Grade 8 Lesson 15.pptx
- 3. LEVELS of INTERACTIONS 01 02 03 04 SCENARIOS: Imagine you are stranded on an island where there is a snall cornfield and 50 chickens. You are not sure when you will be rescued. Remember, you need to stay alive until rescue arrived. 3
- 4. What should I eat to stay alive for a longer period? 4 Eat the corn first, then eat the chicken Eat the chicken first, then eat the corn Pros: Pros: Cons: Cons: OPTIONS OPTION 2 OPTION 1
- 5. 5 ECOSYSTEM -Is an ecological formed by the interaction of living organisms and their non-living environment in a particular area. -- It comprises biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors that an organisms interacts with in its habitat.
- 6. BIOTIC FACTORS - Composes all the organisms 6 ABIOTIC FACTORS - Are physical and chemical features such as light, temperature, water, type of soil, oxygen content and others
- 7. HABITAT Is the place where organism lives such as pond , a stream, a river , a forest or a desert.
- 8. 8 - It is the same species living in a particular area make up a population. Group of Organisms
- 9. How do energy and nutrients flow through an ecosystem? 9 Organisms compromise the producers, consumers, and decomposers. Energy and nutrients are transferred from producers to consumers to decomposer through feeding.
- 10. 10 PRODUCERS They can make or produce food to provide energy an oxygen for the living organisms.
- 11. CONSUMERS 11 Obtain their energy by feeding on other organisms as we discussed in biodiversity. All animals are consumers. Herbivores or the plant –eaters feed directly on plant also known as primary consumers. Meat-eaters or carnivores feed on other animals, hence they are known as secondary consumers. Carnivores that feed on other carnivores are called tertiary consumers.
- 12. DECOMPOSERS 12 Obtain energy by breaking down dead organisms, feces and other excretory products. The broken down materials such as carbon and nitrogen compounds return to the environment and used again by plants.
- 13. FOOD CHAIN 13 13 Is a series of eaten-eater relationship in which energy is transferred.
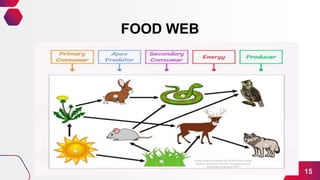
- 14. Food WEB 15.3 Is made up of two or more overlapping food chains that are linked together.
- 15. FOOD WEB 15
- 16. Why are short food chains more efficient in energy transfer?
- 17. A shorter food chain means more energy is available to the final consumer because less energy is lost to the environment. For instance, more energy will be available to a man if he feeds directly on crop plants grown in a given area, rather than eating the meat of the cattle that feed on his crop. 17
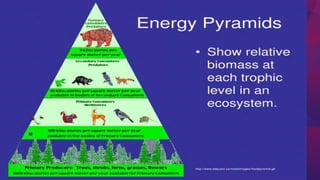
- 18. 15.4 PYRAMID ENERGY 18 In food web, eenrgy is lost when one organisms eats another. The transfer of energy and biomass in food from one trophic level to an other is not one hundred percent used. Biomass- is the total mass of organisms in a food cahin or food web.
- 20. In a typical terrestrial ecosystem, the greatest biomass is the producers. There is a progressive decrease of biomass from lower (base) to higher trophic levels. Thus, the pyramid of biomass is upright. 20 20
- 21. 21 Web design principles Mars is actually a very cold place Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun Venus is the second planet from the Sun Neptune is very far away from us White space Jupiter is the biggest planet of them all Saturn is a gas giant and has rings Movement Unity
- 22. 22 The first source of energy is the sun. The 10% Rule describes how energy is lost when it is passed in an ecosystem from one trophic level to the next. Roughly, only ten percent of energy will be passed on. Energy that is lost as heat cannot be recycled. Hence, energy (in the form of light energy) has to be constantly supplied through the producers.
- 23. 15.5 NUTRIENT CYCLING IN AN ECOSYSTEM 23 Nutrient cycle or ecological recycling is the movement and exchange of organic and inorganic materials back into the production of living matter.
- 24. Detritivores and decomposers play an important role in assuring the survival of producers such as plants, and thus all life, by recycling nutrients back to them. The process is regulated by food web pathways that decompose matter into mineral nutrients. Nutrients cycles occur within ecosystems. The nutrient cycle describes the use, movement and recycling nutrients in the environment. Important elements like carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and phosphorus and nitrogen are essential to life and must be recycled in order for organisms to exists and survive. In balanced ecosystem, nutrients are never lost but are continually recycled. Nutrients cycles involve living and non-living components of the environment. We shall now study some of these cycles to understand the
- 25. THE CARBON CYCLE 25 CARBON, in the form of CARBON DIOXIDE, is constantly being removed from and released into the environment. Organisms use and produce gases through various processes that makes up the carbon cycle.
