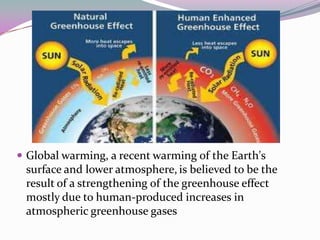
Greenhouse effect
- 2. Is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases, and is re-radiated in all directions. Since part of this re-radiation is back towards the surface, energy is transferred to the surface and the lower atmosphere
- 4. The temperature there is higher than it would be if direct heating by solar radiation were the only warming mechanism
- 5. The greenhouse effect was discovered by Joseph Fourier in 1824, first reliably experimented on by John Tyndall in 1858, and first reported quantitatively by Svante Arrhenius in 1896.
- 6. Global warming, a recent warming of the Earth's surface and lower atmosphere,is believed to be the result of a strengthening of the greenhouse effect mostly due to human-produced increases in atmospheric greenhouse gases
- 7. Greenhouse GasesBy their percentage contribution to the greenhouse effect on Earth the four major gases are:water vapor, 36–70%carbon dioxide, 9–26%methane, 4–9%ozone, 3–7%The major non-gas contributor to the Earth's greenhouse effect, clouds, also absorb and emit infrared radiation and thus have an effect on radiative properties of the atmosphere.
- 8. Role in climatechangeCO2 is produced by fossil fuel burning and other activities such as cement production and tropical deforestation.Measurements of CO2 from the Mauna Loa observatory show that concentrations have increased from about 313 ppm in 1960 to about 389 ppm in 2010. The current observed amount of CO2 exceeds the geological record maxima (~300 ppm) from ice core data. The effect of combustion-produced carbon dioxide on the global climate, a special case of the greenhouse effect first described in 1896 by Svante Arrhenius, has also been called the Callendar effect.