Happy farm canvas and discovery bd
- 1. An Introduction to Customer Development and the Business Model Canvas BOB DORF allegedly retired serial entrepreneur bob@kandsranch.com www.steveblank.com 1
- 2. Our Agenda • What’s a business model? • How do I use the business model? • How do I know if it’s any good????? 2
- 3. Why 95+% of startups die? • All product, no customers • No problem • The “lock step” • Premature scaling • No product/market fit • No more dough • …some of us will fail. Certainly it’s not YOU! 3
- 4. Why 95% of Startups Fail… Product Introduction Model: Two Implicit Assumptions Customer Problem: known Concept/ Product Alpha/Beta Launch/ Seed Round Dev. Test 1st Ship Product Features: known 4
- 5. No Business Plan survives first contact with customers …get customer feedback as early as possible …it starts at the “idea” phase, not much later …and customers help you develop the product 5
- 6. So Search for a Business Model 6
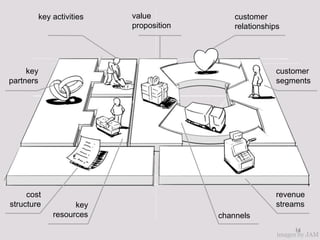
- 7. The Business Model: Any company can be described in 9 building blocks 7
- 8. key activities value customer proposition relationships key customer partners segments cost revenue structure key streams resources channels 8 8 images by JAM
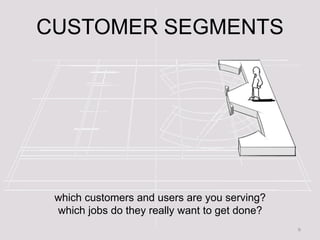
- 9. CUSTOMER SEGMENTS which customers and users are you serving? which jobs do they really want to get done? 9
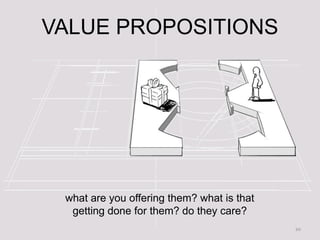
- 10. VALUE PROPOSITIONS what are you offering them? what is that getting done for them? do they care? 10
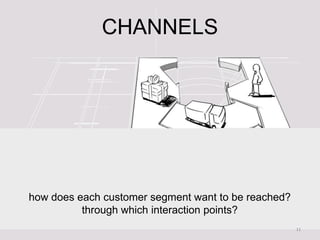
- 11. CHANNELS how does each customer segment want to be reached? through which interaction points? 11
- 12. CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIPS what relationships are you establishing with each segment? personal? automated? acquisitive? retentive? 12
- 13. REVENUE STREAMS what are customers really willing to pay for? how? are you generating transactional or recurring revenues? 13
- 14. key activities value customer proposition relationships key customer partners segments cost revenue structure key streams resources channels 14 14 images by JAM
- 16. 9 Guesses Guess Guess Guess Guess Guess Guess Guess Guess Guess 16
- 17. Our Guesses DON’T Matter • Anybody can build almost anything today (just a few exceptions: anti-gravity, transporters) • What we need are CUSTOMERS!! • Build the customers while building product • …and let customer feedback and your coach guide you all the way through the process! • note: Clones may be different! 17
- 18. How Do You Search For A Business Model? • The Canvas drives the planning process • The Search is Customer Development • Manufacturing iterates based on solid feedback 18
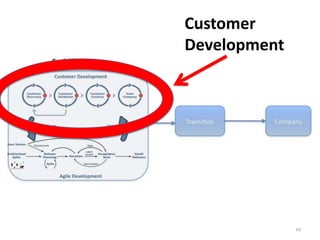
- 19. Customer Development 19
- 20. Customer Development The founders Get Out of the Building 20
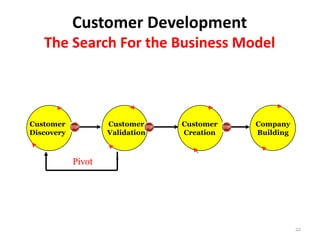
- 21. Customer Development The Search For the Business Model Customer Customer Customer Company Discovery Validation Creation Building Pivot 21
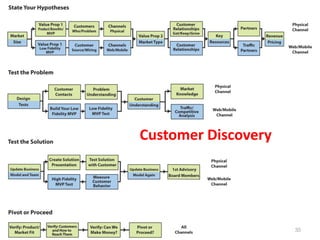
- 22. Customer Discovery Customer Customer Customer Company Discovery Validation Creation Building • Stop selling, start listening • Test your hypotheses • Continuous Discovery • Done by founders 22
- 23. TWO key Discovery phases • FIRST: Does anybody care? …are we solving a serious problem? …are we filling a “big” need? • THEN: Does our product do the job? …do they grab it out of your hands? …are they eager to tell their friends? 23
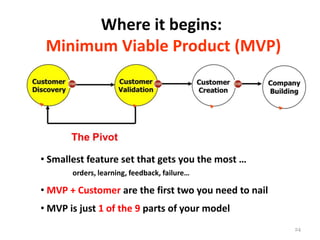
- 24. Where it begins: Minimum Viable Product (MVP) • Smallest feature set that gets you the most … orders, learning, feedback, failure… • MVP + Customer are the first two you need to nail • MVP is just 1 of the 9 parts of your model 24
