GALAXY
- 1. GALAXY
- 2. What is Galaxy? Galaxy is a system of millions or billions of stars, together with gas and dust, held together by gravitational attraction. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias literally "milky", a reference to the Milky Way.
- 4. These galaxies have an irregular shape and are considered to be the result of the collisions galaxies. As a result, they generally contain of a complex mix of interstellar gas and dust, young stars, and old stars. Irregular
- 5. These galaxies have little to no structure, rotation, or interstellar matter. This results in minimal tar formation and a dominance of the long lived, red stars. These ellipsoid- shaped collection of stars are the most common type of galaxy.
- 6. These galaxies are disk-shaped with either a round central hub (unbarred) or a hub shaped like a bar (barred). They rotate with spiral arms that contain interstellar dust and gas, promoting star formation and an abundance of young stars.
- 8. What is Milky Way? It is the name of the barred spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located. The Earth orbits the Sun in the Solar System, and the Solar System is embedded within this vast galaxy of stars. It is just one of hundreds of billions of galaxies in the Universe, and ours is called the Milky Way because the disk of the galaxy appears to be spanning the night sky like a hazy band of glowing white light. In short, our galaxy was named because of the way the haze it casts in the night sky resembled spilled milk. This name is also quite ancient. It is translation from the Latin “Via Lactea“, which in turn was translated from the Greek for Galaxias, referring to the pale band of light formed by stars in the galactic plane as seen from Earth.
- 9. The Milky Way is part of a collection of galaxies called the Local Group. The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains our Solar System. Its name "milky" is derived from its appearance as a dim glowing band arching across the night sky whose individual stars cannot be distinguished by the naked eye. T The ancient Romans called our galaxy the Via Lactea, which literally means “The Road of Milk.” The Milky Way is the second-largest galaxy. Notice that the total size of the Milky Way is about 50,000 light-years in radius, with the Sun a little over halfway from the center. The Milky Way contains between 100- 400 billion stars and at least 100 billion planets
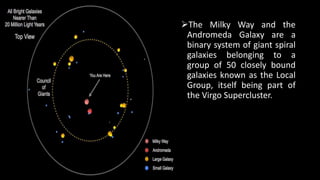
- 10. The Local Group
- 11. The Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy are a binary system of giant spiral galaxies belonging to a group of 50 closely bound galaxies known as the Local Group, itself being part of the Virgo Supercluster.
- 12. The Virgo Supercluster forms part of a greater structure, called Laniakea.
- 13. The "Milky Way" can be seen as a hazy band of white light some 30 degrees wide arcing across the sky. The area of the sky obscured by the Milky Way is called the Zone of Avoidance.
- 14. The Milky Way consists of a bar-shaped core region surrounded by a disk of gas, dust and stars. The gas, dust and stars are organized in roughly logarithmic spiral arm structures
- 16. The Milky Way began as one or several small over densities in the mass distribution in the Universe shortly after the Big Bang. Some of these over densities were the seeds of globular clusters in which the oldest remaining stars in what is now the Milky Way formed.
- 17. Globular clusters are among the oldest objects in the Milky Way, which thus set a lower limit on the age of the Milky Way. The ages of individual stars in the Milky Way can be estimated by measuring the abundance of long-lived radioactive elements such as thorium-232 and uranium-238, then comparing the results to estimates of their original abundance, a technique called nucleocosmochronology. Age
- 18. Our Sun is located in the Orion Arm, a region of space in between the two major arms of the Milky Way, and about 27,000 light years from the galactic core. At the heart of the Milky Way is a super-massive black hole, just like all of the other galaxies, known as Sagittarius A*. This monster is more than 4 million times the mass of the Sun and is believed to have a diameter of 44 million kilometers.