. (1983) were discovered first to recognize the role of Aspergillus as pathogen of farmed fish. Mortalities of at least 20% of stock. Symptoms: Abdominal distention Darkening of color lethargy Incision of body cavity Control Not attempted thus far.
- 20. Fungal Diseases of Shrimp Occur in Bangladesh Fungal Diseases of Shrimp in Bangladesh Some fungal disease of shrimp occur in Bangladesh are given below- 1. Larval Mycosis Common name Lagenidium or Sirolipidium disease. Causetive agent Lagenidium sp., Sirolipidium sp., Haliphthorossp.
- 21. Continued… Susceptible species- Penaeus sp. Pathology Infected eggs don’t hatch larvae lose equilibrium exhibit respiratory difficulties Diagnosis Microscopic demonstration of presence of extensively branched non-septate, fungal hyphae within the body cavity of the shrimp larvae. Treatment 0.2 ppm Treflan or trifluralin for 24 hours.
- 22. Continued… 2. Fusariosis Common name Fusarium disease Black gill disease Causative agent Fusarium solani Species affected All Penaeus species Pathology Infection usually starts on damaged tissues such as wounds Gills damaged from chemical treatments or pollutants Lesions resulting from other disease processes
- 23. Continued… Diagnosis Fusarium spp. are ubiquitous soil fungi. Infection may begin at different loci and spread slowly. Fusarium solani is an opportunistic pathogen of penaeids and are capable of establishing infection in shrimps compromised by other stresses or overcrowding. Prevention and control Preventive measures include the elimination of sources of Fusarium conidiophores and destruction of infected individuals. Several fungicides show prom-is in vitro but none proved to be effective in actual field trials.
- 24. Conclusion Fungal diseases are often indicative of a more serious problem. The best control for all fungal infections is good management: good water quality, good nutrition and proper handling.
- 25. THANK YOU