- 25. What’s a Minimum Viable Product? • Google without ads • Zappos without inventory • Diapers.com without diapers …Fewest possible features to make the point! …Why? It’s hard to truly react to a powerpoint 25
- 26. Discovery: Not just “do you like it?” • How big is the market? Not today…eventually! • Who’s the customer? – What’s their problem/need • What’s the product/service/need? – Does it solve the customer’s problem? • How do you create demand? • How do you deliver the product? • How do you make money? 26
- 27. Hypotheses Testing and Insight 27
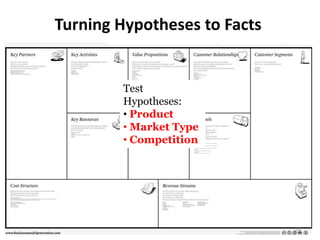
- 28. Turning Hypotheses to Facts Test Hypotheses: • Product • Market Type • Competition 28
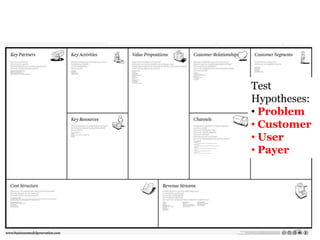
- 29. Test Hypotheses: • Problem • Customer • User • Payer 29
- 30. The Pivot • The heart of Customer Development • Iteration without crisis • Fast, agile and opportunistic 30
- 31. Three Great Pivots • Steve Blank: “Page 6” • Perimeter: “there are 9000 of us” • Groupon: the $12billion pivot • …and hundreds more! 31
- 32. Pivot Cycle Time Matters Search Execution Customer Customer Customer Company Discovery Validation Creation Building Pivot • Speed of cycle minimizes cash needs • Minimum feature set speeds up cycle time • Near instantaneous customer feedback drives feature set 32
- 33. Web/Mobile Versus Physical Custome Customer r Validatio Discover n y Pivot • Web/Mobile startups run faster • Different process steps for web vs. physical • Customer Relationships are radically different 33
- 34. Putting Discovery to Work 34
- 35. Customer Discovery 35
- 36. Who Do I Call On? • Read the Startup Owner’s Manual • Network like heck • Cold calls are a badge of honor • Don’t worry about titles or the right person • …and DO NOT TALK…listen! 36
- 37. What Do I Say? • Remember you are 1st testing the problem • “Hi, I’ve been told you’re the smartest person in this industry. We’re building x and I want to see if I understand the problem. I’d like 10 minutes of your time.” • …give them choices that make them talk • …resist the strong temptation to sell 37
- 38. I Have a Meeting – Now What? • The goal is to test all hypotheses, but first: have you found “product/market fit” • Does the customer care? • How do they solve this problem TODAY? • What channel do they use to buy? • Where will they go to find you? • How will you create demand? • How much will they pay? Do they pay today? 38
- 39. Then what? • Assemble all the data, organize/rank responses • Slam it against industry, third party resources • Get a tighter, more concise view of the market • …and adjust your Business Model as you go! Next: • Test the “solution” in a very similar way • …and determine if you “pivot or proceed” 39
- 40. But wait…there’s MORE! Yeah who says… When Discovery is DONE 40
- 41. Business Model Canvas Score Card Key Partners Key Activities Value Proposition Customer Relationships Customer Segments Who are our key partners/ suppliers Which key activities does the biz What value do we deliver to the What type of relationship does each For whom are we creating value segment require of us model require customer Complete regional overview Populate life cycle data for performance key distinctive product features & product positioning/elevator pitch for identify key market segments guarantees benefits for the target customer each segment (geography/application) and customer segment Prospect roadmap: how to get face-to- segments (e.g. operator versus owner) Educate market on metric: $/kWh- total cost of ownership for segment face with right person at prospects in how many customers in each segment versus alternatives each segment