- 26. 1. During the photosynthesis, carbon dioxide removed by plants from atmosphere to be used in manufacturing of food, for example, the carbohydrates-glucose. 2. When animals feed on plants, the carbon compounds become part of their bodies. These compounds may also be stored in fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas and oil. 3. Then, carbon dioxide is released and returned into environment through respiration, combustion and decomposition. 26 26
- 27. UI/UX Business Web security Most wanted skills for jobs 75% 27 50% 65% Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun Neptune is the farthest planet from the Sun Despite being red, Mars is a cold place
- 28. The cycling of water happens around the environment including the oceans, land, air and living things. It involves the following events. 1. When sunlight warms the surface of the earth, water evaporates from the land, lakes rivers and oceans (evaporations) 2. The escape of water through leaf ( transpiration) adds water vapor to the atmosphere. 3. Upon cooling at high altitude, water vapor condenses which forms clouds ( condensation). 4. Eventually, rain or snow forms (precipitation). On land, water is absorbed by plant roots and replenish the ground. The excess water finally overflows into oceans and the water cycle continues. THE WATER CYCLE 28
- 29. Extra skills 29 Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun and the smallest one in the Solar System Venus has a beautiful name and is the second planet from the Sun Coding Editing Despite being red, Mars is actually a cold place. It's full of iron oxide dust Managing
- 30. The NITROGEN CYCLE 30 Organisms use nitrogen gas to build proteins and nucleic acids necessary for life. The cycling of nitrogen happen whens: 1. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria which can be found in the nodules of legumes, convert nitrogen to ammonia. This process is called nitrogen fixation. 2. In the nitrogen cycle, nitrifying bacteria use ammonia, converting it into nitrate and nitrate by products. These steps are named ammonification and nitrification. These bacteria are essential to ecosystem because they bring nitrogen into the soil for plants to use.
- 31. 3. Animals consume plants and return nitrogen to the soil through waste products and upon death, denitrifying bacteria return nitrogen to the atmosphere which is referred as denitrification process. Then the recycle continues.
- 32. 15.6 How do we affect the ecosystem? 32 Human activities must be carefully monitored to preserve and conserve the environment for the future. Here are some human activities that affects the ecosystem.
- 33. 33 With modern technology, trees are being cleared at a faster rate than they can replaced. This lead to loss of habitats, wildlife lose their homes. Effects are soil erosion, flooding and climate change. Deforestation
- 34. 34 Some method of fishing such as use of cyanide also destroy seabed and marine habitat. Eventually some species may become endangered or even extinct. Uncontrolled fishing practices
- 35. Most product of technology are toxic including factories. These toxic wastes are collected through air and water., threatening the lives in the ecosystem. For examples, chemical fertilizers containing nitrates and phosphate are used to increased the yield of crops. However, the overuse of these fertilizer may cause water pollution. 35 POLLUTION
- 36. 36 Insecticides are used to kill insects. However, this may end up affecting other organisms as well. For example, an insecticide named DDt (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) are non-biodegradable. This means they cannot be broke down by microorganisms like bacteria. DDt is insoluble in water and is not excreted. This means it accumulate in the body of the organism which cause the top consumer to suffer toxic effects in the long run. USE of INSECTICIDES
- 37. USE of FERTILIZER Uncontrolled use of chemical fertilizers may increase soil acidity which can destroy the soil beneficial structure to plants. Fertilizers run off to rivers, ponds and lakes that may cause the death of these water gradually. 37
- 38. Generally to conserve the environment, we should:
- 39. 39 1. Keep the environment clean 2. Effectively manage the use of natural resources 3. Protect wildlife
- 40. 40 40 Taking steps to conserve is a willful act. Doing our part by changing daily habits can be good contribution. Here are some tips to help save our environment.
- 41. 41 1. Try decreasing energy and water consumption. 2. You may create a compost heap in your garden or use a compost bin. This helps recycle food waste and other biodegradeable materials. 3. Bring your own eco-bags and avoid plastic bags as much as possible.
- 42. 42 4. Separate biodegradable and recyclable waste from non- biodegradable and work to reduce the amount of non- biodegradable or recyclable waste. 5. You may join many tree planting trips as you can!