and estimated potential volume for day delivered over life of asset key competitors in each segment and why will segment buy Durathon versus each customer their market share Establish strong partnerships with alternatives (i.e. value proposition) key competitors' characteristics & how do customers make money … key channel partners minimum feature set (i.e. our launch dynamics customer pain/gain points in each configuration) and ultimate feature set What outbound marketing/ segment opportunities to claim IP or trademark advertising/ promotion activities are how are buying decisions made in each / is there freedom to practice needed segment - id process, hurdles, decision 0 what regulatory/ certification/ support tools required by segment makers transportation/ customs requirements (white papers, TCO calc., tradeshow) what does an Earlyvangelist look like in should be met or could be pipeline of leads each segment Key Resources differentiator 25 who influences purchases in each Which key resources does the biz segment (trade groups, key resellers, model require Channels trend watchers) Integrated power system engineering – Through which channel does each compatibility for retrofit and optimized segment want to be reached system solutions Financing options for Power services which segments can only or best be operators reached through a channel partner which channel partners are important to optimize sales in each segment what are channel partners' requirements and cost to become a proactive sales channel initial channel partner response to value proposition & customer segments 12 25 4 50 Cost Structure Revenue Streams What are our cost drivers How much is each segment willing to pay and how would they like to pay us this amount Launch reliability What are price /performance characteristics of competing technology What is the 2013 price target for 1 MM cells What is the 2015 price target for 10 MM cells what is optimum sales method for each segment (asset sale, lease, pay for performance, etc.) 3 X = number of in depth customer data points / data sources used to validate hypothesis x red = low hypothesis confidence x yellow = medium hypothesis confidence green = high hypothesis confidence x 41 41
- 42. When Customer Discovery is Done: Time to Ask for Money! HINT: YOUR VC PITCH WAS HIDING IN THE LAST 12 SLIDES…DISCOVERY 42
- 43. Who has completed serious Customer Discovery? …an example from the USA 43
- 44. Examples: Discovery Learning • Too much process • Benefits too “soft” • The Philadelphia Architect • A day in the freezer 44
- 45. Pivot Example Robotic Weeding Talked to 75 Customers in 8 Weeks 45
- 46. Our initial plan 46 Confidential
- 47. 20 interviews, 6 site visits… We got OUR Boots dirty Mowing Interviewed: • Golf: Stanford Golf course • Parks: Stanford Grounds Supervisor, head of maintenance and lead operator (has crew of 6) • Toro dealer (large mower manufacturer) • User of back-yard mowing system • Maintenance Services for City of Los Altos • Colony Landscaping (Mowing service for stadiums) Weeding Visited two farms in Salinas Valley to better understand problem Interviewed: • Bolthouse Farms, Large Agri-Industry in Bakersfield • White Farms, Large Peanut farmer in Georgia • REFCO Farms, large grower in Salinas Valley • Rincon Farms, large grower in Salinas Valley • Small Organic Corn/Soy grower in Nebraska • Heirloom Organics, small owner/operator, Santa Cruz Mts • Two small organic farmers at farmers market 47 • Ag Services of Salinas, Fertilizer applicator
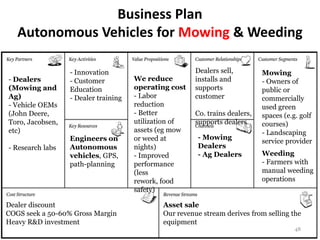
- 48. Business Plan Autonomous Vehicles for Mowing & Weeding - Innovation Dealers sell, Mowing - Dealers - Customer We reduce installs and - Owners of (Mowing and Education operating cost supports public or Ag) - Dealer training - Labor customer commercially - Vehicle OEMs reduction used green (John Deere, - Better Co. trains dealers, spaces (e.g. golf Toro, Jacobsen, utilization of supports dealers courses) etc) assets (eg mow - Landscaping Engineers on or weed at - Mowing service provider - Research labs Autonomous nights) Dealers vehicles, GPS, - Improved - Ag Dealers Weeding path-planning performance - Farmers with (less manual weeding rework, food operations safety) Dealer discount Asset sale COGS seek a 50-60% Gross Margin Our revenue stream derives from selling the Heavy R&D investment equipment 48
- 49. Found weeding in organic crops is HUGE problem; 50 - 75% of costs Crews of 100s-1000 Back-breaking task (Illegal) labor harder to get 1-5 weedings per year/field $250-3,500 per acre and increasing Food contamination risk 49
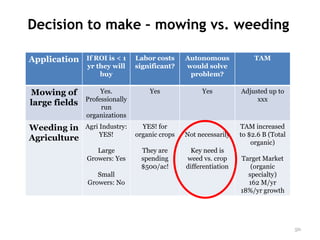
- 50. Decision to make – mowing vs. weeding Application If ROI is < 1 Labor costs Autonomous TAM yr they will significant? would solve buy problem? Mowing of Yes. Yes Yes Adjusted up to Professionally xxx large fields run organizations Weeding in Agri Industry: YES! for TAM increased YES! organic crops Not necessarily to $2.6 B (Total Agriculture organic) Large They are Key need is Growers: Yes spending weed vs. crop Target Market $500/ac! differentiation (organic Small specialty) Growers: No 162 M/yr 18%/yr growth 50
- 51. Autonomous vehicles WEEDING - Innovation Dealers sell, installs - Low density - Ag Dealers - Customer We reduce and supports vegetable growers - Ag Service Education operating cost customer - High density providers - Dealer training - Labor reduction vegetable growers (100 to 1) Co. trains dealers, - Thinning - Research labs - Reduced risk of supports dealers operations contamination - Conventional - Mitigate labor vegetables availability Engineers on concerns - Ag Dealers Machine Vision - Ag Service Two problems: providers - Identification - Elimination Dealer discount Asset sale COGS seek a 50-60% Gross Margin Our revenue stream derives from selling the Heavy R&D investment equipment 51
- 52. World Ag Expo interviews: the need is real and wide spread • 10+ interviews at show – Everyone confirmed the need – Robocrop, UK based, crude competitor sells for $171 K • Revenue Stream – Mid to small growers prefer a service – Large growers prefer to buy, but OK with service until technology is proven – Charging for labor cost saved is OK, as we provide other benefits (food safety, labor availability) 52 Confidential
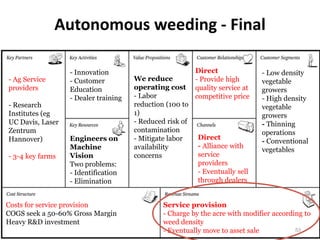
- 53. Autonomous weeding - Final - Innovation Direct - Low density - Ag Service - Customer We reduce - Provide high vegetable providers Education operating cost quality service at growers - Dealer training - Labor competitive price - High density - Research reduction (100 to vegetable Institutes (eg 1) growers UC Davis, Laser - Reduced risk of - Thinning Zentrum contamination operations Hannover) Engineers on - Mitigate labor Direct - Conventional Machine availability - Alliance with vegetables - 3-4 key farms Vision concerns service Two problems: providers - Identification - Eventually sell - Elimination through dealers Costs for service provision Service provision COGS seek a 50-60% Gross Margin - Charge by the acre with modifier according to Heavy R&D investment weed density - Eventually move to asset sale 53
- 54. Customer Validation Search Customer Customer Customer Company Discovery Validation Creation Building Pivot Execution • Repeatable and scalable business model? • Passionate earlyvangelists? • Pivot back to Discovery if no customers 54
- 55. Customer Validation 55
- 56. Questions? 56